Abstract
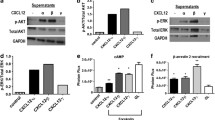
The chemokine receptor CXCR4 is functionally expressed on the cell surface of various cancer cells, and plays a role in cell proliferation and migration of these cells. Specifically, in breast cancer cells the CXCR4/CXCL12 axis has been implicated in cell migration in vitro and in metastasis in vivo, but the underlying signaling mechanisms are incompletely understood. The xenograft-derived MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell line (231mfp), which was shown previously to grow more aggressively than the parent cells, showed increased CXCR4 expression at the mRNA, total protein and cell surface expression level. This correlated with an enhanced response to CXCL12, specifically in augmented and prolonged Akt activation in a Gi, Src family kinase and PI-3 kinase dependent fashion. 231mfp cells migrated towards CXCL12—in contrast to the parent cell line—and this chemotaxis was blocked by inhibition of Gi, Src family kinases, PI-3 kinase and interestingly, Akt itself, as could be shown with two pharmacological inhibitors, a dominant negative Akt construct and with Akt shRNA. Collectively, we have demonstrated that prolonged Akt activation is an important signaling pathway for breast cancer cells expressing CXCR4 and is necessary for CXCL12-dependent cell migration.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PI3K:
-
PI-3 kinase
- MMP:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase
- FCS:
-
Fetal calf serum
- PTX:
-
Pertussis toxin
References
Mueller A, Homey B, Soto H, Ge N, Catron D, Buchanan ME, MaClanahan T, Murphy E, Yuan W, Wagner SN, Barrera JL, Mohar A, Verastegul E, Zlotnik A (2001) Involvement of chemokine receptors in breast cancer metastasis. Nature 410:50–56
Hatse S, Princen K, Bridger G, De Clercq E, Schols D (2002) Chemokine receptor inhibition by AMD3100 is strictly confined to CXCR4. FEBS Lett 527:255
Liang Z, Yoon Y, Votaw J, Goodman MM, Williams L, Shim H (2004) Inhibition of breast cancer metastasis by selective synthetic polypeptide against CXCR4. Cancer Res 64:4302–4308
Liang Z, Yoon Y, Votaw J, Goodman MM, Williams L, Shim H (2005) Silencing of CXCR4 Blocks Breast Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Res 65:967–971
Kang H, Watkins G, Parr C, Douglas-Jones A, Mansel RE, Jiang WG (2005) Stromal cell derived factor-1: its influence on invasiveness and migration of breast cancer cells in vitro, and its association with prognosis and survival in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 7:R402–R410
Salvucci O, Bouchard A, Baccarelli A, Deschenes J, Sauter G, Simon R, Bianchi R, Basik M (2006) The role of CXCR4 receptor expression in breast cancer: a large tissue microarray study. Breast Cancer Res Treat 97:275–283
Su YC, Wu MT, Huang CJ, Hou MF, Yang SF, Chai CY (2006) Expression of CXCR4 is associated with axillary lymph node status in patients with early breast cancer. Breast 15:533–539
Li YM, Pan Y, Wei Y, Cheng X, Zhou BP, Tan M, Zhou X, Xia W, Hortobagyi GN, Yu D, Hung MC (2004) Upregulation of CXCR4 is essential for HER2-mediated tumor metastasis. Cancer Cell 6:459–466
Helbig G, Christopherson KW, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Kumar S, Kishimoto H, Miller KD, Broxmeyer HE, Nakshatri H (2003) NF-κB promotes breast cancer cell migration and metastasis by inducing the expression of the chemokine receptor CXCR4. J Biol Chem 278:21631–21638
Bachelder RE, Wendt RE, Mercurio AM (2002) Vascular endothelial growth factor promotes breast carcinoma invasion in an autocrine manner by regulating the chemokine receptor CXCR4. Cancer Res 62:7203–7206
