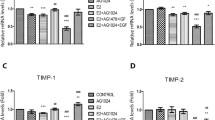
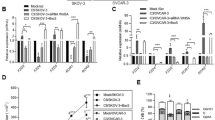
Abstract
In breast tumors the expression of estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) is known to be associated with a more favorable prognosis. ERα expression has been reported to reduce the metastatic potential of breast cancer cells. Recently, we have observed that extracellular matrix proteins activate ERα and that both liganded and unliganded receptor modulate cell invasiveness acting at nuclear level. To explain the mechanisms by which ERα regulates cell adhesion, we have evaluated the expression of α5β1 integrin, prevalently expressed in stationary cells, in response to 17β-estradiol (E2). Here we show that E2/ERα increases the expression of integrin α5β1 through Sp1-mediated binding to a GC-rich region located upstream of an ERE half-site in the 5′ flanking region of the α5 gene forming a ternary ERα–Sp1-DNA complex. Estrogen responsiveness of the α5 gene promoter, as observed in HeLa cells, underlies a general mechanism of regulation which is not strictly linked to the cell type. Our data reveal novel insight into the molecular mechanisms sustaining the reduced invasiveness of ERα expressing cells demonstrating that α5β1 integrin expression is related to the maintenance of the stationary status of the cells, counteracting E2/ERα capability to enhance breast cancer cell migration and invasion.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altucci L, Addeo R, Cicatiello L, Dauvois S, Parker MG, Truss M, Beato M, Sica V, Bresciani F, Weisz A (1996) 17beta-Estradiol induces cyclin D1 gene transcription, p36D1–p34cdk4 complex activation and p105Rb phosphorylation during mitogenic stimulation of G(1)-arrested human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 12(11):2315–2324
Duan R, Xie W, Burghardt RC, Safe S (2001) Estrogen receptor-mediated activation of the serum response element in MCF-7 cells through MAPK-dependent phosphorylation of Elk-1. J Biol Chem 276(15):11590–11598
Planas-Silva MD, Shang Y, Donaher JL, Brown M, Weinberg RA (2001) AIB1 enhances estrogen-dependent induction of cyclin D1 expression. Cancer Res 61(10):3858–3862
Sabbah M, Courilleau D, Mester J, Redeuilh G (1999) Estrogen induction of the cyclin D1 promoter: involvement of a cAMP response-like element. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(20):11217–11222
Weisz A, Bresciani F (1993) Estrogen regulation of proto-oncogenes coding for nuclear proteins. Crit Rev Oncog 4(4):361–388
Liotta LA, Stetler-Stevenson WG (1991) Tumor invasion and metastasis: an imbalance of positive and negative regulation. Cancer Res 51(18 Suppl):5054s–5059s
Thompson EW, Paik S, Brunner N, Sommers CL, Zugmaier G, Clarke R, Shima TB, Torri J, Donahue S, Lippman ME et al (1992) Association of increased basement membrane invasiveness with absence of estrogen receptor and expression of vimentin in human breast cancer cell lines. J Cell Physiol 150(3):534–544
Rochefort H, Platet N, Hayashido Y, Derocq D, Lucas A, Cunat S, Garcia M (1998) Estrogen receptor mediated inhibition of cancer cell invasion and motility: an overview. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 65(1–6):163–168
Woodward TL, Mienaltowski AS, Modi RR, Bennett JM, Haslam SZ (2001) Fibronectin and the alpha(5)beta(1) integrin are under developmental and ovarian steroid regulation in the normal mouse mammary gland. Endocrinology 142(7):3214–3222
Sisci D, Aquila S, Middea E, Gentile M, Maggiolini M, Mastroianni F, Montanaro D, Ando S (2004) Fibronectin and type IV collagen activate ERalpha AF-1 by c-Src pathway: effect on breast cancer cell motility. Oncogene 23(55):8920–8930
Confort C, Rochefort H, Vignon F (1995) Insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) stimulate the release of alpha 1-antichymotrypsin and soluble IGF-II/mannose 6-phosphate receptor from MCF7 breast cancer cells. Endocrinology 136(9):3759–3766
Crowe DL, Brown TN (1999) Transcriptional inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) activity by a c-fos/estrogen receptor fusion protein is mediated by the proximal AP-1 site of the MMP-9 promoter and correlates with reduced tumor cell invasion. Neoplasia 1(4):368–372
