Abstract
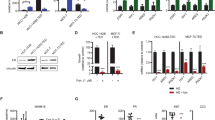
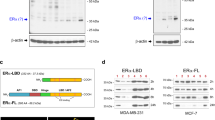
Estrogens play a crucial role in breast tumor growth, which is the rationale for the use of antiestrogens, such as tamoxifen, in women with estrogen receptor (ER)-α-positive breast cancer. However, hormone resistance is a major clinical problem. Altered growth factor signaling to the ERα pathway has been shown to be associated with the development of clinical resistance. We previously have identified a mutation that replaces arginine for lysine at residue 303 (K303R) of ERα, which confers hypersensitive growth in low levels of estrogen. To determine if the K303R mutation could participate in the evolution of hormone resistance, we generated MCF-7 breast cancer cells stably transfected with either wild-type (WT) or K303R ERα. We found that the mutation confers decreased sensitivity to tamoxifen in the presence of the growth factor heregulin, using anchorage-independent growth assays. K303R ERα-expressing cells were hypersensitive to growth factor signals. Our data suggest that phosphorylation of serine 305 within the hinge domain of ERα might play a key role in increasing ligand-independent activity of the mutant receptor. We hypothesize that the mutation adapts the receptor for enhanced bidirectional cross-talk with the HER2 growth factor receptor pathway, which then impacts on responsiveness to tamoxifen.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mangelsdorf DJ, Thummel C, Beato M, Herrlich P, Schutz G, Umesono K, Blumberg B, Kastner P, Mark M, Chambon P, Evans RM (1995) The nuclear receptor superfamily: the second decade. Cell 83(6):835–839. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(95)90199-X
O’Malley BW (2006) Molecular biology. Little molecules with big goals. Science 313(5794):1749–1750. doi:10.1126/science.1132509
Bjornstrom L, Sjoberg M (2005) Mechanisms of estrogen receptor signaling: convergence of genomic and nongenomic actions on target genes. Mol Endocrinol 19(4):833–842. doi:10.1210/me.2004-0486
Fuqua SAW, Wiltschke C, Zhang QX, Borg A, Castles CG, Friedrichs WE, Hopp T, Hilsenbeck S, Mohsin S, O’Connell P, Allred DC (2000) A hypersensitive estrogen receptor-α mutation in premalignant breast lesions. Cancer Res 60(15):4026–4029
Tebbit CL, Bentley RC, Olson JA Jr, Marks JR (2004) Estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1) mutant A908G is not a common feature in benign and malignant proliferations of the breast. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 40(1):51–54. doi:10.1002/gcc.20017
Davies MP, O’Neill PA, Innes H, Sibson DR (2005) Hypersensitive K303R oestrogen receptor-alpha variant not found in invasive carcinomas. Breast Cancer Res 7(1):R113–R118. doi:10.1186/bcr965
Herynk MH, Parra I, Cui Y, Beyer A, Wu MF, Hilsenbeck SG, Fuqua SA (2007) Association between the estrogen receptor alpha A908G mutation and outcomes in invasive breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 13(11):3235–3243. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2608
Conway K, Parrish E, Edmiston SN, Tolbert D, Tse CK, Geradts J, Livasy CA, Singh H, Newman B, Millikan RC (2005) The estrogen receptor-alpha A908G (K303R) mutation occurs at a low frequency in invasive breast tumors: results from a population-based study. Breast Cancer Res 7(6):R871–R880. doi:10.1186/bcr1315
Cui Y, Zhang M, Pestell R, Curran EM, Welshons WV, Fuqua SA (2004) Phosphorylation of estrogen receptor alpha blocks its acetylation and regulates estrogen sensitivity. Cancer Res 64(24):9199–9208. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-2126
Michalides R, Griekspoor A, Balkenende A, Verwoerd D, Janssen L, Jalink K, Floore A, Velds A, van’t Veer L, Neefjes J (2004) Tamoxifen resistance by a conformational arrest of the estrogen receptor alpha after PKA activation in breast cancer. Cancer Cell 5(6):597–605. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2004.05.016
