Abstract
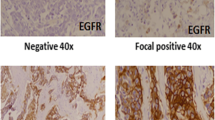
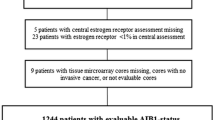
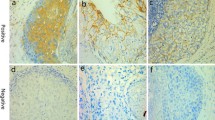
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and the estrogen receptor (ER) modulator Amplified In Breast cancer-1 (AIB1) have been reported to be of importance for the prognosis of breast cancer patients. We have analyzed AIB1 and EGFR by immunohistochemistry in primary breast cancers (n = 297) arranged in a tissue microarray in order to predict outcome after adjuvant endocrine therapy with tamoxifen for two years. High expression of AIB1 was associated with DNA-nondiploidy, high S-phase fraction, HER2 amplification, and short term (≤2 years) distant disease-free survival (DDFS), independent of ER status. High expression of EGFR was strongly associated to ER negativity and also correlated with progesterone receptor negativity, high S-phase fraction, and inversely correlated with nodal metastases. In univariate analysis, high EGFR was associated with shorter DDFS (hazard ratio 2.1; P = 0.017), and reached borderline significance in a multivariate analysis, adjusting for ER, menopausal and lymph node status, tumor size, and HER2 (P = 0.057).
In conclusion, both AIB1 and EGFR were associated to DDFS for breast cancer patients treated with two years of adjuvant tamoxifen; AIB1 with the development of early distant recurrences, indicating association between high AIB1 and resistance to tamoxifen during treatment, and EGFR with distant recurrences up to a follow up of five years.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group (EBCTCG) (2005) Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15–year survival: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet 365:1687–1717
Johnston S (2005) Molecular insights into endocrine resistance. Eur J Cancer Suppl 3:225–236
Osborne K, Shou J, Massarweh S, Schiff R (2005) Crosstalk between estrogen receptor and growth factor receptor pathways as a cause for endocrine therapy resistance in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res Suppl 11:865–870
Arpino G, Weiss H, Lee A, Schiff R, De Placido S, Osborne K, Elledge R (2005) Estrogen receptor–positive, progesterone receptor–negative breast cancer: association with growth factor receptor expression and tamoxifen resistance. J Natl Cancer Inst 97:1254–1261
Kurebayashi J (2005) Resistence to endocrine therapy in breast cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol Suppl 1 56:39–46
Arpino G, Green S, Allred C, Lew D, Martino S, Osborne K, Elledge R (2004) HER-2 amplification, HER-1 expression, and tamoxifen response in estrogen receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer: A Southwest Oncology Group Study. Clin Cancer Res 10:5670–5676
Ellis M, Coop A, Singh B, Mauriac L, Llombert-Cussac A, Jänicke F, Miller W, Evans D, Dugan M, Brady C, Quebe-Fehling E, Borgs M (2001) Letrozole is more effective neoadjuvant endocrine therapy than tamoxifen for erbB-1– and/or erbB-2–positive, estrogen receptor–positive primary breast cancer: evidence from a phase III randomized trial. J Clin Oncol 19:3808–3816
Knoop AS, Bentzen SM, Nielsen MM, Rasmussen BB, Rose C (2001) Value of epidermal growth factor receptor, HER2, p53, and steroid receptors in predicting the efficacy of tamoxifen in high-risk postmenopausal breast cancer patients. J Clin Oncol 19:3376–3384
Dowsett M, Houghton J, Iden C, Salter J, Farndon J, Hern RA, Sainsbury R, Baum M (2006) Benefit from adjuvant tamoxifen therapy in primary breast cancer patients according oestrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, EGF receptor and HER2 status. Ann Oncol 17:818–826
Osborne K, Bardou V, Hopp T, Chamness G, Hilsenbeck S, Fuqua S, Wong J, Allred C, Clark G, Schiff R (2003) Role of the estrogen receptor coactivator AIB1 (SRC-3) and HER-2/neu in tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 95:353–361
Kirkegaard T, McGlynn L, Campbell F, Müller S, Tovey S, Dunne B, Nielsen K, Cooke T, Bartlett J (2007) Amplified in breast cancer 1 in human epidermal growth factor receptor-positive tumors of tamoxifen-treated breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 13:1405–1411
