Abstract
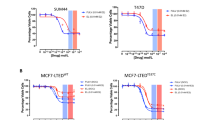
Endothelin-1 (ET-1) and endothelin A receptor (ETAR) contribute to the development and progression of breast carcinomas by modulating cell proliferation, angiogenesis, and anti-apoptosis. We investigated antitumoral effects of the specific ETAR antagonist ZD4054 in breast cancer cells and xenografts, and assessed antitumoral efficacy of the combinations of ZD4054 with aromatase inhibitors and fulvestrant. Gene expression changes were assessed by quantitative real-time PCR. Cell proliferation was measured using alamarBlue®; migration and invasion assays were performed using modified Boyden chambers. Evaluating the antitumoral efficacy of ZD4054 in vivo, different breast cancer models were employed using nude mice xenografts. ZD4054 reduced ET-1 and ETAR expression in MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, and MDA-MB-468 breast cancer cells in a concentration-dependent manner. ZD4054 inhibited invasion by up to 37.1% (P = 0.022). Combinations of ZD4054 with either anastrozole or letrozole produced significant reductions in migration of aromatase-overexpressing MCF-7aro cells (P < 0.05). Combination of ZD4054 with fulvestrant reduced MCF-7 cell migration and invasion by 36.0% (P = 0.027) and 56.7% (P < 0.001), respectively, with effects significantly exceeding those seen with either compound alone. Regarding tumor volume reduction in vivo, ZD4054 (10 mg/kg) was equipotent to fulvestrant (200 mg/kg) and exhibited additive effects with anastrozole (0.5 mg/kg). These data are the first indicating that selective ETAR antagonism by ZD4054 displays antitumoral activity on breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Our data strongly support a rationale for the clinical use of ZD4054 in combination with endocrine therapies.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yanagisawa M, Kurihara H, Kimura S et al (1988) A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vasuclar endothelial cells. Nature 322:411–415
Bagnato A, Rosanò L (2008) The endothelin axis in cancer. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 40:1443–1451
Smollich M, Wülfing P (2008) Targeting the endothelin system: novel therapeutic options in gynecological, urological and breast cancers. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 8:1481–1493
Wülfing P, Diallo R, Kersting C et al (2003) Expression of endothelin-1, endothelin-A and endothelin-B receptor in human breast cancer and correlation with long-term follow-up. Clin Cancer Res 9:4125–4131
Wülfing P, Kersting C, Tio J et al (2004) Endothelin-1-, endothelin-A-, and endothelin-B-receptor expression is correlated with vascular endothelial growth factor expression and angiogenesis in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 10:2393–2400
Rosanò L, Di Castro V, Spinella F et al (2006) ZD4054, a potent endothelin receptor A antagonist, inhibits ovarian carcinoma cell proliferation. Exp Biol Med 231:1132–1135
Smollich M, Götte M, Kersting C et al (2008) Selective ET(A)R antagonist atrasentan inhibits hypoxia-induced breast cancer cell invasion. Breast Cancer Res Treat 108:175–182
Smollich M, Götte M, Kersting C et al (2007) On the role of endothelin-converting enzyme-1 (ECE-1) and neprilysin in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 106:361–369
Bradbury RH, Bath C, Butlin RJ et al (1997) New non-peptide endothelin-A receptor antagonists: synthesis, biological properties, and structure-activity relationships of 5-(dimethylamino)-N-pyridyl-,-N-pyrimidinyl-,-N-pyridazinyl-, and -N-pyrazinyl-1-naph-thalenesulfonamides. J Med Chem 40:996–1004
Rosanò L, Di Castro V, Spinella F, Nicotra MR, Natali PG, Bagnato A (2007) ZD4054, a specific antagonist of the endothelin A receptor, inhibits tumor growth and enhances paclitaxel activity in human ovarian carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther 6:2003–2011
Rosanò L, Di Castro V, Spinella F et al (2007) A combined targeting of endothelin A receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor in ovarian cancer shows enhanced antitumor activity. Cancer Res 67:6351–6359
Carducci MA, Jimeno A (2006) Targeting bone metastasis in prostate cancer with endothelin receptor antagonists. Clin Cancer Res 12:6296–6300
James ND, Borre M, Zonnenberg B et al. (2007) ZD4054, a potent, specific endothelin A receptor antagonist, improves overall survival in pain-free or mildly symptomatic patients with hormone-resistant prostate cancer (HRPC) and bone metastases. Eur J Cancer Suppl 5:3LB