Wang RA, Mazumdar A, Vadlamudi RK, Kumar R (2002) P21-activated kinase-1 phosphorylates and transactivates estrogen receptor-alpha and promotes hyperplasia in mammary epithelium. EMBO J 21(20):5437–5447. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdf543
Rayala SK, Talukder AH, Balasenthil S, Tharakan R, Barnes CJ, Wang RA, Aldaz M, Khan S, Kumar R (2006) P21-activated kinase 1 regulation of estrogen receptor-alpha activation involves serine 305 activation linked with serine 118 phosphorylation. Cancer Res 66(3):1694–1701. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2922
Fan P, Wang J, Santen RJ, Yue W (2007) Long-term treatment with tamoxifen facilitates translocation of estrogen receptor alpha out of the nucleus and enhances its interaction with EGFR in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 67(3):1352–1360. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1020
Levin ER (2003) Bidirectional signaling between the estrogen receptor and the epidermal growth factor receptor. Mol Endocrinol 17(3):309–317. doi:10.1210/me.2002-0368
Song RX, Santen RJ (2006) Membrane initiated estrogen signaling in breast cancer. Biol Reprod 75(1):9–16. doi:10.1095/biolreprod.105.050070
Lee AV, Cui X, Oesterreich S (2001) Cross-talk among estrogen receptor, epidermal growth factor, and insulin-like growth factor signaling in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 7(12 Suppl):4429s–4435s (discussion 4411s–4412s)
Nicholson RI, McClelland RA, Robertson JF, Gee JM (1999) Involvement of steroid hormone and growth factor cross-talk in endocrine response in breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 6(3):373–387. doi:10.1677/erc.0.0060373
Schiff R, Massarweh S, Shou J, Osborne CK (2003) Breast cancer endocrine resistance: how growth factor signaling and estrogen receptor coregulators modulate response. Clin Cancer Res 9((1 Pt 2)):447S–454S
Schiff R, Massarweh SA, Shou J, Bharwani L, Mohsin SK, Osborne CK (2004) Cross-talk between estrogen receptor and growth factor pathways as a molecular target for overcoming endocrine resistance. Clin Cancer Res 10((1 Pt 2)):331S–336S. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-031212
Arpino G, Green SJ, Allred DC, Lew D, Martino S, Osborne CK, Elledge RM (2004) HER-2 amplification, HER-1 expression, and tamoxifen response in estrogen receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer: a southwest oncology group study. Clin Cancer Res 10(17):5670–5676. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0110
Berry DA, Muss HB, Thor AD, Dressler L, Liu ET, Broadwater G, Budman DR, Henderson IC, Barcos M, Hayes D, Norton L (2000) HER-2/neu and p53 expression versus tamoxifen resistance in estrogen receptor-positive, node-positive breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 18(20):3471–3479
Shou J, Massarweh S, Osborne CK, Wakeling AE, Ali S, Weiss H, Schiff R (2004) Mechanisms of tamoxifen resistance: increased estrogen receptor-HER2/neu cross-talk in ER/HER2-positive breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 96(12):926–935
Perez-Tenorio G, Stal O (2002) Activation of AKT/PKB in breast cancer predicts a worse outcome among endocrine treated patients. Br J Cancer 86(4):540–545. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6600126
Gee JM, Robertson JF, Ellis IO, Nicholson RI (2001) Phosphorylation of ERK1/2 mitogen-activated protein kinase is associated with poor response to anti-hormonal therapy and decreased patient survival in clinical breast cancer. Int J Cancer 95(4):247–254. doi:10.1002/1097-0215(20010720)95:4<247::AID-IJC1042>3.0.CO;2-S
Nicholson S, Halcrow P, Sainsbury JR, Angus B, Chambers P, Farndon JR, Harris AL (1988) Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFr) status associated with failure of primary endocrine therapy in elderly postmenopausal patients with breast cancer. Br J Cancer 58(6):810–814
