Abstract
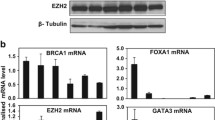
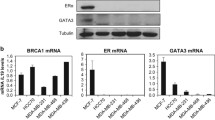
To understand the mechanism of transcriptional down-regulation of BRCA1 by promoter methylation, we screened 51 breast cancer cell lines and identified HCC38 as another BRCA1 promoter-methylated cell line in addition to UACC3199. There was low expression of BRCA1 mRNA and BRCA1 protein in both cell lines as measured by quantitative RT-PCR and western blot analysis. After transient treatment with 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (5-aza-CdR) and trichostatin A (TSA), re-expression of BRCA1 mRNA and BRCA1 protein was detected in UACC3199 cells, but not in HCC38 cells. Another demethylating agent, zebularine, did not induce BRCA1 re-expression in either cell line. To test the hypothesis that methylation of CpG sites may affect accessibility of the BRCA1 promoter to transcription factors and consequently cause down-regulation of BRCA1, we analyzed the binding of four transcription factors (CTCF, Sp1, E2F1 and E2F6) to the BRCA1 promoter using chromatin immunoprecipitation assay (ChIP) and quantitative PCR. CTCF and E2F1 were enriched at the unmethylated BRCA1 promoter in MCF-7 cells. In contrast, these two transcription factors were not enriched at the methylated BRCA1 promoter in UACC3199 and HCC38 cells. Following demethylating drug treatment, E2F1 was enriched at the BRCA1 promoter in the demethylated UACC3199 cells. This indicates that reduced accessibility of transcription factors to the methylated promoter is one of the mechanisms for down-regulation of BRCA1 in heavily methylated cancer cells.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Futreal PA, Liu Q, Shattuck-Eidens D, Cochran C, Harshman K, Tavtigian S, Bennett LM, Haugen-Strano A, Swensen J, Miki Y et al (1994) BRCA1 mutations in primary breast and ovarian carcinomas. Science 266(5182):120–122. doi:10.1126/science.7939630
Newman B, Mu H, Butler LM, Millikan RC, Moorman PG, King MC (1998) Frequency of breast cancer attributable to BRCA1 in a population-based series of American women. JAMA 279(12):915–921. doi:10.1001/jama.279.12.915
Esteller M, Silva JM, Dominguez G, Bonilla F, Matias-Guiu X, Lerma E, Bussaglia E, Prat J, Harkes IC, Repasky EA et al (2000) Promoter hypermethylation and BRCA1 inactivation in sporadic breast and ovarian tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst 92(7):564–569. doi:10.1093/jnci/92.7.564
Mueller CR, Roskelley CD (2003) Regulation of BRCA1 expression and its relationship to sporadic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 5(1):45–52. doi:10.1186/bcr557
Jones PA, Baylin SB (2002) The fundamental role of epigenetic events in cancer. Nat Rev Genet 3(6):415–428
Herman JG, Baylin SB (2003) Gene silencing in cancer in association with promoter hypermethylation. N Engl J Med 349(21):2042–2054. doi:10.1056/NEJMra023075
Jones PA, Baylin SB (2007) The epigenomics of cancer. Cell 128(4):683–692. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.01.029
Catteau A, Morris JR (2002) BRCA1 methylation: a significant role in tumour development? Semin Cancer Biol 12(5):359–371. doi:10.1016/S1044-579X(02)00056-1
Rice JC, Massey-Brown KS, Futscher BW (1998) Aberrant methylation of the BRCA1 CpG island promoter is associated with decreased BRCA1 mRNA in sporadic breast cancer cells. Oncogene 17(14):1807–1812. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202086
Wilson CA, Ramos L, Villasenor MR, Anders KH, Press MF, Clarke K, Karlan B, Chen JJ, Scully R, Livingston D et al (1999) Localization of human BRCA1 and its loss in high-grade, non-inherited breast carcinomas. Nat Genet 21(2):236–240. doi:10.1038/6029
Rice JC, Ozcelik H, Maxeiner P, Andrulis I, Futscher BW (2000) Methylation of the BRCA1 promoter is associated with decreased BRCA1 mRNA levels in clinical breast cancer specimens. Carcinogenesis 21(9):1761–1765. doi:10.1093/carcin/21.9.1761