Phillips RJ, Mestas J, Gharaee-Kermani M, Burdick MD, Sica A, Belperio JA, Keane MP, Strieter RM (2005) Epidermal growth factor and hypoxia-induced expression of CXC chemokine receptor 4 on non-small cell lung cancer cells is regulated by the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/PTEN/AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway and activation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α. J Biol Chem 280:22473–22481
Porcile C, Bajetto A, Barbero S, Pirani P, Schettini G (2004) CXCR4 activation induces epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation in an ovarian cancer cell line. Ann NY Acad Sci 1030:162–169
Cabioglu N, Summy J, Miller C, Parikh NU, Sahin AA, Tuzlali S, Pumiglia K, Gallick GE, Price JE (2005) CXCL-12/stromal cell-derived factor-1α transactivates HER2-neu in breast cancer cells by a novel pathway involving Src kinase activation. Cancer Res 65:6493–6497
Fernandis AZ, Prasad A, Band H, Klosel R, Ganju RK (2004) Regulation of CXCR4-mediated chemotaxis and chemoinvasion of breast cancer cells. Oncogene 23:157–166
Lee BC, Lee TH, Avraham S, Avraham HK (2004) Involvement of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 and its ligand stromal cell-derived factor 1α in breast cancer cell migration through human brain microvascular endothelial cells. Mol Cancer Res 2:327–338
Bendall LJ, Baraz R, Juarez J, Shen W, Bradstock KF (2005) Defective p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling impairs chemotaxic but not proliferative responses to stromal-derived factor-1α in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Res 65:3290–3298
Inngjerdingen M, Torgersen KM, Maghazachi AA (2002) Lck is required for stromal cell-derived factor 1α (CXCL12)-induced lymphoid cell chemotaxis. Blood 99:4318–4325
Sun Y, Cheng Z, Ma L, Pei G (2002) β-Arrestin2 is critically involved in CXCR4-mediated chemotaxis, and this is mediated by its enhancement of p38 MAPK activation. J Biol Chem 277:49212–49219
Dancey J, Sausville EA (2003) Issues and progress with protein kinase inhibitors for cancer treatment. Nat Rev Drug Disc 2:296
Mills GB, Lu Y, Fang X, Wang H, Eder A, Mao M, Swaby R, Cheng KW, Stokoe D, Siminovitch K, Jaffe R, Gray J (2001) The role of genetic abnormalities of PTEN and the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway in breast and ovarian tumorigenesis, prognosis, and therapy. Semin Oncol 28:125–141
Cicenas J, Urban P, Vuaroqueaux V, Labuhn M, Kung W, Wight E, Mayhew M, Eppenberger U, Eppenberger-Castori S (2005) Increased level of phosphorylated Akt measured by chemiluminescence-linked immunosorbent assay is a predictor of poor prognosis in primary breast cancer overexpressing ErbB-2. Breast Cancer Res 7:R394–R401
Lee MJ, Thangada S, Paik JH, Sapkota GP, Ancellin N, Chae SS, Wu M, Morales-Ruiz M, Sessa WC, Alessi DR, Hla T (2001) Akt-mediated phosphorylation of the G protein-coupled receptor EDG-1 is required for endothelial cell chemotaxis. Mol Cell 8:693–700
Zhou GL, Tucker DF, Bae SS, Bhatheja K, Birnbaum MJ, Field J (2006) Opposing roles for Akt1 and Akt2 in Rac/Pak signaling and cell migration. J Biol Chem 281:36443–36453
Sasaki T, Irie-Sasaki J, Jones RG, Oliveira-dos-Santos AJ, Stanford WL, Bolon B, Wakeham A, Itie A, Bouchard D, Kozieradzki I, Joza N, Mak TW, Ohashi PS, Suzuki A, Penninger JM (2000) Function of PI3K in thymocyte development, T Cell activation, and neutrophil migration. Science 287:1040–1046
Zhao M, DiScipio RG, Wimmer AG, Schraufstatter IU (2006) Regulation of CXCR4-mediated nuclear translocation of ERK1/2. Mol Pharmacol 69:66–75
Delgado-Esteban M, Martin-Zanca D, Andres-Martin L, Almeida A, Bolanos JP (2007) Inhibition of PTEN by peroxynitrite activates the phosphoinositide-3-kinase/Akt neuroprotective signaling pathway. J Neurochem 102:194–205