Sharp ZD, Mancini MG, Hinojos CA, Dai F, Berno V, Szafran AT, Smith KP, Lele TP, Ingber DE, Mancini MA (2006) Estrogen-receptor-alpha exchange and chromatin dynamics are ligand- and domain-dependent. J Cell Sci 119((Pt 19)):4101–4116. doi:10.1242/jcs.03161
Berno V, Amazit L, Hinojos C, Zhong J, Mancini MG, Sharp ZD, Mancini MA (2008) Activation of estrogen receptor-alpha by E2 or EGF induces temporally distinct patterns of large-scale chromatin modification and mRNA transcription. PLoS One 3(5):e2286. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002286
Berno V, Hinojos CA, Amazit L, Szafran AT, Mancini MA (2006) High-resolution, high-throughput microscopy analyses of nuclear receptor and coregulator function. Methods Enzymol 414:188–210. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(06)14011-2
Smith CL, Conneely OM, O’Malley BW (1993) Modulation of the ligand-independent activation of the human estrogen receptor by hormone and antihormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90(13):6120–6124. doi:10.1073/pnas.90.13.6120
Bardou VJ, Arpino G, Elledge RM, Osborne CK, Clark GM (2003) Progesterone receptor status significantly improves outcome prediction over estrogen receptor status alone for adjuvant endocrine therapy in two large breast cancer databases. J Clin Oncol 21(10):1973–1979. doi:10.1200/JCO.2003.09.099
Ravdin PM, Green S, Dorr TM, McGuire WL, Fabian C, Pugh RP, Carter RD, Rivkin SE, Borst JR, Belt RJ et al (1992) Prognostic significance of progesterone receptor levels in estrogen receptor-positive patients with metastatic breast cancer treated with tamoxifen: results of a prospective southwest oncology group study. J Clin Oncol 10(8):1284–1291
Elledge RM, Green S, Pugh R, Allred DC, Clark GM, Hill J, Ravdin P, Martino S, Osborne CK (2000) Estrogen receptor (ER) and progesterone receptor (PgR), by ligand-binding assay compared with ER, PgR and pS2, by immuno-histochemistry in predicting response to tamoxifen in metastatic breast cancer: a southwest oncology group study. Int J Cancer 89(2):111–117. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(20000320)89:2<111::AID-IJC2>3.0.CO;2-W
Goss PE, Ingle JN, Martino S, Robert NJ, Muss HB, Piccart MJ, Castiglione M, Tu D, Shepherd LE, Pritchard KI, Livingston RB, Davidson NE, Norton L, Perez EA, Abrams JS, Cameron DA, Palmer MJ, Pater JL (2007) Efficacy of letrozole extended adjuvant therapy according to estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor status of the primary tumor: National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group MA.17. J Clin Oncol 25(15):2006–2011. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.09.4482
Cui X, Schiff R, Arpino G, Osborne CK, Lee AV (2005) Biology of progesterone receptor loss in breast cancer and its implications for endocrine therapy. J Clin Oncol 23(30):7721–7735. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.09.004
Lange CA, Shen T, Horwitz KB (2000) Phosphorylation of human progesterone receptors at serine-294 by mitogen-activated protein kinase signals their degradation by the 26S proteasome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(3):1032–1037. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.3.1032
Hopp TA, Weiss HL, Hilsenbeck SG, Cui Y, Allred DC, Horwitz KB, Fuqua SA (2004) Breast cancer patients with progesterone receptor PR-A-rich tumors have poorer disease-free survival rates. Clin Cancer Res 10(8):2751–2760. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-03-0141
Migliaccio A, Di Domenico M, Castoria G, Nanayakkara M, Lombardi M, de Falco A, Bilancio A, Varricchio L, Ciociola A, Auricchio F (2005) Steroid receptor regulation of epidermal growth factor signaling through Src in breast and prostate cancer cells: steroid antagonist action. Cancer Res 65(22):10585–10593. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-0912
Wong CW, McNally C, Nickbarg E, Komm BS, Cheskis BJ (2002) Estrogen receptor-interacting protein that modulates its nongenomic activity-crosstalk with Src/Erk phosphorylation cascade. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(23):14783–14788. doi:10.1073/pnas.192569699
