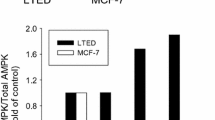
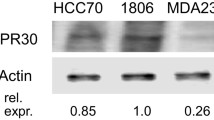
Abstract
Estrogen is known to stimulate breast cancer development in humans. Ironically, high doses of estrogen can induce regression of hormone-dependent breast cancer in postmenopausal women. The mechanism by which estrogen induces tumour regression in breast cancer is still unknown. We found that under low growth-stimulated conditions, high concentrations of 17-β-estradiol (estradiol) induces apoptosis and concomitantly increases phosphorylation of c-jun in estrogen receptor (ER)-positive breast cancer cell line, MCF-7, but not in ER-negative breast cancer cell line MDA-MB 231 suggesting an ER-mediated event. Interestingly, when the c-jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) signalling pathway was disrupted by the JNK inhibitor SP600125, the ability of estradiol to inhibit the growth of MCF-7 cells and to induce apoptosis was completely blocked. These data suggest that JNK plays a central role in mediating the anticancer effect of high concentrations of estradiol in MCF-7 cells. Our data showing the apoptotic effect of estradiol in low growth-stimulated conditions suggest potential implications for the pharmacological control of breast cancer with high dose estrogen in postmenopausal women. Furthermore, our results indicate that augmenting JNK activity could be an efficient novel approach for treating breast cancer.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Katzenellenbogen BS, Frasor J (2004) Therapeutic targeting in the estrogen receptor hormonal pathway. Semin Oncol 31:28–38
Jordan VC, Lewis JS, Osipo C, Cheng D (2005) The apoptotic action of estrogen following exhaustive antihormonal therapy: a new clinical treatment strategy. Breast 14:624–630
Song RX, Santen RJ (2003) Apoptotic action of estrogen. Apoptosis 8:55–60
Peethambaram PP, Ingle JN, Suman VJ, Hartmann LC, Loprinzi CL (1999) Randomized trial of diethylstilbestrol vs. tamoxifen in postmenopausal women with metastatic breast cancer. An updated analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 54:117–122
Agrawal A, Robertson JF, Cheung K (2006) Efficacy and tolerability of high dose “ethinylestradiol” in post-menopausal advanced breast cancer patients heavily pre-treated with endocrine agents. World J Surg Oncol 11:44
Santen RJ, Lobenhofer EK, Afshari CA, Bao Y, Song RX (2005) Adaptation of estrogen-regulated genes in long-term estradiol deprived MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 94:213–223
Song RX, Mor G, Naftolin F, McPherson RA, Song J, Zhang Z, Yue W, Wang J, Santen RJ (2001) Effect of long-term estrogen deprivation on apoptotic responses of breast cancer cells to 17 β-estradiol. J Natl Cancer Inst 93:1714–1723
Lewis JS, Meeke K, Osipo C, Ross EA, Kidawi N, Li T, Bell E, Chandel NS, Jordan VC (2005) Intrinsic mechanism of estradiol-induced apoptosis in breast cancer cells resistant to estrogen deprivation. J Natl Cancer Inst 97:1746–1759
Chang L, Karin M (2001) Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades. Nature 410:37–40
Bennett BL, Sasaki DT, Murray BW, O’Leary EC, Sakata ST, Xu W, Leisten JC, Motiwala A, Pierce S, Satoh Y, Bhagwat SS, Manning AM, Anderson DW (2001) SP600125, an anthrapyrazolone inhibitor of Jun N-terminal kinase. PNAS 98:13681–13686
Hengartner MO (2000) The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature 407:771–776
Zheng TS, Schlosser SF, Dao T, Hingorani R, Crispe IN, Boyer JL, Flavell RA (1998) Caspase-3 controls both cytoplasmic and nuclear events associated with Fas-mediated apoptosis in vivo. PNAS 95:13618–13623
Weston CR, Davis RJ (2002) The JNK signal transduction pathway. Curr Opin Genet Dev 12:14–21
Lacroix M, Toillon RA, Leclercq G (2006) p53 and breast cancer, an update. Endocr Relat Cancer 13:293–325
Okumura N, Saji S, Eguchi H, Hayashi S, Nakashima S (2002) Estradiol stabilizes p53 protein in breast cancer cell line, MCF-7. Jpn J Cancer Res 93:867–873
Jiang NS, Ryan RJ, Albert A (1973) Radioimmunoassay of serum estrogen. Clin Chem 19:740–747
Yao K, Lee ES, Bentrem DJ, England G, Schafer JI, O’Regan RM, Jordan VC (2000) Antitumor action of physiological estradiol on tamoxifen-stimulated breast tumors grown in athymic mice. Clin Cancer Res 6:2028–2036
Lee Y, Renaud RA, Friedrich TC, Gorski J (1998) Estrogen causes cell death of estrogen receptor stably transfected cells via apoptosis. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 67:327–332
Cho SG, Choi EJ (2002) Apoptotic signaling pathways: caspases and stress-activated protein kinases. J Biochem Mol Biol 35:24–27
Liu J, Lin A (2005) Role of JNK activation in apoptosis: a double-edged sword. Cell Res 15:36–42
Kawauchi T, Chihama K, Nabeshima Y, Hoshino M (2003) The in vivo roles of STEF/Tiam1, Rac1 and JNK in cortical neuronal migration. EMBO J 22:4190–4201
Stahli BE, Camici GG, Steffel J, Akhmedov A, Shojaati K, Graber M, Luscher TF, Tanner FC (2006) Paclitaxel enhances thrombin-induced endothelial tissue factor expression via c-Jun terminal NH2 kinase activation. Circ Res 99:149–155
Weihua Z, Andersson S, Cheng G, Simpson ER, Warner M, Gustafsson JA (2003) Update on estrogen signaling. FEBS Lett 546:17–24
Sak K, Everaus H (2004) Nongenomic effects of 17beta-estradiol-diversity of membrane binding sites. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 88:323–335
Kelly MJ, Levin ER (2001) Rapid actions of plasma membrane estrogen receptors. Trends Endocrinol Metab 12:152–156
Fotsis T, Zhang Y, Pepper MS, Adlercreutz H, Montesano R, Nawroth PP, Schweigerer L (1994) The endogenous oestrogen metabolite 2-methoxyoestradiol inhibits angiogenesis and suppresses tumour growth. Nature 368:237–239
Shimada K, Nakamura M, Ishida E, Kishi M, Konishi N (2003) Roles of p38- and c-jun NH2-terminal kinase-mediated pathways in 2-methoxyestradiol-induced p53 induction and apoptosis. Carcinogenesis 24:1067–1075
Han GZ, Liu ZJ, Shimoi K, Zhu BT (2005) Synergism between the anticancer actions of 2-methoxyestradiol and microtubule-disrupting agents in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 65:387–393
Waetzig V, Herdegen T (2005) Context-specific inhibition of JNKs: overcoming the dilemma of protection and damage. Trends Pharmacol Sci 26:455–461
Koyuturk M, Ersoz M, Altiok N (2004) Simvastatin induces proliferation inhibition and apoptosis in C6 glioma cells via c-jun N-terminal kinase. Neurosci Lett 370:212–217
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Istanbul Science University Institute of Medical Sciences and Johns Hopkins University Institutional research grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Altiok, N., Koyuturk, M. & Altiok, S. JNK pathway regulates estradiol-induced apoptosis in hormone-dependent human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 105, 247–254 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-006-9451-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-006-9451-1