Zhao M, Wimmer A, Trieu K, DiScipio RG, Schraufstatter IU (2004) Arrestin regulates MAPK activation and prevents NADPH oxidase-dependent death of cells expressing CXCR2. J Biol Chem 279:49259–49267
Porath J, Olin B (1993) Immobilized metal affinity adsorption and immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography of biomaterials. Serum protein affinities for gel-immobilized iron and nickel ions. Biochemistry 22:1621–1630
Jessani N, Humphrey M, McDonald WH, Niessen S, Masuda K, Gangadharan B, Yates JR, Mueller BM, Cravatt BF (2004) Carcinoma and stromal enzyme activity profiles associated with breast tumor growth in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101:13756–13761
Sun P, Dong P, Dai K, Hannon JH, Beach D (1998) p53-Independent Role of MDM2 in TGF-1 Resistance. Science 282:2270–2272
Liu Y, Mueller BM (2006) Protease-activated receptor-2 regulates vascular endothelial growth factor expression in MDA-MB-231 cells via MAPK pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 344:1263–1270
Su L, Zhang J, Xu H, Wang Y, Chu Y, Liu R, Xiong S (2005) Differential expression of CXCR4 is associated with the metastatic potential of human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 11:8273–8280
Vicente-Manzanares M, Cabrero JR, Rey M, Perez-Martinez M, Ursa A, Itoh K, Sanchez-Madrid F (2002) A role for the Rho-p160 Rho coiled-coil kinase axis in the chemokine stromal cell-derived factor-1α-induced lymphocyte actomyosin and microtubular organization and chemotaxis. J Immunol 168:400–410
Hers I, Wherlock M, Homma Y, Yagisawa H, Tavare JM (2006) Identification of p122RhoGAP (deleted in liver cancer-1) serine 322 as a substrate for protein kinase B and ribosomal S6 kinase in insulin-stimulated cells. J Biol Chem 281:4762–4770
Smith MC, Luker KE, Garbow JR, Prior JL, Jackson E, Piwnica-Worms D, Luker GD (2004) CXCR4 regulates growth of both primary and metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Res 64:8604–8612
Kim J, Takeuchi H, Lam ST, Turner RR, Wang HJ, Juo C, Foshag L, Bilchik AJ, Hoon DS (2005) Chemokine receptor CXCR4 expression in colorectal cancer patients increases the risk for recurrence and for poor survival. J Clin Oncol 23:2744–2753
Scala S, Ottaiano A, Ascierto PA, Cavalli M, Simeone E, Giuliano P, Napolitano M, Franco R, Botti G, Castello G (2005) Expression of CXCR4 predicts poor prognosis in patients with malignant melanoma. Clin Cancer Res 11:1835–1841
Schioppa T, Uranchimeg B, Saccani A, Biswas SK, Doni A, Rapisarda A, Bernasconi S, Saccani S, Nebuloni M, Vago L, Mantovani A, Melillo G, Sica A (2003) Regulation of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 by hypoxia. J Exp Med 198:1391–1402
Kukreja P, Abdel-Mageed AB, Mondal D, Liu K, Agrawal KC (2005) Up-regulation of CXCR4 expression in PC-3 cells by stromal-derived factor-1α (CXCL12) increases endothelial adhesion and transendothelial migration: role of MEK/ERK signaling pathway-dependent NF-κB activation. Cancer Res 65:9891–9898
Staller P, Sulitkova J, Lisztwan J, Moch H, Oakeley EJ, Krek W (2003) Chemokine receptor CXCR4 downregulated by von Hippel-Lindau tumour suppressor pVHL. Nature 425:307–311
Orimo A, Gupta PB, Sgroi DC, Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Delaunay T, Naeem R, Carey VJ, Richardson AL, Weinberg RA (2005) Stromal fibroblasts present in invasive human breast carcinomas promote tumor growth and angiogenesis through elevated SDF-1/CXCL12 secretion. Cell 121:335–344
Bhattacharya M, Peri K, Ribeiro-da-Silva A, Almazan G, Shichi H, Hou X, Varma DR, Chemtob S (1999) Localization of functional prostaglandin E2 receptors EP3 and EP4 in the nuclear envelope. J Biol Chem 274:15719–15724
