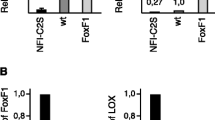
Abstract
Forkhead box M1 (FoxM1) transcription factor is known to play important role in human cancers which, in part, is mediated by its ability to modulate cell cycle regulatory proteins as well as genes involved in cell proliferation and differentiation. In breast cancer, FoxM1 down-regulation is increasingly being recognized as an important mechanism for the targeted activity of anti-cancer agents. However, the mechanistic insight in support of the role of FoxM1 in aggressive breast cancer is poorly understood. We have tested the biological consequence of FoxM1 down-regulation and up-regulation in breast cancer cell lines and found that the down-regulation of FoxM1 in MDA-MB-231 and SUM149 cells by siRNA approach inhibited cell growth, clonogenicity, migration, and invasion. We also found decreased expression of CDK2 and E2F1 with concomitant increase in p21 and p27 proteins, suggesting an important role of FoxM1 in cell cycle progression. In contrast, over-expression of FoxM1 by cDNA transfection, in breast cancer cells (SUM102 and SKBR3) expressing low levels of FoxM1, resulted in increased cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Moreover, down-regulation of FoxM1 inhibited the expression of many factors that are involved in the degradation of extra cellular matrix and angiogenesis such as uPA, uPAR, MMP-2, MMP-9, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) as well as inhibited the activity of MMP-9 and VEGF. Interestingly, over-expression of uPA by cDNA transfection abrogated the cellular effects that were observed by the down-regulation of FoxM1. Taken together, these results suggest the potential application of FoxM1 down-regulation as a novel approach for the treatment of aggressive breast cancer.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Myatt SS, Lam EW (2007) The emerging roles of forkhead box (Fox) proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 7:847–859
Ye H, Holterman AX, Yoo KW, Franks RR, Costa RH (1999) Premature expression of the winged helix transcription factor HFH-11B in regenerating mouse liver accelerates hepatocyte entry into S phase. Mol Cell Biol 19:8570–8580
Wang X, Kiyokawa H, Dennewitz MB, Costa RH (2002) The forkhead box m1b transcription factor is essential for hepatocyte DNA replication and mitosis during mouse liver regeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:16881–16886
Wonsey DR, Follettie MT (2005) Loss of the forkhead transcription factor FoxM1 causes centrosome amplification and mitotic catastrophe. Cancer Res 65:5181–5189
Kalinichenko VV, Major ML, Wang X, Petrovic V, Kuechle J, Yoder HM, Dennewitz MB, Shin B, Datta A, Raychaudhuri P, Costa RH (2004) Foxm1b transcription factor is essential for development of hepatocellular carcinomas and is negatively regulated by the p19ARF tumor suppressor. Genes Dev 18:830–850
Kalin TV, Wang IC, Ackerson TJ, Major ML, Detrisac CJ, Kalinichenko VV, Lyubimov A, Costa RH (2006) Increased levels of the FoxM1 transcription factor accelerate development and progression of prostate carcinomas in both TRAMP and LADY transgenic mice. Cancer Res 66:1712–1720
Kim IM, Ackerson T, Ramakrishna S, Tretiakova M, Wang IC, Kalin TV, Major ML, Gusarova GA, Yoder HM, Costa RH, Kalinichenko VV (2006) The forkhead box m1 transcription factor stimulates the proliferation of tumor cells during development of lung cancer. Cancer Res 66:2153–2161
Liu M, Dai B, Kang SH, Ban K, Huang FJ, Lang FF, Aldape KD, Xie TX, Pelloski CE, Xie K, Sawaya R, Huang S (2006) FoxM1B is overexpressed in human glioblastomas and critically regulates the tumorigenicity of glioma cells. Cancer Res 66:3593–3602
Dai B, Kang SH, Gong W, Liu M, Aldape KD, Sawaya R, Huang S (2007) Aberrant FoxM1B expression increases matrix metalloproteinase-2 transcription and enhances the invasion of glioma cells. Oncogene 26:6212–6219
Zhang Y, Zhang N, Dai B, Liu M, Sawaya R, Xie K, Huang S (2008) FoxM1B transcriptionally regulates vascular endothelial growth factor expression and promotes the angiogenesis and growth of glioma cells. Cancer Res 68:8733–8742