Okochi E, Miyamoto K, Wakazono K, Shima H, Sugimura T, Ushijima T (2002) Reduced Brca1 protein expression in 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4, 5-b]pyridine-induced rat mammary carcinomas. Mol Carcinog 34(4):211–218. doi:10.1002/mc.10065
Matros E, Wang ZC, Lodeiro G, Miron A, Iglehart JD, Richardson AL (2005) BRCA1 promoter methylation in sporadic breast tumors: relationship to gene expression profiles. Breast Cancer Res Treat 91(2):179–186. doi:10.1007/s10549-004-7603-8
Wei M, Grushko TA, Dignam J, Hagos F, Nanda R, Sveen L, Xu J, Fackenthal J, Tretiakova M, Das S et al (2005) BRCA1 promoter methylation in sporadic breast cancer is associated with reduced BRCA1 copy number and chromosome 17 aneusomy. Cancer Res 65(23):10692–10699. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1277
Yoo CB, Jones PA (2006) Epigenetic therapy of cancer: past, present and future. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5(1):37–50. doi:10.1038/nrd1930
Lin KT, Momparler RL, Rivard GE (1981) High-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of chemical stability of 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine. J Pharm Sci 70(11):1228–1232. doi:10.1002/jps.2600701112
Juttermann R, Li E, Jaenisch R (1994) Toxicity of 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine to mammalian cells is mediated primarily by covalent trapping of DNA methyltransferase rather than DNA demethylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91(25):11797–11801. doi:10.1073/pnas.91.25.11797
Stresemann C, Brueckner B, Musch T, Stopper H, Lyko F (2006) Functional diversity of DNA methyltransferase inhibitors in human cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 66(5):2794–2800. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2821
Cheng JC, Matsen CB, Gonzales FA, Ye W, Greer S, Marquez VE, Jones PA, Selker EU (2003) Inhibition of DNA methylation and reactivation of silenced genes by zebularine. J Natl Cancer Inst 95(5):399–409
Cheng JC, Weisenberger DJ, Gonzales FA, Liang G, Xu GL, Hu YG, Marquez VE, Jones PA (2004) Continuous zebularine treatment effectively sustains demethylation in human bladder cancer cells. Mol Cell Biol 24(3):1270–1278. doi:10.1128/MCB.24.3.1270-1278.2004
Cheng JC, Yoo CB, Weisenberger DJ, Chuang J, Wozniak C, Liang G, Marquez VE, Greer S, Orntoft TF, Thykjaer T et al (2004) Preferential response of cancer cells to zebularine. Cancer Cell 6(2):151–158. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2004.06.023
Butcher DT, Mancini-DiNardo DN, Archer TK, Rodenhiser DI (2004) DNA binding sites for putative methylation boundaries in the unmethylated region of the BRCA1 promoter. Int J Cancer 111(5):669–678. doi:10.1002/ijc.20324
Wang A, Schneider-Broussard R, Kumar AP, MacLeod MC, Johnson DG (2000) Regulation of BRCA1 expression by the Rb-E2F pathway. J Biol Chem 275(6):4532–4536. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.6.4532
Oberley MJ, Inman DR, Farnham PJ (2003) E2F6 negatively regulates BRCA1 in human cancer cells without methylation of histone H3 on lysine 9. J Biol Chem 278(43):42466–42476. doi:10.1074/jbc.M307733200
Bindra RS, Gibson SL, Meng A, Westermark U, Jasin M, Pierce AJ, Bristow RG, Classon MK, Glazer PM (2005) Hypoxia-induced down-regulation of BRCA1 expression by E2Fs. Cancer Res 65(24):11597–11604. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2119
Herman JG, Graff JR, Myohanen S, Nelkin BD, Baylin SB (1996) Methylation-specific PCR: a novel PCR assay for methylation status of CpG islands. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93(18):9821–9826. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.18.9821
Wei M, Xu J, Dignam J, Nanda R, Sveen L, Fackenthal J, Grushko TA, Olopade OI (2008) Estrogen receptor alpha, BRCA1, and FANCF promoter methylation occur in distinct subsets of sporadic breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res Treat 111(1):113–120. doi:10.1007/s10549-007-9766-6
