Abstract
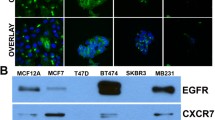
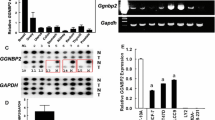
Expression of the chemokine receptor CXCR4, a G protein-coupled receptor, and HER2, a receptor tyrosine kinase, strongly correlates with the aggressive and metastatic potential of breast cancer cells. We studied estrogen regulation of CXCR4 in estrogen receptor (ER)-positive MCF-7 breast cancer cells overexpressing HER2 (MCF7-HER2). Although estrogen evoked no change in CXCR4 mRNA levels, CXCR4 protein was significantly up-regulated after estrogen treatment of these cells, whereas estrogen had no effect on CXCR4 protein level in parental MCF7 cells that are low in HER2. Use of the CXCR4 specific inhibitor, AMD 3100, indicated that this increase in CXCR4 protein was partially responsible for the increase in estrogen-induced migration of these cells. The estrogen-induced increase in CXCR4 protein in MCF-7-HER2 cells was abrogated by the antiestrogen ICI 182780 and by gefitinib (Iressa; a phospho-tyrosine kinase inhibitor), indicating an ER-mediated effect and confirming involvement of receptor tyrosine kinases, respectively. Using specific pathway inhibitors, we show that the estrogen-induced increase in CXCR4 involves PI3K/AKT, MAPK and mTOR pathways. PI3K/AKT and MAPK pathways are known to result in the phosphorylation and functional inactivation of tuberin (TSC2) of tuberous sclerosis complex thereby negating its inhibitory effects on mTOR, which in turn stimulates the translational machinery. Small interfering RNA (siRNA) mediated knockdown of tuberin elevated the level of CXCR4 protein in MCF7-HER2 cells and also nullified further estrogen up-regulation of CXCR4. This study suggests a pivotal role of PI3 K, MAPK and mTOR pathways, via tuberin, in post-transcriptional control of CXCR4, initiated through estrogen-stimulated crosstalk between ER and HER2. Thus, post-transcriptional regulation of CXCR4 by estrogens acting through ER via kinase pathways may play a critical role in determining the metastatic potential of breast cancer cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- E2:
-
17β-Estradiol
- ER:
-
Estrogen receptor
- ICI:
-
ICI 182,780
- CXCR4:
-
Chemokine receptor (CXC) 4
- PI3K:
-
Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin
References
Muller A, Homey B, Soto H, Ge N, Catron D, Buchanan ME et al (2001) Involvement of chemokine receptors in breast cancer metastasis. Nature 410:50–56. doi:10.1038/35065016
Konecny G, Pauletti G, Pegram M, Untch M, Dandekar S, Aguilar Z et al (2003) Quantitative association between HER-2/neu and steroid hormone receptors in hormone receptor-positive primary breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 95:142–153
Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG, Levin WJ, Ullrich A, McGuire WL (1987) Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science 235:177–182. doi:10.1126/science.3798106
Yu D, Hung MC (2000) Overexpression of ErbB2 in cancer and ErbB2-targeting strategies. Oncogene 19:6115–6121. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1203972
Chen Y, Stamatoyannopoulos G, Song CZ (2003) Down-regulation of CXCR4 by inducible small interfering RNA inhibits breast cancer cell invasion in vitro. Cancer Res 63:4801–4804
Lapteva N, Yang AG, Sanders DE, Strube RW, Chen SY (2005) CXCR4 knockdown by small interfering RNA abrogates breast tumor growth in vivo. Cancer Gene Ther 12:84–89. doi:10.1038/sj.cgt.7700770
Smith MC, Luker KE, Garbow JR, Prior JL, Jackson E, Piwnica-Worms D et al (2004) CXCR4 regulates growth of both primary and metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Res 64:8604–8612. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1844
Liang Z, Wu T, Lou H, Yu X, Taichman RS, Lau SK et al (2004) Inhibition of breast cancer metastasis by selective synthetic polypeptide against CXCR4. Cancer Res 64:4302–4308. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-3958