Chan DW, Yu SY, Chiu PM, Yao KM, Liu VW, Cheung AN, Ngan HY (2008) Over-expression of FOXM1 transcription factor is associated with cervical cancer progression and pathogenesis. J Pathol 215:245–252
Li Q, Zhang N, Jia Z, Le X, Dai B, Wei D, Huang S, Tan D, Xie K (2009) Critical role and regulation of transcription factor FoxM1 in human gastric cancer angiogenesis and progression. Cancer Res 69:3501–3509
Wang IC, Chen YJ, Hughes DE, Ackerson T, Major ML, Kalinichenko VV, Costa RH, Raychaudhuri P, Tyner AL, Lau LF (2008) FoxM1 regulates transcription of JNK1 to promote the G1/S transition and tumor cell invasiveness. J Biol Chem 283:20770–20778
Wang IC, Meliton L, Tretiakova M, Costa RH, Kalinichenko VV, Kalin TV (2008) Transgenic expression of the forkhead box M1 transcription factor induces formation of lung tumors. Oncogene 27:4137–4149
Yoshida Y, Wang IC, Yoder HM, Davidson NO, Costa RH (2007) The forkhead box M1 transcription factor contributes to the development and growth of mouse colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology 132:1420–1431
Wang Z, Banerjee S, Kong D, Li Y, Sarkar FH (2007) Down-regulation of forkhead box M1 transcription factor leads to the inhibition of invasion and angiogenesis of pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res 67:8293–8300
Rahman KW, Li Y, Wang Z, Sarkar SH, Sarkar FH (2006) Gene expression profiling revealed survivin as a target of 3,3′-diindolylmethane-induced cell growth inhibition and apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 66:4952–4960
Kwok JM, Myatt SS, Marson CM, Coombes RC, Constantinidou D, Lam EW (2008) Thiostrepton selectively targets breast cancer cells through inhibition of forkhead box M1 expression. Mol Cancer Ther 7:2022–2032
McGovern UB, Francis RE, Peck B, Guest SK, Wang J, Myatt SS, Krol J, Kwok JM, Polychronis A, Coombes RC, Lam EW (2009) Gefitinib (Iressa) represses FOXM1 expression via FOXO3a in breast cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 8:582–591
Ahmad A, Banerjee S, Wang Z, Kong D, Sarkar FH (2008) Plumbagin-induced apoptosis of human breast cancer cells is mediated by inactivation of NF-kappaB and Bcl-2. J Cell Biochem 105:1461–1471
Ahmad A, Kong D, Sarkar SH, Wang Z, Banerjee S, Sarkar FH (2009) Inactivation of uPA and its receptor uPAR by 3,3′-diindolylmethane (DIM) leads to the inhibition of prostate cancer cell growth and migration. J Cell Biochem 107:516–527
Ahmad A, Kong D, Wang Z, Sarkar SH, Banerjee S, Sarkar FH (2009) Down-regulation of uPA and uPAR by 3,3′-diindolylmethane contributes to the inhibition of cell growth and migration of breast cancer cells. J Cell Biochem doi:10.1002/jcb.22323
Ali S, Banerjee S, Ahmad A, El-Rayes BF, Philip PA, Sarkar FH (2008) Apoptosis-inducing effect of erlotinib is potentiated by 3,3′-diindolylmethane in vitro and in vivo using an orthotopic model of pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 7:1708–1719
Dass K, Ahmad A, Azmi AS, Sarkar SH, Sarkar FH (2008) Evolving role of uPA/uPAR system in human cancers. Cancer Treat Rev 34:122–136
Katoh M, Katoh M (2004) Human FOX gene family (review). Int J Oncol 25:1495–1500
Halasi M, Gartel AL (2009) A novel mode of FoxM1 regulation: positive auto-regulatory loop. Cell Cycle 8:1966–1967
Radhakrishnan SK, Bhat UG, Hughes DE, Wang IC, Costa RH, Gartel AL (2006) Identification of a chemical inhibitor of the oncogenic transcription factor forkhead box M1. Cancer Res 66:9731–9735
Adami GR, Ye H (2007) Future roles for FoxM1 inhibitors in cancer treatments. Future Oncol 3:1–3
Radhakrishnan SK, Gartel AL (2008) FOXM1: the Achilles’ heel of cancer? Nat Rev Cancer 8:c1
Pilarsky C, Wenzig M, Specht T, Saeger HD, Grutzmann R (2004) Identification and validation of commonly overexpressed genes in solid tumors by comparison of microarray data. Neoplasia 6:744–750
Li Y, Hussain M, Sarkar SH, Eliason J, Li R, Sarkar FH (2005) Gene expression profiling revealed novel mechanism of action of Taxotere and Furtulon in prostate cancer cells. BMC Cancer 5:7
Li Y, Hong X, Hussain M, Sarkar SH, Li R, Sarkar FH (2005) Gene expression profiling revealed novel molecular targets of docetaxel and estramustine combination treatment in prostate cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 4:389–398