Song RX, McPherson RA, Adam L, Bao Y, Shupnik M, Kumar R, Santen RJ (2002) Linkage of rapid estrogen action to MAPK activation by ERalpha-Shc association and Shc pathway activation. Mol Endocrinol 16(1):116–127. doi:10.1210/me.16.1.116
Sun M, Paciga JE, Feldman RI, Yuan Z, Coppola D, Lu YY, Shelley SA, Nicosia SV, Cheng JQ (2001) Phosphatidylinositol-3-OH Kinase (PI3K)/AKT2, activated in breast cancer, regulates and is induced by estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) via interaction between ERalpha and PI3K. Cancer Res 61(16):5985–5991
Herynk MH, Beyer AR, Cui Y, Weiss H, Anderson E, Green TP, Fuqua SA (2006) Cooperative action of tamoxifen and c-Src inhibition in preventing the growth of estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 5(12):3023–3031. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0394
Nicholson RI, Hutcheson IR, Harper ME, Knowlden JM, Barrow D, McClelland RA, Jones HE, Wakeling AE, Gee JM (2001) Modulation of epidermal growth factor receptor in endocrine-resistant, oestrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 8(3):175–182. doi:10.1677/erc.0.0080175
Vogel CL, Cobleigh MA, Tripathy D, Gutheil JC, Harris LN, Fehrenbacher L, Slamon DJ, Murphy M, Novotny WF, Burchmore M, Shak S, Stewart SJ, Press M (2002) Efficacy and safety of trastuzumab as a single agent in first-line treatment of HER2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 20(3):719–726. doi:10.1200/JCO.20.3.719
Romond EH, Perez EA, Bryant J, Suman VJ, Geyer CE Jr, Davidson NE, Tan-Chiu E, Martino S, Paik S, Kaufman PA, Swain SM, Pisansky TM, Fehrenbacher L, Kutteh LA, Vogel VG, Visscher DW, Yothers G, Jenkins RB, Brown AM, Dakhil SR, Mamounas EP, Lingle WL, Klein PM, Ingle JN, Wolmark N (2005) Trastuzumab plus adjuvant chemotherapy for operable HER2-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med 353(16):1673–1684. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa052122
Likhite VS, Stossi F, Kim K, Katzenellenbogen BS, Katzenellenbogen JA (2006) Kinase-specific phosphorylation of the estrogen receptor changes receptor interactions with ligand, deoxyribonucleic acid, and coregulators associated with alterations in estrogen and tamoxifen activity. Mol Endocrinol 20(12):3120–3132. doi:10.1210/me.2006-0068
Kim MY, Woo EM, Chong YT, Homenko DR, Kraus WL (2006) Acetylation of estrogen receptor alpha by p300 at lysines 266 and 268 enhances the deoxyribonucleic acid binding and transactivation activities of the receptor. Mol Endocrinol 20(7):1479–1493. doi:10.1210/me.2005-0531
Sentis S, Le Romancer M, Bianchin C, Rostan MC, Corbo L (2005) Sumoylation of the estrogen receptor alpha hinge region regulates its transcriptional activity. Mol Endocrinol 19(11):2671–2684. doi:10.1210/me.2005-0042
Lannigan DA (2003) Estrogen receptor phosphorylation. Steroids 68(1):1–9. doi:10.1016/S0039-128X(02)00110-1
Karas RH, Gauer EA, Bieber HE, Baur WE, Mendelsohn ME (1998) Growth factor activation of the estrogen receptor in vascular cells occurs via a mitogen-activated protein kinase-independent pathway. J Clin Invest 101(12):2851–2861. doi:10.1172/JCI1416
Encarnacion CA, Ciocca DR, McGuire WL, Clark GM, Fuqua SA, Osborne CK (1993) Measurement of steroid hormone receptors in breast cancer patients on tamoxifen. Breast Cancer Res Treat 26(3):237–246. doi:10.1007/BF00665801
Brunner N, Frandsen TL, Holst-Hansen C, Bei M, Thompson EW, Wakeling AE, Lippman ME, Clarke R (1993) MCF7/LCC2: a 4-hydroxytamoxifen resistant human breast cancer variant that retains sensitivity to the steroidal antiestrogen ICI 182, 780. Cancer Res 53(14):3229–3232
Herynk MH, Fuqua SA (2004) Estrogen receptor mutations in human disease. Endocr Rev 25(6):869–898. doi:10.1210/er.2003-0010
Conway K, Parrish E, Edmiston SN, Tolbert D, Tse CK, Moorman P, Newman B, Millikan RC (2007) Risk factors for breast cancer characterized by the estrogen receptor alpha A908G (K303R) mutation. Breast Cancer Res 9(3):R36. doi:10.1186/bcr1731
