Summary
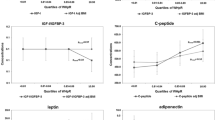
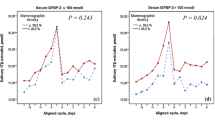
Epidemiologic evidence suggests obese premenopausal women experience a reduced risk of breast cancer. The mechanism underlying this protection is not fully understood although it is well documented that abdominal obesity may impair ovulatory function and reduce gonadal steroidogenesis. We measured levels of several metabolic markers that are modified by obesity [measured by body mass index (BMI, (weight (kg)/height (m2)))] and play a role in the reproductive axis, including, leptin, insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I), insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 (IGFBP3), C-peptide and prolactin in 233 cases and 251 controls participating in a retrospective study of breast cancer in young women conducted in the Seattle/Puget Sound region between 1990 and 1992. Consistent with the finding of a reduced risk with increasing BMI, risks declined with leptin levels, although to a lesser degree with odds ratios (OR) for the highest vs. lowest quartile of BMI=0.34 (95% C.I. 0.3–0.8) and for leptin=0.71 (95% C.I. 0.5–1.3). IGF-I, IGFBP3, C-peptide and prolactin were not related to breast cancer risk in a dose-dependent manner. With the possible exception of leptin, our findings do not suggest that these markers explain the breast cancer protection provided by obesity in premenopausal women.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Key TJ, Appleby PN, Reeves GK, Roddam A, Dorgan JF, Longcope C, Stanczyk FZ, Stephenson HE Jr, Falk RT, Miller R, Schatzkin A, Allen DS, Fentiman IS, Key TJ, Wang DY, Dowsett M, Thomas HV, Hankinson SE, Toniolo P, Akhmedkhanov A, Koenig K, Shore RE, Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A, Berrino F, Muti P, Micheli A, Krogh V, Sieri S, Pala V, Venturelli E, Secreto G, Barrett-Connor E, Laughlin GA, Kabuto M, Akiba S, Stevens RG, Neriishi K, Land CE, Cauley JA, Kuller LH, Cummings SR, Helzlsouer KJ, Alberg AJ, Bush TL, Comstock GW, Gordon GB, Miller SR, Longcope C, 2003. Endogenous hormones breast cancer collaborative group. Body mass index, serum sex hormones, and breast cancer risk in postmenopausal women J Natl Cancer Inst. 95:1218–1226
Van den Brandt PA, Spiegelman D, Yaun SS, Adami HO, Beeson L, Folsom AR, Fraser G, Goldbohm RA, Graham S, Kushi L, Marshall JR, Miller AB, Rohan T, Smith-Warner SA, Speizer FE, Willett WC, Wolk A, Hunter DJ, 2000. Pooled analysis of prospective cohort studies on height, weight, and breast cancer risk Am J Epidemiol 152:514–527
Hu Xin, Juneja SC, Maihle NJ, Cleary MP, 2002. Leptin-A growth factor in normal and malignant breast cells and for normal mammary gland development J Natl Cancer Inst 94:1704–1711
Petridou E, Papadiamantis Y, Markopoulos C, Spanos E, Dessypris N, Trichopoulos D, 2000. Leptin and insulin growth factor I in relation to breast cancer (Greece) Cancer Causes Control 11:383–388
Mantzoros CS, Bolhke K, Moschos S, Cramer DW, 1999. Leptin in relation to carcinoma in situ of the breast: a study of pre-menopausal cases and controls Int J Cancer 80:523–526
Gomez JM, Maravall FJ, Gomez N, Navarro MA, Casamitjana R, Soler J, 2003. Interactions between serum leptin, the insulin-like growth factor-I system, and sex, age, anthropometric and body composition variables in a healthy population randomly selected Clin Endocrinol 58:213–219
Kaaks R, Bellati C, Venturelli E, Rinaldi S, Secreto G, Biessy C, Pala V, Sieri S, Berrino F, 2003. Effects of dietary intervention on IGF-I and IGF-binding proteins, and related alterations in sex steroid metabolism: the Diet and Androgens (DIANA) Randomised Trial Eur J Clin Nutr 57:1079–1088
