Summary
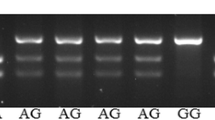
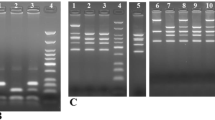
Human breast cancer cells with high metastatic potential show reduced expression of the metastasis-suppressor gene NME1. There are two polymorphic sites for the restriction enzymes BglII and EcoRI, both detectable by Southern blot analysis. Although the BglII site has been analyzed for loss of heterozygosity, the biallelic EcoRI site polymorphism has not been studied in association with breast cancer, complications or metastasis. We analyzed EcoRI site allele frequencies in Mexican patients with breast cancer, using polymerase chain reaction -restriction fragment length polymorphisms. The polymorphic allelic frequencies in the cases and reference groups were 0.4215 and 0.3375, respectively; this difference was not statistically significant (χ2=0.8687, p=0.3512). Thus, EcoR1 polymorphic site was not associated with breast cancer in this series, but could be analyzed in association with metastases and might be informative in the evaluation of loss of heterozygosity in women with breast cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
SINAIS (Sistema Nacional de Información en Salud) estadísticas de mortalidad de mujeres y en edad reproductiva en México y en Jalisco, 2002. Available at www.ssa.gob.mx. Accessed May 26, 2005
Liotta LA, Kohn E, Steeg PS, Stetler-Stevenson W, Molecular biology of metastasis In: Broder S (ed). Molecular Foundations of Oncology Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore 1991 pp 57–81
Steeg PS, Bevilacqua G, Kooper L, Thorgeirsson UP, Talmadge JE, Liotta LA, Sobel ME, Evidence for a novel gene associated with a low tumor metastatic potential J Natl Cancer Inst 80:200–204, 1998
Bevilacqua G, Sobel ME, Liotta LA, Steeg PS, Association of low nm23 RNA levels in human primary infiltrating ductal breast carcinomas with lymph node involvement and other histopathological indicators of high metastatic potential Cancer Res49:5185–5190, 1989
Steeg PS, Hartsough MT, Clare SE, Nm23, breast differentiation and cancer metastasis In: Bowcock AM (ed). Breast Cancer: Molecular Genetics, Pathogenesis, and Therapeutics Humana Press Inc. Totowa 1999 pp 267–283
Engel M, Seifert M, Theisinger B, Seyfert U, Welter C, Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and nm23-H1/nucleoside diphosphate kinase A. Two old enzymes combine for the novel Nm23 protein phosphotransferase function J Biol Chem273:20058–20065, 1998
Khan MH, Yasuda M, Higashino F, Haque S, Kohgo T, Nakamura M, Shindoh M, Nm23-H1 suppresses invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma-derived cell lines without modifying matrix metalloproteinase-2 and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression Am J Pathol158(5):1785–1791, 2001
Cipollini G, Moretti A, Ghimenti C, Viacava P, Bevilacqua G, Caligo MA, Mutational analysis of the Nm23-H1 gene in human breast cancer Cancer Genet Cytogenet121(2):181–185, 2000
Chang CL, Zhu X, Thoraval DH, Ungar D, Rawwas J, Hora N, Strahler J, Hanash S, Radany E, Nm23-H1 mutation in neuroblastomaNature 370(6488):335–336, 1994
Hartsough MT, Steeg PS, Nm23-H1: genetic alterations and expression patterns in tumor metastasis Am J Hum Genet63(1):6–10, 1998
Yagüe J, Juan M, Leone A, Romero M, Cardesa A, Vives J, Steeg PS, Campo E: BgLII and EcoRI polymorphism of human nm23-H1 gene (NME1) Nucleic Acids Res19(23):6663, 1991
Goelz SE, Hamilton SR, Vogelstein B, Purification of DNA from formaldehyde fixed and paraffin embedded human tissue Biochem Biophys Res Commun130(1):118–126, 1985
Gustincich S, Manfioletti G, Del Sal G, Schneider C, Carninci P, A fast method for high-quality genomic DNA extraction from whole human blood Biotechniques11(3):298–300, 302, 1991
Nacional Center of Biotechnology Information. Available at http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/. Accessed April 30, 2003
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T, Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual 3 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press New York 2001
Sanguinetti CJ, Dias NE, Simpson AJ, Rapid silver staining and recovery of PCR products separated on polyacrylamide gels Biotechniques17(5):914–921, 1994
O’Shaughnessy J, Moscow JA, Cowan KH: Breast cancer into the 1990s In: Broder S, (ed) Molecular Foundations of Oncology Williams & Wilkins Baltimore 1991, pp 311–338
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rubio, S.A.G., Martinez, S.E.F., Corona, J.S. et al. EcoRI polymorphism of the metastasis-suppressor gene NME1 in Mexican patients with breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 96, 159–161 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-005-9072-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-005-9072-0