Wülfing P, Götte M, Sonntag B et al (2005) Overexpression of endothelin-A-receptor in breast cancer: regulation by estradiol and cobalt-chloride induced hypoxia. Int J Oncol 26:951–960
Brooks SC, Locke ER, Soule HD (1973) Estrogen receptor in a human cell line (MCF-7) from breast carcinoma. J Biol Chem 248:6251–6253
Langlois AJ, Holder WD Jr, Iglehart JD, Nelson-Rees WA, Wells SA Jr, Blognesi DP (1979) Morphological and biochemical properties of a new human breast cancer cell line. Cancer Res 39:2604–2613
Lasfargues EY, Coutinho WG, Redfield ES (1978) Isolation of two human tumor epithelial cell lines from solid breast carcinomas. J Natl Cancer Inst 61:967–978
Sun XZ, Zhou D, Chen S (1997) Autocrine and paracrine actions of breast tumor aromatase. A three-dimensional cell culture study involving aromatase transfected MCF-7 and T-47D cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 63:29–36
Macedo LF, Guo Z, Tilghman SL, Sabnis GJ, Qiu Y, Brodie A (2006) Role of androgens on MCF-7 breast cancer cell growth and on the inhibitory effect of letrozole. Cancer Res 66:7775–7782
Cailleau R, Young R, Olivé M, Reeves WJ Jr (1974) Breast tumor cell lines from pleural effusions. J Natl Cancer Inst 53:661–674
Brodie A, Jelovac D, Long BJ (2003) Predictions from a preclinical model: studies of aromatase inhibitors and antiestrogens. Clin Cancer Res 9:455–459
Sumitomo M, Shen R, Nanus DM (2005) Involvement of neutral endopeptidase in neoplastic progression. Biochim Biophys Acta 1751:52–59
Sorokin A, Kohan DE (2003) Physiology and pathology of endothelin-1 in renal mesangium. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 285:579–589
Nilsson D, Wackenfors A, Gustafsson L et al (2008) PKC and MAPK signalling pathways regulate vascular endothelin receptor expression. Eur J Pharmacol 580:190–200
Orzechowski HD, Günther A, Menzel S et al (1998) Endothelial expression of endothelin-converting enzyme-1 beta mRNA is regulated by the transcription factor Ets-1. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 3:55–57
Graf K, Koehne P, Gräfe M, Zhang M, Auch-Schwelk W, Fleck E (1995) Regulation and differential expression of neutral endopeptidase 24.11 in human endothelial cells. Hypertension 26:230–235
Zhang WM, Zhou J, Ye QJ (2008) Endothelin-1 enhances proliferation of lung cancer cells by increasing intracellular free Ca(2+). Life Sci 82:764–771
Grant K, Knowles J, Dawas K, Burnstock G, Taylor I, Loizidou M (2007) Mechanisms of endothelin 1-stimulated proliferation in colorectal cancer cell lines. Br J Surg 94:106–112
Dosanjh A, Zuraw B (2003) Endothelin-1 (ET-1) decreases human bronchial epithelial cell migration and proliferation: implications for airway remodeling in asthma. J Asthma 40:883–886
Mizuno N, Kokubu H, Sato M et al (2005) G protein-coupled receptor signaling through Gq and JNK negatively regulates neural progenitor cell migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:12365–12370
Yamazaki D, Kurisu S, Takenawa T (2005) Regulation of cancer cell motility through actin reorganization. Cancer Sci 96:379–386
Milan J, Charalambous C, Elhag R et al (2006) Multiple signalling pathways are involved in endothelin-1-induced brain endothelial cell migration. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 291:155–164
Naik MU, Naik TU, Suckow AT, Duncan MK, Naik UP (2008) Attenuation of junctional adhesion molecule-A is a contributing factor for breast cancer cell invasion. Cancer Res 68:2194–2203
Mehlen P, Bredesen DE (2004) The dependence receptor hypothesis. Apoptosis 9:37–49
Arya M, Ahmed H, Silhi N, Williamson M, Patel HR (2007) Clinical importance and therapeutic implications of the pivotal CXCL12-CXCR4 (chemokine ligand-receptor) interaction in cancer cell migration. Tumor Biol 28:123–131
Hofmann UB, Houben R, Brocker EB, Becker JC (2005) Role of matrix metalloproteinases in melanoma cell invasion. Biochimie 87:307–314
Duffy MJ, Maguire TM, Hill A, McDermott E, O’Higgins N (2000) Metalloproteinases: role in breast carcinogenesis, invasion and metastasis. Breast Cancer Res 2:252–257
Rosanò L, Salani D, Di Castro V, Spinella F, Natali PG, Bagnato A (2002) Endothelin-1 promotes proteolytic activity of ovarian carcinoma. Clin Sci (Lond) 103:306–309