Abbas Abidi SM, Howard EW, Dmytryk JJ, Pento JT (1997) Differential influence of antiestrogens on the in vitro release of gelatinases (type IV collagenases) by invasive and non-invasive breast cancer cells. Clin Exp Metastasis 15(4):432–439
Lynch L, Vodyanik PI, Boettiger D, Guvakova MA (2005) Insulin-like growth factor I controls adhesion strength mediated by alpha5beta1 integrins in motile carcinoma cells. Mol Biol Cell 16(1):51–63
Keely PJ, Fong AM, Zutter MM, Santoro SA (1995) Alteration of collagen-dependent adhesion, motility, and morphogenesis by the expression of antisense alpha 2 integrin mRNA in mammary cells. J Cell Sci 108(Pt 2):595–607
DiMilla PA, Stone JA, Quinn JA, Albelda SM, Lauffenburger DA (1993) Maximal migration of human smooth muscle cells on fibronectin and type IV collagen occurs at an intermediate attachment strength. J Cell Biol 122(3):729–737
Huttenlocher A, Ginsberg MH, Horwitz AF (1996) Modulation of cell migration by integrin-mediated cytoskeletal linkages and ligand-binding affinity. J Cell Biol 134(6):1551–1562
Yang JT, Bader BL, Kreidberg JA, Ullman-Cullere M, Trevithick JE, Hynes RO (1999) Overlapping and independent functions of fibronectin receptor integrins in early mesodermal development. Dev Biol 215(2):264–277
Delcommenne M, Streuli CH (1995) Control of integrin expression by extracellular matrix. J Biol Chem 270(45):26794–26801
Woodward TL, Xie J, Fendrick JL, Haslam SZ (2000) Proliferation of mouse mammary epithelial cells in vitro: interactions among epidermal growth factor, insulin-like growth factor I, ovarian hormones, and extracellular matrix proteins. Endocrinology 141(10):3578–3586
Watt FM, Hodivala KJ (1994) Cell adhesion. Fibronectin and integrin knockouts come unstuck. Curr Biol 4(3):270–272
Birkenmeier TM, McQuillan JJ, Boedeker ED, Argraves WS, Ruoslahti E, Dean DC (1991) The alpha 5 beta 1 fibronectin receptor. Characterization of the alpha 5 gene promoter. J Biol Chem 266(30):20544–20549
Suzuki T, Fujisawa JI, Toita M, Yoshida M (1993) The trans-activator tax of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) interacts with cAMP-responsive element (CRE) binding and CRE modulator proteins that bind to the 21-base-pair enhancer of HTLV-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90(2):610–614
Jia Y, Zeng ZZ, Markwart SM, Rockwood KF, Ignatoski KM, Ethier SP, Livant DL (2004) Integrin fibronectin receptors in matrix metalloproteinase-1-dependent invasion by breast cancer and mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Res 64(23):8674–8681
Larouche K, Leclerc S, Salesse C, Guerin SL (2000) Expression of the alpha 5 integrin subunit gene promoter is positively regulated by the extracellular matrix component fibronectin through the transcription factor Sp1 in corneal epithelial cells in vitro. J Biol Chem 275(50):39182–39192
Petz LN, Nardulli AM (2000) Sp1 binding sites and an estrogen response element half-site are involved in regulation of the human progesterone receptor A promoter. Mol Endocrinol 14(7):972–985
Safe S (2001) Transcriptional activation of genes by 17 beta-estradiol through estrogen receptor–Sp1 interactions. Vitam Horm 62:231–252
Safe S, Kim K (2004) Nuclear receptor-mediated transactivation through interaction with Sp proteins. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 77:1–36
Anderson I, Gorski J (2000) Estrogen receptor alpha interaction with estrogen response element half-sites from the rat prolactin gene. Biochemistry 39(13):3842–3847
Wang F, Hoivik D, Pollenz R, Safe S (1998) Functional and physical interactions between the estrogen receptor Sp1 and nuclear aryl hydrocarbon receptor complexes. Nucleic Acids Res 26(12):3044–3052
Porter W, Wang F, Wang W, Duan R, Safe S (1996) Role of estrogen receptor/Sp1 complexes in estrogen-induced heat shock protein 27 gene expression. Mol Endocrinol 10(11):1371–1378
Khan S, Abdelrahim M, Samudio I, Safe S (2003) Estrogen receptor/Sp1 complexes are required for induction of cad gene expression by 17beta-estradiol in breast cancer cells. Endocrinology 144(6):2325–2335
Nerlich AG, Wiest I, Wagner E, Sauer U, Schleicher ED (1997) Gene expression and protein deposition of major basement membrane components and TGF-beta 1 in human breast cancer. Anticancer Res 17(6D):4443–4449
Ronnov-Jessen L, Petersen OW, Bissell MJ (1996) Cellular changes involved in conversion of normal to malignant breast: importance of the stromal reaction. Physiol Rev 76(1):69–125