Liang Z, Yoon Y, Votaw J, Goodman MM, Williams L, Shim H (2005) Silencing of CXCR4 blocks breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Res 65:967–971
Kang Y, Siegel PM, Shu W, Drobnjak M, Kakonen SM, Cordon-Cardo C et al (2003) A multigenic program mediating breast cancer metastasis to bone. Cancer Cell 3:537–549. doi:10.1016/S1535-6108(03)00132-6
Minn AJ, Gupta GP, Siegel PM, Bos PD, Shu W, Giri DD et al (2005) Genes that mediate breast cancer metastasis to lung. Nature 436:518–524. doi:10.1038/nature03799
Salvucci O, Bouchard A, Baccarelli A, Deschenes J, Sauter G, Simon R et al (2006) The role of CXCR4 receptor expression in breast cancer: a large tissue microarray study. Breast Cancer Res Treat 97:275–283. doi:10.1007/s10549-005-9121-8
Slamon DJ, Leyland-Jones B, Shak S, Fuchs H, Paton V, Bajamonde A et al (2001) Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2 for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. N Engl J Med 344:783–792. doi:10.1056/NEJM200103153441101
Read LD, Keith D Jr, Slamon DJ, Katzenellenbogen BS (1990) Hormonal modulation of HER-2/neu protooncogene messenger ribonucleic acid and p185 protein expression in human breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 50:3947–3951
Lal P, Tan LK, Chen B (2005) Correlation of HER-2 status with estrogen and progesterone receptors and histologic features in 3, 655 invasive breast carcinomas. Am J Clin Pathol 123:541–546. doi:10.1309/YMJ3A83TB39MRUT9
Osborne CK, Shou J, Massarweh S, Schiff R (2005) Crosstalk between estrogen receptor and growth factor receptor pathways as a cause for endocrine therapy resistance in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 11:865s–870s
Benz CC, Scott GK, Sarup JC, Johnson RM, Tripathy D, Coronado E et al (1992) Estrogen-dependent, tamoxifen-resistant tumorigenic growth of MCF-7 cells transfected with HER2/neu. Breast Cancer Res Treat 24:85–95. doi:10.1007/BF01961241
Li YM, Pan Y, Wei Y, Cheng X, Zhou BP, Tan M et al (2004) Upregulation of CXCR4 is essential for HER2-mediated tumor metastasis. Cancer Cell 6:459–469. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2004.09.027
Frasor J, Danes JM, Komm B, Chang KC, Lyttle CR, Katzenellenbogen BS (2003) Profiling of estrogen up- and down-regulated gene expression in human breast cancer cells: insights into gene networks and pathways underlying estrogenic control of proliferation and cell phenotype. Endocrinology 144:4562–4574. doi:10.1210/en.2003-0567
Shou J, Massarweh S, Osborne CK, Wakeling AE, Ali S, Weiss H et al (2004) Mechanisms of tamoxifen resistance: increased estrogen receptor-HER2/neu cross-talk in ER/HER2-positive breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 96:926–935
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
De Clercq E (2003) The bicyclam AMD3100 story. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2:581–587. doi:10.1038/nrd1134
Ma L, Chen Z, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Pandolfi PP (2005) Phosphorylation and functional inactivation of TSC2 by Erk: implications for tuberous sclerosis and cancer pathogenesis. Cell 121:179–193. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.02.031
Berger MS, Locher GW, Saurer S, Gullick WJ, Waterfield MD, Groner B et al (1988) Correlation of c-erbB-2 gene amplification and protein expression in human breast carcinoma with nodal status and nuclear grading. Cancer Res 48:1238–1243
Gago FE, Fanelli MA, Ciocca DR (2006) Co-expression of steroid hormone receptors (estrogen receptor alpha and/or progesterone receptors) and Her2/neu (c-erbB-2) in breast cancer: clinical outcome following tamoxifen-based adjuvant therapy. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 98:36–40. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2005.07.002
Carroll JS, Meyer CA, Song J, Li W, Geistlinger TR, Eeckhoute J et al (2006) Genome-wide analysis of estrogen receptor binding sites. Nat Genet 38:1289–1297. doi:10.1038/ng1901