Worthylake R, Opresko LK, Wiley HS (1999) ErbB-2 amplification inhibits down-regulation and induces constitutive activation of both ErbB-2 and epidermal growth factor receptors. J Biol Chem 274(13):8865–8874. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.13.8865
Wang LM, Kuo A, Alimandi M, Veri MC, Lee CC, Kapoor V, Ellmore N, Chen XH, Pierce JH (1998) ErbB2 expression increases the spectrum and potency of ligand-mediated signal transduction through ErbB4. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95(12):6809–6814. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.12.6809
Samanta A, LeVea CM, Dougall WC, Qian X, Greene MI (1994) Ligand and p185c-neu density govern receptor interactions and tyrosine kinase activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91(5):1711–1715. doi:10.1073/pnas.91.5.1711
Arpino G, Wiechmann L, Osborne CK, Schiff R (2008) Crosstalk between the estrogen receptor and the HER tyrosine kinase receptor family: molecular mechanism and clinical implications for endocrine therapy resistance. Endocr Rev 29(2):217–233. doi:10.1210/er.2006-0045
Benz CC, Scott GK, Sarup JC, Johnson RM, Tripathy D, Coronado E, Shepard HM, Osborne CK (1992) Estrogen-dependent, tamoxifen-resistant tumorigenic growth of MCF-7 cells transfected with HER2/neu. Breast Cancer Res Treat 24(2):85–95. doi:10.1007/BF01961241
Nicholson RI, Gee JM, Knowlden J, McClelland R, Madden TA, Barrow D, Hutcheson I (2003) The biology of antihormone failure in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 80(Suppl 1):S29–S34. doi:10.1023/A:1025467500433 (discussion S35)
Hutcheson IR, Knowlden JM, Madden TA, Barrow D, Gee JM, Wakeling AE, Nicholson RI (2003) Oestrogen receptor-mediated modulation of the EGFR/MAPK pathway in tamoxifen-resistant MCF-7 cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 81(1):81–93. doi:10.1023/A:1025484908380
Kurokawa H, Lenferink AE, Simpson JF, Pisacane PI, Sliwkowski MX, Forbes JT, Arteaga CL (2000) Inhibition of HER2/neu (erbB-2) and mitogen-activated protein kinases enhances tamoxifen action against HER2-overexpressing, tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 60(20):5887–5894
Slamon DJ, Godolphin W, Jones LA, Holt JA, Wong SG, Keith DE, Levin WJ, Stuart SG, Udove J, Ullrich A et al (1989) Studies of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer. Science 244(4905):707–712. doi:10.1126/science.2470152
De Laurentiis M, Arpino G, Massarelli E, Ruggiero A, Carlomagno C, Ciardiello F, Tortora G, D’Agostino D, Caputo F, Cancello G, Montagna E, Malorni L, Zinno L, Lauria R, Bianco AR, De Placido S (2005) A meta-analysis on the interaction between HER-2 expression and response to endocrine treatment in advanced breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 11(13):4741–4748. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-2569
Osborne CK, Bardou V, Hopp TA, Chamness GC, Hilsenbeck SG, Fuqua SA, Wong J, Allred DC, Clark GM, Schiff R (2003) Role of the estrogen receptor coactivator AIB1 (SRC-3) and HER-2/neu in tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 95(5):353–361
Yeon CH, Pegram MD (2005) Anti-erbB-2 antibody trastuzumab in the treatment of HER2-amplified breast cancer. Invest New Drugs 23(5):391–409. doi:10.1007/s10637-005-2899-8
Tokunaga E, Oki E, Nishida K, Koga T, Egashira A, Morita M, Kakeji Y, Maehara Y (2006) Trastuzumab and breast cancer: developments and current status. Int J Clin Oncol 11(3):199–208. doi:10.1007/s10147-006-0575-4
Carter P, Presta L, Gorman CM, Ridgway JB, Henner D, Wong WL, Rowland AM, Kotts C, Carver ME, Shepard HM (1992) Humanization of an anti-p185HER2 antibody for human cancer therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89(10):4285–4289. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.10.4285