Hayashido Y, Lucas A, Rougeot C, Godyna S, Argraves WS, Rochefort H (1998) Estradiol and fibulin-1 inhibit motility of human ovarian- and breast-cancer cells induced by fibronectin. Int J Cancer 75(4):654–658
Giretti MS, Fu XD, De Rosa G, Sarotto I, Baldacci C, Garibaldi S, Mannella P, Biglia N, Sismondi P, Genazzani AR et al (2008) Extra-nuclear signalling of estrogen receptor to breast cancer cytoskeletal remodelling, migration and invasion. PLoS One 3(5):e2238
Saji S, Kawakami M, Hayashi S, Yoshida N, Hirose M, Horiguchi S, Itoh A, Funata N, Schreiber SL, Yoshida M et al (2005) Significance of HDAC6 regulation via estrogen signaling for cell motility and prognosis in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Oncogene 24(28):4531–4539
Planas-Silva MD, Waltz PK (2007) Estrogen promotes reversible epithelial-to-mesenchymal-like transition and collective motility in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 104(1–2):11–21
Gehlsen KR, Dickerson K, Argraves WS, Engvall E, Ruoslahti E (1989) Subunit structure of a laminin-binding integrin and localization of its binding site on laminin. J Biol Chem 264(32):19034–19038
Bronner-Fraser M (1985) Alterations in neural crest migration by a monoclonal antibody that affects cell adhesion. J Cell Biol 101(2):610–617
Giancotti FG, Ruoslahti E (1990) Elevated levels of the alpha 5 beta 1 fibronectin receptor suppress the transformed phenotype of Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cell 60(5):849–859
Woods Ignatoski KM, Grewal NK, Markwart S, Livant DL, Ethier SP (2003) p38MAPK induces cell surface alpha4 integrin downregulation to facilitate erbB-2-mediated invasion. Neoplasia 5(2):128–134
Dubik D, Shiu RP (1992) Mechanism of estrogen activation of c-myc oncogene expression. Oncogene 7(8):1587–1594
Krishnan V, Wang X, Safe S (1994) Estrogen receptor–Sp1 complexes mediate estrogen-induced cathepsin D gene expression in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 269(22):15912–15917
Rishi AK, Shao ZM, Baumann RG, Li XS, Sheikh MS, Kimura S, Bashirelahi N, Fontana JA (1995) Estradiol regulation of the human retinoic acid receptor alpha gene in human breast carcinoma cells is mediated via an imperfect half-palindromic estrogen response element and Sp1 motifs. Cancer Res 55(21):4999–5006
Panno ML, Mauro L, Marsico S, Bellizzi D, Rizza P, Morelli C, Salerno M, Giordano F, Ando S (2006) Evidence that the mouse insulin receptor substrate-1 belongs to the gene family on which the promoter is activated by estrogen receptor alpha through its interaction with Sp1. J Mol Endocrinol 36(1):91–105
Salvatori L, Ravenna L, Felli MP, Cardillo MR, Russo MA, Frati L, Gulino A, Petrangeli E (2000) Identification of an estrogen-mediated deoxyribonucleic acid-binding independent transactivation pathway on the epidermal growth factor receptor gene promoter. Endocrinology 141(6):2266–2274
Schultz JR, Petz LN, Nardulli AM (2003) Estrogen receptor alpha and Sp1 regulate progesterone receptor gene expression. Mol Cell Endocrinol 201(1–2):165–175
Castro-Rivera E, Samudio I, Safe S (2001) Estrogen regulation of cyclin D1 gene expression in ZR-75 breast cancer cells involves multiple enhancer elements. J Biol Chem 276(33):30853–30861
Korah R, Boots M, Wieder R (2004) Integrin alpha5beta1 promotes survival of growth-arrested breast cancer cells: an in vitro paradigm for breast cancer dormancy in bone marrow. Cancer Res 64(13):4514–4522
Spangenberg C, Lausch EU, Trost TM, Prawitt D, May A, Keppler R, Fees SA, Reutzel D, Bell C, Schmitt S et al (2006) ERBB2-mediated transcriptional up-regulation of the alpha5beta1 integrin fibronectin receptor promotes tumor cell survival under adverse conditions. Cancer Res 66(7):3715–3725
Acknowledgments
Financial support: AIRC 2007, MIUR Ex 60%, and Regione Calabria.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Diego Sisci and Emilia Middea contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sisci, D., Middea, E., Morelli, C. et al. 17β-Estradiol enhances α5 integrin subunit gene expression through ERα–Sp1 interaction and reduces cell motility and invasion of ERα-positive breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 124, 63–77 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-009-0713-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-009-0713-6