Frasor J, Stossi F, Danes JM, Komm B, Lyttle CR, Katzenellenbogen BS (2004) Selective estrogen receptor modulators: Discrimination of agonistic versus antagonistic activities by gene expression profiling in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 64:1522–1533. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-3326
Green KA, Carroll JS (2007) Oestrogen-receptor-mediated transcription and the influence of co-factors and chromatin state. Nat Rev Cancer 7:713–722. doi:10.1038/nrc2211
Lin CY, Vega VB, Thomsen JS, Zhang T, Kong SL, Xie M et al (2007) Whole-genome cartography of estrogen receptor alpha binding sites. PLoS Genet 3:e87. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.0030087
Barnett DH, Sheng S, Howe Charn T, Waheed A, Sly WS, Lin C-Y et al (2008) Estrogen receptor regulation of carbonic anhydrase XII through a distal enhancer in breast cancer. Cancer Res 68:3505–3515. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6151
Katzenellenbogen BS, Frasor J (2004) Therapeutic targeting in the estrogen receptor hormonal pathway. Semin Oncol 31:28–38. doi:10.1053/j.seminoncol.2004.01.004
Harrington WR, Kim SH, Funk CC, Madak-Erdogan Z, Schiff R, Katzenellenbogen JA et al (2006) Estrogen dendrimer conjugates that preferentially activate extranuclear, nongenomic versus genomic pathways of estrogen action. Mol Endocrinol 20:491–502. doi:10.1210/me.2005-0186
Madak-Erdogan Z, Kieser KJ, Kim SH, Komm B, Katzenellenbogen JA, Katzenellenbogen BS (2008) Nuclear and extranuclear pathway inputs in the regulation of global gene expression by estrogen receptors. Mol Endocrinol 22:2116–2127. doi:10.1210/me.2008-0059
Massarweh S, Schiff R (2007) Unraveling the mechanisms of endocrine resistance in breast cancer: new therapeutic opportunities. Clin Cancer Res 13:1950–1954. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2540
Osborne CK, Schiff R (2005) Estrogen-receptor biology: continuing progress and therapeutic implications. J Clin Oncol 23:1616–1622. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.10.036
Pietras RJ, Marquez-Garban DC (2007) Membrane-associated estrogen receptor signaling pathways in human cancers. Clin Cancer Res 13:4672–4676. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-1373
Kato M, Kitayama J, Kazama S, Nagawa H (2003) Expression pattern of CXC chemokine receptor-4 is correlated with lymph node metastasis in human invasive ductal carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res 5:R144–R150. doi:10.1186/bcr627
Kelleher RJ 3rd, Govindarajan A, Jung HY, Kang H, Tonegawa S (2004) Translational control by MAPK signaling in long-term synaptic plasticity and memory. Cell 116:467–479. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00115-1
Rae JM, Johnson MD, Scheys JO, Cordero KE, Larios JM, Lippman ME (2005) GREB1 is a critical regulator of hormone dependent breast cancer growth. Breast Cancer Res Treat 92:141–149. doi:10.1007/s10549-005-1483-4
Astrinidis A, Henske EP (2005) Tuberous sclerosis complex: linking growth and energy signaling pathways with human disease. Oncogene 24:7475–7481. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209090
Massarweh S, Osborne CK, Jiang S, Wakeling AE, Rimawi M, Mohsin SK et al (2006) Mechanisms of tumor regression and resistance to estrogen deprivation and fulvestrant in a model of estrogen receptor-positive, HER-2/neu-positive breast cancer. Cancer Res 66:8266–8273. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4045
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by NIH grant CA 18119 and a grant from The Breast Cancer Research Foundation (to B.S.K.), and by NIH Breast Cancer SPORE grant P50 CA58183 (to R.S.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sengupta, S., Schiff, R. & Katzenellenbogen, B.S. Post-transcriptional regulation of chemokine receptor CXCR4 by estrogen in HER2 overexpressing, estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 117, 243–251 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-008-0186-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-008-0186-z