Godara G, Cannon GW, Cannon GM Jr, Bies RR, Nelson JB, Pflug BR (2005) Role of endothelin axis in progression to aggressive phenotype of prostate adenocarcinoma. Prostate 65:27–34
Spinella F, Rosanò L, Di Castro V et al (2007) Endothelin-1 and endothelin-3 promote invasive behavior via hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in human melanoma cells. Cancer Res 67:1725–1734
Liu Y, Geisbuhler B, Jones A (1992) Activation of multiple mechanisms including phospholipase D by endothelin-1 in rat aorta. Am J Physiol 262:941–949
Zheng Y, Rodrik V, Toschi A et al (2006) Phospholipase D couples survival and migration signals in stress response of human cancer cells. J Biol Chem 281:15862–15868
Milde-Langosch K, Röder H, Andritzky B et al (2004) The role of the AP-1 transcription factors c-Fos, FosB, Fra-1 and Fra-2 in the invasion process of mammary carcinomas. Breast Cancer Res Treat 86:139–152
Briggs J, Chamboredou S, Castellazzi M, Kerry JA, Bos TJ (2002) Transcriptional upregulation of SPARC, in response to c-Jun overexpression, contributes to increased motility and invasion of MCF7 breast cancer cells. Oncogene 21:7077–7091
Grande M, Carlström K, Stege R, Pousette A, Faxén M (2002) Estrogens affect endothelin-1 mRNA expression in LNCaP human prostate carcinoma cells. Eur Urol 41:568–572
Duan J, Xu H, Dai S et al (2008) Phytoestrogen alpha-zearalanol inhibits homocysteine-induced endothelin-1 expression and oxidative stress in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis 197:549–555
Morey AK, Razandi M, Pedram A, Hu RM, Prins BA, Levin ER (1998) Oestrogen and progesterone inhibit the stimulated production of endothelin-1. Biochem J 330:1097–1105
Martin LA, Pancholi S, Chan CM et al (2005) The anti-oestrogen ICI 182.780, but not tamoxifen, inhibits growth of MCF-7 breast cancer cells refractory to long-term oestrogen deprivation through down-regulation of oestrogen receptor and IGF signalling. Endocr Relat Cancer 12:1017–1036
Hoffmann J, Sommer A (2005) Steroid hormone receptors as targets for the therapy of breast and prostate cancer—recent advances, mechanisms of resistance, and new approaches. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 93:191–200
Lloyd DG, Smith HM, O’Sullivan T, Zisterer DM, Meegan MJ (2005) Synthesis, structure-activity relationships and antagonistic effects in human MCF-7 breast cancer cells of flexible estrogen receptor modulators. Med Chem 1:335–353
Musa MA, Khan MO, Cooperwood JS (2007) Medicinal chemistry and emerging strategies applied to the development of selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs). Curr Med Chem 14:1249–1261
Fu XD, Giretti MS, Goglia L et al (2008) Comparative actions of progesterone, medroxyprogesterone acetate, drospirenone and nestorone on breast cancer cell migration and invasion. BMC Cancer 8:166
Chambers AF, Groom AC, MacDonald IC (2002) Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nat Rev Cancer 2:563–572
Rosano L, Varmi M, Salani D, Di Castro V, Spinella F, Natali PG, Bagnato A (2001) Endothelin-1 induces tumor proteinase activation and invasiveness of ovarian carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 61:8340–8346
Simonson MS (1993) Endothelins: multifunctional renal peptides. Physiol Rev 73:357–411
Perez-Vizcaino F, Cooper AC, Corder R, Fournier A, Warner TD (1995) Rapid degradation of entothelin-1 by an enzyme released by the rat isolated perfused mesentery. Br J Pharmacol 114:867–871
Okazawa M, Shiraki T, Ninomiya H, Kobayashi S, Masaki T (1998) Endothelin-induced apoptosis of A375 human melanoma cells. J Biol Chem 273:12584–12592
Bohm F, Pernow J, Lindstrom J, Ahlborg G (2003) ETA receptors mediate vasoconstriction, whereas ETB receptors clear endothelin-1 in the splanchnic and renal circulation of healthy men. Clin Sci (Lond) 104:143–151
Acknowledgments
We thank Barbara Kloke and Birgit Pers for their excellent technical assistance. Funding was provided by Münster University Hospital “Innovative Medizinische Forschung” IMF grants WÜ 120332 and WÜ 110527.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smollich, M., Götte, M., Fischgräbe, J. et al. ETAR antagonist ZD4054 exhibits additive effects with aromatase inhibitors and fulvestrant in breast cancer therapy, and improves in vivo efficacy of anastrozole. Breast Cancer Res Treat 123, 345–357 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-009-0644-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-009-0644-2