Abstract
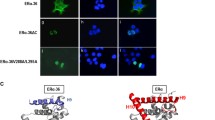
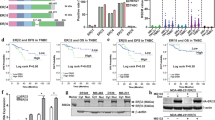
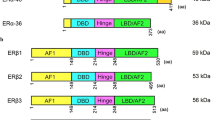
Estrogen receptor β gene codes for a variety of transcript isoforms resulting from alternative splicing, which are expressed both in mammary gland and in breast cancer cells. We studied the function of two exon-deleted ERβ isoforms recently identified by our group in comparison to ERβ1 in regulation of growth, apoptosis and gene expression of two breast cancer cell lines with different ERα status. Overexpression of ERβ1, but not of the exon-deleted variants exerted strong antitumoral effects both on ERα-positive MCF-7 and ERα-negative SK-BR-3 cells. ERβ1 overexpression slowed growth of MCF-7 and SK-BR-3 cells in the absence of E2 and also inhibited E2-triggered growth stimulation of MCF-7 cells, but overexpression of the exon-skipped variants did not affect cell growth. Whereas overexpression of ERβ1 triggered an increased basal and tamoxifen-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 and SK-BR-3 cells, the isoforms ERβδ125 or ERβδ1256 did not affect cellular tamoxifen response. The observed lack of function of the exon-deleted variants in terms of regulation of proliferation was accompanied both by their inability to affect expression of cyclins D1 and A2, p21 (WAF1) and PR and their disability to modulate estrogen response element (ERE) activation. In contrast, our results demonstrating antitumoral effects of ERβ1 on breast cancer cells with different ERα-status support the hypothesis that ERβ is able to exert antitumoral actions both on ERα-positive and -negative breast cancer cells.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali S, Coombes RC (2002) Endocrine-responsive breast cancer and strategies for combating resistance. Nat Rev Cancer 2(2):101–112
Kuiper GG, Enmark E, Pelto-Huikko M, Nilsson S, Gustafsson J-A (1996) Cloning of a novel receptor expressed in rat prostate and ovary. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93(12):5925–5930
Leygue E, Dotzlaw H, Watson P, Murphy L (1998) Altered estrogen receptor alpha and beta mRNA expression during human breast tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 58:3197–3201
Jarvinen T, Pelto-Huikko M, Holli K, Isola J (2000) Estrogen receptor beta is coexpressed with ERalpha and PR and associated with nodal status grade and proliferation rate in breast cancer. Am J Pathol 156:29–35
Forster C, Makela S, Warri A, Kietz S, Becker D, Hultenby K, Warner M, Gustafsson J (2002) Involvement of estrogen receptor b in terminal differentiation of mammary gland epithelium. PNAS 99:15578–15583
Hall J, McDonnell D (1999) The estrogen receptor betaisoform (ERbeta) of the human estrogen receptor modulates ERalpha transcriptional activity and is a key regulator of the cellular response to estrogens and antiestrogens. Endocrinology 140:5566–5578
Weihua Z, Saji S, Makinen S, Cheng G, Jensen E, Warner M, Gustaffson JA (2000) Estrogen receptor (ER) b a modulator of ERa in the uterus. PNAS 97:5936–5941
Peng B, Lu B, Leygue E, Murphy L (2003) Putative functional characteristics of human estrogen receptor-beta isoforms. J Mol Endocrinol 30:13–29
Roger P, Sahla M, Makela S, Gustafsson J.A, Baldet P, Rochefort H (2001) Decreased expression of estrogen receptor beta protein in proliferative preinvasive mammary tumors. Cancer Res 61:2537–2541
Skliris G, Munot K, Bell S, Carder P, Lane S, Horgan K, Lansdown M, Parkes A, Hanby A, Markham A, Speirs V (2003) Reduced expression of oestrogen receptor beta in invasive breast cancer and its re-expression using DNA methyltransferase inhibitors in a cell line model. J Pathol 201:213–220
Dotzlaw H, Leygue E, Watson P, Murphy L (1999) Estrogen receptor-b messenger RNA expression in human breast tumor biopsies: relationship to steroid receptor status and regulation by progestins. Cancer Res 59:529–532
Speirs V (2002) Oestrogen receptor beta in breast cancer: good bad or still too early to tell? J Pathol 197:143–147