Britton DJ, Hutcheson IR, Knowlden JM, Barrow D, Giles M, McClelland RA, Gee JM, Nicholson RI (2006) Bidirectional cross talk between ERalpha and EGFR signaling pathways regulates tamoxifen-resistant growth. Breast Cancer Res Treat 96(2):131–146. doi:10.1007/s10549-005-9070-2
Chung YL, Sheu ML, Yang SC, Lin CH, Yen SH (2002) Resistance to tamoxifen-induced apoptosis is associated with direct interaction between Her2/neu and cell membrane estrogen receptor in breast cancer. Int J Cancer 97(3):306–312. doi:10.1002/ijc.1614
Razandi M, Alton G, Pedram A, Ghonshani S, Webb P, Levin ER (2003) Identification of a structural determinant necessary for the localization and function of estrogen receptor alpha at the plasma membrane. Mol Cell Biol 23(5):1633–1646. doi:10.1128/MCB.23.5.1633-1646.2003
Kato S, Endoh H, Masuhiro Y, Kitamoto T, Uchiyama S, Sasaki H, Masushige S, Gotoh Y, Nishida E, Kawashima H, Metzger D, Chambon P (1995) Activation of the estrogen receptor through phosphorylation by mitogen-activated protein kinase. Science 270(5241):1491–1494. doi:10.1126/science.270.5241.1491
Martin MB, Franke TF, Stoica GE, Chambon P, Katzenellenbogen BS, Stoica BA, McLemore MS, Olivo SE, Stoica A (2000) A role for Akt in mediating the estrogenic functions of epidermal growth factor and insulin-like growth factor I. Endocrinology 141(12):4503–4511. doi:10.1210/en.141.12.4503
Nawaz Z, Lonard DM, Dennis AP, Smith CL, O’Malley BW (1999) Proteasome-dependent degradation of the human estrogen receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(5):1858–1862. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.5.1858
Zwart W, Griekspoor A, Berno V, Lakeman K, Jalink K, Mancini M, Neefjes J, Michalides R (2007) PKA-induced resistance to tamoxifen is associated with an altered orientation of ERalpha towards co-activator SRC-1. EMBO J 26(15):3534–3544. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7601791
Balasenthil S, Barnes CJ, Rayala SK, Kumar R (2004) Estrogen receptor activation at serine 305 is sufficient to upregulate cyclin D1 in breast cancer cells. FEBS Lett 567(2–3):243–247. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2004.04.071
Varricchio L, Migliaccio A, Castoria G, Yamaguchi H, de Falco A, Di Domenico M, Giovannelli P, Farrar W, Appella E, Auricchio F (2007) Inhibition of estradiol receptor/Src association and cell growth by an estradiol receptor alpha tyrosine-phosphorylated peptide. Mol Cancer Res 5(11):1213–1221. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-07-0150
Dowsett M, Harper-Wynne C, Boeddinghaus I, Salter J, Hills M, Dixon M, Ebbs S, Gui G, Sacks N, Smith I (2001) HER-2 amplification impedes the antiproliferative effects of hormone therapy in estrogen receptor-positive primary breast cancer. Cancer Res 61(23):8452–8458
Balleine RL, Earl MJ, Greenberg ML, Clarke CL (1999) Absence of progesterone receptor associated with secondary breast cancer in postmenopausal women. Br J Cancer 79(9–10):1564–1571. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6690249
Cui X, Zhang P, Deng W, Oesterreich S, Lu Y, Mills GB, Lee AV (2003) Insulin-like growth factor-I inhibits progesterone receptor expression in breast cancer cells via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway: progesterone receptor as a potential indicator of growth factor activity in breast cancer. Mol Endocrinol 17(4):575–588. doi:10.1210/me.2002-0318
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank A. Beyer for expert technical assistance, and R. Sample for administrative assistance. This work was supported by NIH/NCI CA72038 to SAWF, and by an AIRC grant 2007 to CG.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giordano, C., Cui, Y., Barone, I. et al. Growth factor-induced resistance to tamoxifen is associated with a mutation of estrogen receptor α and its phosphorylation at serine 305. Breast Cancer Res Treat 119, 71–85 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-009-0334-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-009-0334-0