Elias JJ, Armstrong RC, 1973. Brief communication: hyperplastic and metaplastic responses of human mammary fibroadenomas and dysplasias in organ culture J Natl Cancer Inst 51:1341–1343
Renehan AG, Zwahlen M, Minder C, O’Dwyer ST, Shalet SM, Egger M, 2004. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF binding protein-3, and cancer risk: systematic review and meta-regression analysis Lancet 363:1346–1353
Bruning PF, Bonfrer JMG, van Noord PAH, Hart AAM, De Jong-Bakker M, Nooijen WJ, 1992. Insulin resistance and breast-cancer risk Int J Cancer 52: 511–516
Del Guidice ME, Fantus IG, Ezzat S, McKeown-Eyssen G, Page D, Goodwin PJ, 1998. Insulin and related factors in premenopausal breast cancer risk Breast Cancer Res Treat 47:111–120
Malin A, Dai Q, Yu H, Shu X, Jin F, Gao Y, Zheng W, 2004. Evaluation of the synergistic effect of insulin resistance and insulin-like growth factors on the risk of breast carcinoma Cancer 100: 694–700
Yang G, Lu G, Jin F, Dai Q, Best R, Shu XO, Chen JR, Pan XY, Shrubsole M, Zheng W, 2001. Population-based, case–control study of blood c-peptide levels and breast cancer risk Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 10: 1207–1211
Jernstrom H, Barrett-Connor E, 1999. Obesity, weight change, fasting insulin, proinsulin, c-peptide, and insulin-like growth factor-1 levels in women with and without breast cancer: the Rancho Bernardo Study J Womens Health Gend Based Med 8:1265–1272
Keinan-Boker L, Bas Bueno de Mesquita H, Kaaks R, van Gils CH, van Noord PAH, Rinaldi S, Riboli E, Seidell JC, Grobbee DE, Peeters PHM, 2003. Circulating levels of insulin-like growth factor I, its binding proteins -1, -2, -3, c-peptide and risk of postmenopausal breast cancer Int J Cancer 106: 90–95
Toniolo P, Bruning PF, Akhmedkhanov A, Bonfrer JMG, Koenig KL, Lukanova A, Shore RE, Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A, 2000. Serum insulin-like growth factor-I and breast cancer Int J Cancer 88:828–832
Michels KB, Solomon CG, Hu FB, et al. 2003. Type 2 diabetes and subsequent incidence of breast cancer in the Nurses’ Health Study Diabetes Care 26:1752–1758
Hankinson SE, Willett WC, Coldtiz GA, Hunter DJ, Michaud DS, Derpp B, Rosner B, Speizer FE, Pollak M, 1999. Circulating concentrations of insulin-like growth factor-I and risk of breast cancer Lancet 8: 1393–1396
Muti P, Quattrin T, Grant BJ, Krogh V, Micheli A, Schunemann HJ, Ram M, Freudenheim JL, Sieri S, Trevisan M, Berrino F, 2002. Fasting glucose is a risk factor for breast cancer: a prospective study Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 11:1361–1368
Rinaldi S, Toniolo P, Muti P, Lundin E, Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A, Arslan A, Micheli A, Lenner P, Dossus L, Krogh V, Shore RE, Koenig KL, Riboli E, Stattin P, Berrino F, Hallmans G, Lukanova A, Kaaks R, 2005. IGF-I, IGFBP-3 and breast cancer in young women: a pooled re-analysis of three prospective studiesEur J Cancer Prev 14:493–496
Kaaks R, Lundin E, Manjer J, Rinaldi S, Biessy C, Soderberg S, Lenner P, Janzon L, Riboli E, Berglund G, Hallmans G, 2003. Prospective study of IGF-I, IGF-binding proteins, and breast cancer risk, in Northern and Southern Sweden Cancer Causes Control 13: 307–316
Bohlke K, Cramer DW, Trichopoulos D, Mantzoros CS, 2003. Insulin-like growth factor-I in relation to premenopausal ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast Epidemiology 9:570–573
Flint DJ, Binart N, Kopchick J, Kelly P, 2003. Effects of growth hormone and prolactin on adipose tissue development and function Pituitary 6:97–102
Clevenger CV, Furth PA, Hankinson SE, Schuler LA, 2003. The role of prolactin in mammary carcinoma Endocrine Rev 24:1–27