Gobeil F, Bernier SG, Vazquez-Tello A, Brault S, Beauchamp MH, Quiniou C, Marrache AM, Checchin D, Sennlaub F, Hou X, Nader M, Bkaily G, Ribeiro-da-Silva A, Goetzl EJ, Chemtob S (2003) Modulation of pro-inflammatory gene expression by nuclear lysophosphatidic acid receptor type-1. J Biol Chem 278:38875–38883
Vroon A, Heijnen CJ, Raatgever R, Touw IP, Ploemacher RE, Premont RT, Kavelaars A (2004) GRK6 deficiency is associated with enhanced CXCR4-mediated neutrophil chemotaxis in vitro and impaired responsiveness to G-CSF in vivo. J Leukoc Biol 75:698–704
Okabe S, Fukuda S, Kim YJ, Niki M, Pelus LM, Ohyashiki K, Pandolfi PP, Broxmeyer HE (2005) Stromal cell-derived factor-1α/CXCL12-induced chemotaxis of T cells involves activation of the RasGAP-associated docking protein p62Dok-1. Blood 105:474–480
Fernandis AZ, Cherla RP, Ganju RK (2003) Differential regulation of CXCR4-mediated T-cell chemotaxis and mitogen-activated protein kinase activation by the membrane tyrosine phosphatase, CD45. J Biol Chem 278:9536–9543
Gao P, Wange RL, Zhang N, Oppenheim JJ, Howard OM (2005) Negative regulation of CXCR4-mediated chemotaxis by the lipid phosphatase activity of tumor suppressor PTEN. Blood 106:2619–2626
Clutter SD, Fortney J, Gibson LF (2005) MMP-2 is required for bone marrow stromal cell support of pro-B-cell chemotaxis. Exp Hematol 33:1192–1200
Volinsky N, Gantman A, Yablonski D (2006) A Pak- and Pix-dependent branch of the SDF-1α signalling pathway mediates T cell chemotaxis across restrictive barriers. Biochem J 397:213–222
Petit I, Goichberg P, Spiegel A, Peled A, Brodie C, Seger R, Nagler A, Alon R, Lapidot T (2005) Atypical PKC-ζ regulates SDF-1-mediated migration and development of human CD34+ progenitor cells. J Clin Invest 115:168–176
Lu Y, Yu Q, Liu JH, Zhang J, Wang H, Koul D, McMurray JS, Fang X, Yung WKA, Siminovitch KA, Mills GB (2003) Src family protein-tyrosine kinases alter the function of PTEN to regulate phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT cascades. J Biol Chem 278:40057–40066
Vlahakis SR, Villasis-Keever A, Gomez T, Vanegas M, Vlahakis N, Paya CV (2002) G protein-coupled chemokine receptors induce both survival and apoptotic signaling pathways. J Immunol 169:5546–5554
Yoon SO, Shin S, Mercurio AM (2005) Hypoxia stimulates carcinoma invasion by stabilizing microtubules and promoting the Rab11 trafficking of the α6β4 integrin. Cancer Res 65:2761–2769
Chung CY, Potikyan G, Firtel RA (2001) Control of cell polarity and chemotaxis by Akt/PKB and PI3 kinase through the regulation of PAKa. Mol Cell 7:937–947
Cantley LC (2002) The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science 296:1655–1657
Peng SB, Peek V, Zhai Y, Paul DC Lou Q, Xia X, Eessalu T, Kohn W, Tang S (2005) Akt activation, but not extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation, is required for SDF-1α/CXCR4-mediated migration of epitheloid carcinoma cells. Mol Cancer Res 3:227–236
Campbell RA, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Patel NM, Constantinidou D, Ali S, Nakshatri H (2001) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT-mediated activation of estrogen receptor α. A new model for anti-estrogen resistance. J Biol Chem 276:9817–9824
Duong BN, Elliott S, Frigo DE, Melnik LI, Vanhoy L, Tomchuck S, Lebeau HP, David O, Beckman BS, Alam J, Bratton MR, McLachlan JA, Burow ME (2006) AKT regulation of estrogen receptor β transcriptional activity in breast cancer. Cancer Res 66:8373–8381
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by BCRP Grant BC052149 and TRDRP 13RT-0083 to IUS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, M., Mueller, B.M., DiScipio, R.G. et al. Akt plays an important role in breast cancer cell chemotaxis to CXCL12. Breast Cancer Res Treat 110, 211–222 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-007-9712-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-007-9712-7