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25(4):402–408. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Frank SR, Schroeder M, Fernandez P, Taubert S, Amati B (2001) Binding of c-Myc to chromatin mediates mitogen-induced acetylation of histone H4 and gene activation. Genes Dev 15(16):2069–2082. doi:10.1101/gad.906601
Bell AC, West AG, Felsenfeld G (1999) The protein CTCF is required for the enhancer blocking activity of vertebrate insulators. Cell 98(3):387–396. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81967-4
Filippova GN, Thienes CP, Penn BH, Cho DH, Hu YJ, Moore JM, Klesert TR, Lobanenkov VV, Tapscott SJ (2001) CTCF-binding sites flank CTG/CAG repeats and form a methylation-sensitive insulator at the DM1 locus. Nat Genet 28(4):335–343. doi:10.1038/ng570
Hark AT, Schoenherr CJ, Katz DJ, Ingram RS, Levorse JM, Tilghman SM (2000) CTCF mediates methylation-sensitive enhancer-blocking activity at the H19/Igf2 locus. Nature 405(6785):486–489. doi:10.1038/35013106
Nakagawa H, Chadwick RB, Peltomaki P, Plass C, Nakamura Y, de La Chapelle A (2001) Loss of imprinting of the insulin-like growth factor II gene occurs by biallelic methylation in a core region of H19-associated CTCF-binding sites in colorectal cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(2):591–596. doi:10.1073/pnas.011528698
Ishihara K, Oshimura M, Nakao M (2006) CTCF-dependent chromatin insulator is linked to epigenetic remodeling. Mol Cell 23(5):733–742. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2006.08.008
Wijermans P, Lubbert M, Verhoef G, Bosly A, Ravoet C, Andre M, Ferrant A (2000) Low-dose 5-aza-2’-deoxycytidine, a DNA hypomethylating agent, for the treatment of high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome: a multicenter phase II study in elderly patients. J Clin Oncol 18(5):956–962
Issa JP, Garcia-Manero G, Giles FJ, Mannari R, Thomas D, Faderl S, Bayar E, Lyons J, Rosenfeld CS, Cortes J et al (2004) Phase 1 study of low-dose prolonged exposure schedules of the hypomethylating agent 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (decitabine) in hematopoietic malignancies. Blood 103(5):1635–1640. doi:10.1182/blood-2003-03-0687
Issa JP, Gharibyan V, Cortes J, Jelinek J, Morris G, Verstovsek S, Talpaz M, Garcia-Manero G, Kantarjian HM (2005) Phase II study of low-dose decitabine in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia resistant to imatinib mesylate. J Clin Oncol 23(17):3948–3956. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.11.981
Yoo CB, Cheng JC, Jones PA (2004) Zebularine: a new drug for epigenetic therapy. Biochem Soc Trans 32(Pt 6):910–912. doi:10.1042/BST0320910
Chuang JC, Yoo CB, Kwan JM, Li TW, Liang G, Yang AS, Jones PA (2005) Comparison of biological effects of non-nucleoside DNA methylation inhibitors versus 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine. Mol Cancer Ther 4(10):1515–1520. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-05-0172
Acknowledgments
Grant support: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences grant P50 ES012382, NIH-National Cancer Institute Cancer Center Support grant 3P30 CA 23074, the Breast Cancer Research Foundation, the National Women’s Cancer Research Alliance, and the Falk Medical Research Trust (O.I. Olopade). We thank Olopade lab members for helpful discussion. We also thank Michelle Porcellino and Lisa Sveen for critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Huo, D., Chen, Y. et al. CpG island methylation affects accessibility of the proximal BRCA1 promoter to transcription factors. Breast Cancer Res Treat 120, 593–601 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-009-0422-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-009-0422-1