Swanson CA, Coates RJ, Schoenberg JB, Malone KE, Gammon MD, Stanford JL, Shorr IJ, Potischman NA, Brinton LA. 1996. Body size and breast cancer risk among women under age 45 years Am J Epidemiol 143:698–706
Sturgeon SR, Potischman N, Malone KE, Dorgan JF, Daling J, Schairer C, Brinton LA, 2004. Serum levels of sex hormones and breast cancer risk in premenopausal women: a case–control study (USA) Cancer Causes Control 15:45–53
Wilkinson L, 1986. SYSTAT: The System for Statistics. SYSTAT, Inc., Evanston IL
Pasquali R, Pelusi C, Genghini S, Cacciari M, Gambineri A: Obesity and reproductive disorders in women. Hum Reprod Update 9: 359–372, 2003
Caprio M, Fabbrini E, Isidori AM, Aversa A, Fabbri A, 2001. Leptin in reproduction Trends Endocrinol Metab 12:65
Giesthövel F, Meysing A, Brabant G, 1998. C-peptide and insulin, but not C19-steroids, support the predictive value of body mass index on leptin in serum of premenopausal women Human Reprod 13:547–553
Messinis IE, Papageorgiou I, Milingos S, Asprodini E, Kollios G, Seferiadis K, 2001. Oestradiol plus progesterone treatment increases serum leptin concentrations in normal women Hum Reprod 16:1827–1832
Brannian JD, Hansen KA, 2002. Leptin and ovarian folliculogenesis: implications for ovulation induction and ART outcomes Semin Reprod Med 20:103–112
Yu H, Rohan T, 2000. Role of the insulin-like growth factor family in cancer development and progression J Natl Cancer Inst 92:1472–1489
Kwandwala HM, et al. 2000. The effects of insulin-like growth factors on tumorigenesis and neoplasic growth Endocrin Rev 21:215–244
Kaaks R, Lukanova A, 2001. Energy balance and cancer: the role of insulin and sinlin-like growth factor-I Proc Nutr Soc 60:91–106
Thissen JP, Ketelslegers JM, Underwood LE, 1994. Nutritional regulation of the insulin-like growth factors Endocrine Rev 15: 80–101
Sugumar A, Liu YC, Xia Q, Koh YS, Matsuo K, 2004. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF-binding protein 3 and the risk of premenopausal breast cancer: a meta-analysis of literature Int J Cancer 111:293–297
Shi R, Yu H, McLarty J, Glass J, 2004. IGF-I and breast cancer: a meta-analysis Int J Cancer 111:418–423
Fletcher O, Gibson L, Johnson N, Altmann DR, Holly JM, Ashworth A, Peto J, Silva Idos S, 2005. Polymorphisms and circulating levels in the insulin-like growth factor system and risk of breast cancer: a systematic review Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 14:2–19
Vonderhaar BK, 1999. Prolactin involvement in breast cancer Endocr Relat Cancer 6:389–404
Kwa HG, Cleton F, Wang DY, Bulbrook RD, Bulstrode JC, Hayward JL, Millis RR, Cusick J, 1981. A prospective study of plasma prolactin levels and subsequent risk of breast cancer Int J Cancer 28:673–676
Hankinson SE, Willett WC, Michaud DS, Manson JE, Colditz GA, Longcope C, Rosner B, Speizer FE, 1999. Plasma prolactin levels and subsequent risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women J Natl Cancer Inst 91:629–634
Wang DY, DeStavola BL, Bulbrook RD, Allen DS, Kwa HG, Fentiman IS, Hayward JL, Millis RR, 1992. Relationship of blood prolactin levels and the risk of subsequent breast cancer Int J Epidemiol 21:214–221
Allen NE, Appleby PN, Kaaks R, Rinaldi S, Davey GK, Key TJ, 2003. Lifestyle determinants of serum insulin-like growth-factor-I (IGF-I), C-peptide and hormone binding protein levels in British women Cancer Cause Control 14: 65–74
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Falk, R.T., Brinton, L.A., Madigan, M.P. et al. Interrelationships between serum leptin, IGF-1, IGFBP3, C-peptide and prolactin and breast cancer risk in young women. Breast Cancer Res Treat 98, 157–165 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-005-9144-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-005-9144-1