Fuqua S, Schiff R, Parra I, Friedrichs W, Su J, McKee D, Slentz-Kesler K, Moore L, Willson T, Moore J (1999) Expression of wild-type estrogen receptor beta and variant isoforms in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 59:5425–5428
Saji S, Omoto Y, Shimizu C, Warner M, Hayashi Y, Horiguchi S, Watanabe T, Hayashi S, Gustafsson J (2002b) Expression of estrogen receptor (ER) (beta)cx protein in ER(alpha)-positive breast cancer: specific correlation with progesterone receptor. Cancer Res 62:4849–4853
Saji S, Omoto Y, Shimizu C, Horiguchi S, Watanabe T, Funata N, Hayash S, Gustafsson J, Toi M (2002a) A clinical impact of assay of estrogen receptor beta cx in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 9:303–307
Mann S, Laucirica R, Carlson N, Younes PS, Ali N, Younes A, Li Y, Younes M (2001) Estrogen receptor beta expression in invasive breast cancer. Hum Pathol 32(1):113–118
Murphy L, Cherlet T, Lewis A, Banu Y, Watson P (2003) New insights into estogen receptor function in human breast cancer. Ann Med 35:614–631
Esslimani-Sahla M, Simony-Lafontaine J, Kramar A, Lavaill R, Mollevi C, Warner M, Gustafsson J-A, Rochefort H (2004) Estrogen receptor beta (ERbeta) level but not its ERbeta-cx variant helps to predict tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 10:5769–5776
Fleming F, Hill A, McDermott E, O’Higgins N, Young L (2004) Differential recruitment of coregulator proteins steroid receptor coactivator-1 and silencing mediator for retinoid and thyroid receptors to the estrogen receptorestrogen response element by beta-estradiol and 4-hydroxytamoxifen in human breast cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:375–383
Hopp TA, Weiss HL, Parra IS, Cui Y, Osborne CK, Fuqua SA (2004) Low levels of estrogen receptor beta protein predict resistance to tamoxifen therapy in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 10(22):7490–7499
Saji S, Hirose M, Toi M (2005) Clinical significance of estrogen receptor beta in breast cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 56:21–26
Monroe DG, Secreto FJ, Subramaniam M, Getz BJ, Khosla S, Spelsberg TC (2005) Estrogen receptor alpha and beta heterodimers exert unique effects on estrogen- and tamoxifen-dependent gene expression in human U2OS osteosarcoma cells. Mol Endocrinol 19(6):1555–1568
Osborne C (1998) Steroid hormone receptors in breast cancer management. Breast Cancer Res Treat 51:227–238
Jensen E, Cheng G, Palmieri C, Saji S, Makela S, Van Noorden S, Wahlstrom T, Warner M, Coombes R, Gustafsson J-A (2001) Estrogen receptors and proliferation markers in primary and recurrent breast cancer. PNAS 98:15197–15202
O’Neill P, Davies M, Shaaban A, Innes H, Torevell A, Sibson D, Foster C (2004) Wild-type oestrogen receptor beta (ERbeta1) mRNA and protein expression in Tamoxifen treated post-menopausal breast cancers. Br J Cancer 91:1694–1702
Ogawa S, Inoue S, Watanabe T, Orimo A, Hosoi T, Ouchi Y, Muramatsu M (1998) Molecular cloning and characterization of human estrogen receptor bcx: potential inhibitor of estrogen action in human. Nucleic Acids Res 26:3505–3512
Poola I, Abraham J, Liu A (2002a) Estrogen receptor beta splice variant mRNAs are differentially altered during breast carcinogenesis. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 82(2–3):169–179
Price RH Jr, Butler CA, Webb P, Uht R, Kushner P, Handa RJ (2001) A splice variant of estrogen receptor beta missing exon 3 displays altered subnuclear localization and capacity for transcriptional activation. Endocrinology 142(5):2039–2049
Herynk MH, Fuqua SA (2004) Estrogen receptor mutations in human disease. Endocr Rev 25(6):869–898
Price RH Jr, Lorenzon N, Handa RJ (2000) Differential expression of estrogen receptor beta splice variants in rat brain: identification and characterization of a novel variant missing exon 4. Mol Brain Res 80(2):260–268
Speirs V, Adams IP, Walton DS, Atkin SL (2000) Identification of wild-type and exon 5 deletion variants of estrogen receptor beta in normal human mammary gland. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85(4):1601–1605