Laoukili J, Kooistra MR, Bras A, Kauw J, Kerkhoven RM, Morrison A, Clevers H, Medema RH (2005) FoxM1 is required for execution of the mitotic programme and chromosome stability. Nat Cell Biol 7:126–136
Laoukili J, Stahl M, Medema RH (2007) FoxM1: at the crossroads of ageing and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1775:92–102
Costa RH (2005) FoxM1 dances with mitosis. Nat Cell Biol 7:108–110
Major ML, Lepe R, Costa RH (2004) Forkhead box M1B transcriptional activity requires binding of Cdk-cyclin complexes for phosphorylation-dependent recruitment of p300/CBP coactivators. Mol Cell Biol 24:2649–2661
Tan Y, Raychaudhuri P, Costa RH (2007) Chk2 mediates stabilization of the FoxM1 transcription factor to stimulate expression of DNA repair genes. Mol Cell Biol 27:1007–1016
Lee MH, Yang HY (2001) Negative regulators of cyclin-dependent kinases and their roles in cancers. Cell Mol Life Sci 58:1907–1922
Coqueret O (2003) New roles for p21 and p27 cell-cycle inhibitors: a function for each cell compartment? Trends Cell Biol 13:65–70
Wang X, Krupczak-Hollis K, Tan Y, Dennewitz MB, Adami GR, Costa RH (2002) Increased hepatic Forkhead Box M1B (FoxM1B) levels in old-aged mice stimulated liver regeneration through diminished p27Kip1 protein levels and increased Cdc25B expression. J Biol Chem 277:44310–44316
Wang IC, Chen YJ, Hughes D, Petrovic V, Major ML, Park HJ, Tan Y, Ackerson T, Costa RH (2005) Forkhead box M1 regulates the transcriptional network of genes essential for mitotic progression and genes encoding the SCF (Skp2-Cks1) ubiquitin ligase. Mol Cell Biol 25:10875–10894
Curran S, Murray GI (2000) Matrix metalloproteinases: molecular aspects of their roles in tumour invasion and metastasis. Eur J Cancer 36:1621–1630
Chetty C, Bhoopathi P, Rao JS, Lakka SS (2009) Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-2 enhances radiosensitivity by abrogating radiation-induced FoxM1-mediated G2/M arrest in A549 lung cancer cells. Int J Cancer 124:2468–2477
Loges S, Mazzone M, Hohensinner P, Carmeliet P (2009) Silencing or fueling metastasis with VEGF inhibitors: antiangiogenesis revisited. Cancer Cell 15:167–170
Wang Z, Kong D, Banerjee S, Li Y, Adsay NV, Abbruzzese J, Sarkar FH (2007) Down-regulation of platelet-derived growth factor-D inhibits cell growth and angiogenesis through inactivation of Notch-1 and nuclear factor-kappaB signaling. Cancer Res 67:11377–11385
Wang Z, Banerjee S, Li Y, Rahman KM, Zhang Y, Sarkar FH (2006) Down-regulation of notch-1 inhibits invasion by inactivation of nuclear factor-kappaB, vascular endothelial growth factor, and matrix metalloproteinase-9 in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res 66:2778–2784
Kong D, Li Y, Wang Z, Banerjee S, Sarkar FH (2007) Inhibition of angiogenesis and invasion by 3,3′-diindolylmethane is mediated by the nuclear factor-kappaB downstream target genes MMP-9 and uPA that regulated bioavailability of vascular endothelial growth factor in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 67:3310–3319
Pillay V, Dass CR, Choong PF (2007) The urokinase plasminogen activator receptor as a gene therapy target for cancer. Trends Biotechnol 25:33–39
Han B, Nakamura M, Mori I, Nakamura Y, Kakudo K (2005) Urokinase-type plasminogen activator system and breast cancer (review). Oncol Rep 14:105–112
Bhat UG, Halasi M, Gartel AL (2009) Thiazole antibiotics target FoxM1 and induce apoptosis in human cancer cells. PLoS ONE 4:e5592
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10549-016-3904-y.
The paper is retracted at the request of the publisher because in Figs. 5a and 5b, and 6c micrograph images are re-used and re-labeled to represent different conditions.
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmad, A., Wang, Z., Kong, D. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: FoxM1 down-regulation leads to inhibition of proliferation, migration and invasion of breast cancer cells through the modulation of extra-cellular matrix degrading factors. Breast Cancer Res Treat 122, 337–346 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-009-0572-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-009-0572-1