Iwase H, Omoto Y, Toyama T, Yamashita H, Hara Y, Sugiura H, Zhang Z (2003) Clinical significance of AIB1 expression in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 80:339–345
Swedish Breast Cancer Cooperative Group (1996) Randomized trial of two versus five years of adjuvant tamoxifen for postmenopausal early stage breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 88:1543–1549
Rydén L, Jönsson P-E, Chebil G, Dufmats M, Fernö M, Jirström K, Källström A-C, Landberg G, Stål O, Thorstenson S, Nordenskjöld B (2005) Two years of adjuvant tamoxifen in premenopausal patients with breast cancer: a randomised, controlled trial with long-term follow-up. Eur J Cancer 41:256–264
Chebil G, Bendahl PO, Idvall I, Ferno M (2003) Comparison of immunohistochemical and biological assay of steroid receptors in primary breast cancer–clinical associations and reasons for discrepancies. Acta Oncol 42:719–725
Sigurdsson H, Baldetorp B, Borg Å, Dalberg M, Fernö M, Killander D, Olsson H (1990) Indicators of prognosis in node-negative breast caner. N Engl J Med 322:1045–1053
Isola J, Tanner M, Forsyth A, Cooke TG, Watters AD, Bartlett JM (2004) Interlaboratory comparison of HER-2 oncogene aplification as detected by chromogenic and fluoroscence in situ hybridization. Clin Cancer Res 10:4793–4798
Sarvilinna N, Eronen H, Miettinen S, Vienonen A, Ylikomi T (2006) Steroid hormone receptors and coregulators in endocrine-resistant and estrogen-independent breast cancer cells. Int J Cancer 118:832–840
Yarden RI, Wilson MA, Chrysogelos SA (2001) Estrogen suppression of EGFR expression in breast cancer cells: A possible mechanism to modulate growth. J Cell Biochem 81(Suppl. 36):232–246
Schiff R, Massarweh SA, Shou J, Bharwani L, Moshin S, Osborne K (2004) Cross-talk between estrogen receptor and growth factor pathways as a molecular target for overcoming endocrine resistance. Clin Cancer Res 10(Suppl):331–336
De Placido S, De Laurentiis M, Carlomagno C, Gallo C, Perrone F, Pepe S, Ruggiero A, Marinelli A, Pagliarulo C, Panico L, Pettinato G, Petrella G, Bianco A (2003) Twenty-year results of the Naples GUN randomized trial: predictive factors of adjuvant tamoxifen efficacy in early breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 9:1039–1046
Henriksen KL, Rasmussen BB, Lykkesfeldt AE, Moller S, Ejlertsen B, Mouridsen HT (2006) Semi-quantitative scoring of potentially predictive markers for endocrine treatment of breast cancer: A comparison between whole sections and tissue microarrays J Clin Pathol 60:397–404
Ferrero JM, Ramaioli A, Largillier R, Formento JL, Francoual M, Ettore F, Namer M, Milano G (2001) Epidermal growth factor receptor expression in 780 breast cancer patients: a reappraisal of the prognostic value based on an eight-year median follow-up. Ann Oncol 12:841–846
DiGiovanna MP, Stern DF, Edgerton SM, Whalen SG, More II D, Thor AD (2005) Relationship of epidermal growth factor receptor expression to ErbB-2 signaling activity and prognosis in breast cancer patients. J Clin Oncol 23:1152–1160
Niu Y, Fu X, Lv A, Fan Y, Wang Y (2002) Potential markers predicting distant metastasis in axillary node-negative breast carcinoma. Int J Cancer 98:754–760
Tsutsui S, Ohno S, Murakami S, Hachitanda Y, Oda S (2002) Prognostic value of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and its relationship to the estrogen receptor status in 1029 patients with breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 71:67–75
Acknowledgments
We are indebted to participating departments of the South Sweden Breast Cancer Group for providing us with breast cancer samples and clinical follow-up data. The study was supported by funds from the Swedish Cancer Society, the Swedish Research Council, the Gunnar, Arvid, and Elisabeth Nilsson Foundation, the Mrs Berta Kamprad Foundation, and the University Hospital of Lund Research Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dihge, L., Bendahl, PO., Grabau, D. et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and the estrogen receptor modulator amplified in breast cancer (AIB1) for predicting clinical outcome after adjuvant tamoxifen in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 109, 255–262 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-007-9645-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-007-9645-1