Zhao C, Toresson G, Xu L, Koehler KF, Gustafsson JA, Dahlman-Wright K (2005) Mouse estrogen receptor beta isoforms exhibit differences in ligand selectivity and coactivator recruitment. Biochemistry 44(22):7936–7944
Sierens JE, Scobie GA, Wilson J, Saunders PT (2004) Cloning of oestrogen receptor beta from Old and New World primates: identification of splice variants and functional analysis. J Mol Endocrinol 32(3):703–718
Treeck O, Pfeiler G, Horn F, Federhofer B, Houlihan H, Vollmer A, Ortmann O (2007) Novel estrogen receptor beta transcript variants identified in human breast cancer cells affect cell growth and apoptosis of COS-1 cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 264:50–60
Ståhlberg A, Åman P, Ridell B, Mostad P, Kubista M (2003) A quantitative real-time PCR method for detection of B-Lymphocyte monoclonality by comparison of kappa and lambda Immunoglobulin Light Chain Expression. Clin Chem 49(1):51–59
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2^( -delta delta Ct ) method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Cheng J, Lee EJ, Madison LD, Lazennec G (2004) Expression of estrogen receptor beta in prostate carcinoma cells inhibits invasion and proliferation and triggers apoptosis. FEBS Lett 566(1–3):169–172
Helguero LA, Faulds MH, Gustafsson JA, Haldosen LA (2005) Estrogen receptors alpha (ERalpha) and beta (ERbeta) differentially regulate proliferation and apoptosis of the normal murine mammary epithelial cell line HC11. Oncogene 24(44):6605–6616
Treeck O, Pfeiler G, Mitter D, Lattrich C, Piendl G, Ortmann O (2007) Estrogen receptor β1 exerts antitumoral effects on SK-OV-3 ovarian cancer cells. J Endocrinol 193(3):421–433
Vladusic EA, Hornby AE, Guerra-Vladusic FK, Lakins J, Lupu R (2000) Expression and regulation of estrogen receptor beta in human breast tumors and cell lines. Oncol Rep 7(1):157–167
Lazennec G, Bresson D, Lucas A, Chauveau C, Vignon F (2001) ER beta inhibits proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells. Endocrinology 142(9):4120–4130
Guerini V, Sau D, Scaccianoce E, Rusmini P, Ciana P, Maggi A, Martini PG, Katzenellenbogen BS, Martini L, Motta M, Poletti A (2005) The androgen derivative 5alpha-androstane-3beta, 17beta-diol inhibits prostate cancer cell migration through activation of the estrogen receptor beta subtype. Cancer Res 65(12):5445–5453
Lu B, Leygue E, Dotzlaw H, Murphy LJ, Murphy LC, Watson PH (1998) Estrogen receptor-beta mRNA variants in human and murine tissues. Mol Cell Endocrinol 138(1–2):199–203
Vladusic EA, Hornby AE, Guerra-Vladusic FK, Lupu R (1998) Expression of estrogen receptor beta messenger RNA variant in breast cancer. Cancer Res 58(2):210–214
Poola I, Abraham J, Baldwin K (2002b) Identification of ten exon deleted ERbeta mRNAs in human ovary, breast, uterus and bone tissues: alternate splicing pattern of estrogen receptor beta mRNA is distinct from that of estrogen receptor alpha. FEBS Lett 516(1–3):133–138
Omoto Y, Eguchi H, Yamamoto-Yamaguchi Y, Hayashi S (2003) Estrogen receptor (ER) beta1 and ERbetacx/beta2 inhibit ERalpha function differently in breast cancer cell line MCF7. Oncogene 22:5011–5020
Paruthiyil S, Parmar H, Kerekatte V, Cunha GR, Firestone GL, Leitman DC (2004) Estrogen receptor beta inhibits human breast cancer cell proliferation and tumor formation by causing a G2 cell cycle arrest. Cancer Res 64(1):423–428
Hartman J, Lindberg K, Morani A, Inzunza J, Strom A, Gustafsson JA (2006) Estrogen receptor beta inhibits angiogenesis and growth of T47D breast cancer xenografts. Cancer Res 66(23):11207–11213
Strom A, Hartman J, Foster JS, Kietz S, Wimalasena J, Gustafsson JA (2004) Estrogen receptor beta inhibits 17beta-estradiol-stimulated proliferation of the breast cancer cell line T47D. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(6):1566–1571
Lindberg MK, Moverare S, Skrtic S, Gao H, Dahlman-Wright K, Gustafsson JA, Ohlsson C (2003) Estrogen receptor (ER)-beta reduces ERalpha-regulated gene transcription,supporting a “ying yang” relationship between ERalpha and ERbeta in mice. Mol Endocrinol 17(2):203–208
Stossi F, Barnett DH, Frasor J, Komm B, Lyttle CR, Katzenellenbogen BS (2004) Transcriptional profiling of estrogen-regulated gene expression via estrogen receptor (ER) alpha or ERbeta in human osteosarcoma cells: distinct and common target genes for these receptors. Endocrinology 145(7):3473–3486
Chang EC, Frasor J, Komm B, Katzenellenbogen BS (2006) Impact of estrogen receptor beta on gene networks regulated by estrogen receptor alpha in breast cancer cells. Endocrinology 147(10):4831–4842
Lin CY, Ström A, Li Kong S, Kietz S, Thomsen JS, Tee JB, Vega VB, Miller LD, Smeds J, Bergh J, Gustafsson JA, Liu ET, (2007) Inhibitory effects of estrogen receptor beta on specific hormone-responsive gene expression and association with disease outcome in primary breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 9(2):R25
Carroll JS, Swarbrick A, Musgrove EA, Sutherland RL (2002) Mechanisms of growth arrest by c-myc antisense oligonucleotides in MCF-7 breast cancer cells: implications for the antiproliferative effects of antiestrogens. Cancer Res 62:3126–3131
Watts CK, Sweeney KJ, Warlters A, Musgrove EA, Sutherland RL (1994) Antiestrogen regulation of cell cycle progression and cyclin D1 gene expression in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 31:95–105
Foster JS, Henley DC, Bukovsky A, Seth P, Wimalasena J (2001) Multifaceted regulation of cell cycle progression by estrogen: regulation of Cdk inhibitors and Cdc25A independent of cyclin D1-Cdk4 function. Mol Cell Biol 21:794–810
Liu MM, Albanese C, Anderson CM, Hilty K, Webb P, Uht RM, Price RH Jr, Pestell RG, Kushner PJ (2002) Opposing action of estrogen receptors alpha and beta on cyclin D1 gene expression. J Biol Chem 277(27):24353–24360
Hodges LC, Cook JD, Lobenhofer EK, Li L, Bennett L, Bushel PR, Aldaz CM, Afshari CA, Walker CL (2003) Tamoxifen functions as a molecular agonist inducing cell cycle-associated genes in breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res 1:300–311
Hui R, Finney GL, Carroll JS, Lee CS, Musgrove EA, Sutherland RL (2002) Constitutive overexpression of cyclin D1 but not cyclin E confers acute resistance to antiestrogens in T-47D breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 62:6916–6923
Doisneau-Sixou SF, Sergio CM, Carroll JS, Hui R, Musgrove EA, Sutherland RL (2003) Estrogen and antiestrogen regulation of cell cycle progression in breast cancer cells. Endocr Relat Cancer 10:179–186
Thomas TJ, Faaland CA, Adhikarakunnathu S, Watkins LF, Thomas T (1998) Induction of p21 (CIP1/WAF1/SID1) by estradiol in a breast epithelial cell line transfected with the recombinant estrogen receptor gene: a possible mechanism for a negative regulatory role of estradiol. Breast Cancer Res Treat 47(2):181–193
Iwase H, Zhang Z, Omoto Y, Sugiura H, Yamashita H, Toyama T, Iwata H, Kobayashi S (2003) Clinical significance of the expression of estrogen receptors alpha and beta for endocrine therapy of breast cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 52(Suppl 1):34–38
Gruvberger-Saal SK, Bendahl PO, Saal LH, Laakso M, Hegardt C, Eden P, Peterson C, Malmström P, Isola J, Borg A, Fernö M (2007) Estrogen receptor beta expression is associated with tamoxifen response in ERalpha-negative breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 13(7):1987–1994
Acknowledgements
We thank Angelika Vollmer, Gerhard Piendl and Helena Houlihan for expert technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Treeck, O., Juhasz-Boess, I., Lattrich, C. et al. Effects of exon-deleted estrogen receptor β transcript variants on growth, apoptosis and gene expression of human breast cancer cell lines. Breast Cancer Res Treat 110, 507–520 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-007-9749-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-007-9749-7