Summary
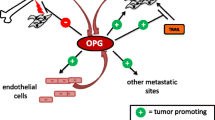
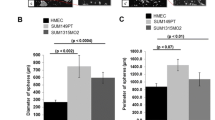
In addition to its role in bone turnover, osteoprotegerin (OPG) has been reported to bind to and inhibit Tumour necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL). TRAIL is produced in tumours by invading monocytes, inducing apoptosis in neoplastic cells sensitive to this cytokine. OPG production by tumour cells would therefore be a novel mechanism whereby cancer cells evade host defences and gain a growth advantage. In this study we show that OPG produced by breast cancer cells enhances tumour cell survival by inhibiting TRAIL-induced apoptosis. OPG expression by breast cancer cells (MDA-MB 436/231) grown in vitro was examined using PCR and ELISA, and the sensitivity of these cells to TRAIL was determined. The effects of OPG on TRAIL induced apoptosis was investigated by exposing MDA-MB 436 cells to TRAIL, in the presence or absence of OPG, followed by assessment of nuclear morphology. We found that the levels of OPG produced were sufficient to inhibit TRAIL-induced apoptosis, suggesting that OPG may play a role in tumour cell survival. We also examined the expression pattern of OPG in a selection of breast tumours (n=400) by immunohistochemistry, and related OPG expression to the clinico-pathological data for each tumour. OPG expression was found to be negatively correlated with increasing tumour grade. To our knowledge these results are the first to demonstrate that OPG can act as an endocrine survival factor for breast cancer cells, as well as reporting the expression patterns of OPG in a large cohort of human breast tumours.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EGF:
-
epidermal growth factor
- OPG:
-
osteoprotegerin
- RANKL:
-
receptor activator of nuclear factor κB ligand
- TGF:
-
tumour growth factor
- TNF:
-
tumour necrosis factor
- TRAIL:
-
tumour necrosis factor related apoptosis inducing ligand
References
RM Locksley N Killeen MJ Lenardo (2001) ArticleTitleThe TNF and TNF receptor superfamilies: integrating mammalian biology Cell 104 IssueID4 487–501 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00237-9 Occurrence Handle11239407
FC Kischkel S Hellbardt I Behrmann M Germer M Pawlita PH Krammer (1995) ArticleTitleCytotoxicity-dependent APO-1 (Fas/CD95)- associated proteins form a death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) with the receptor EMBO J 14 5579–5588 Occurrence Handle8521815
FH Igney PH Krammer (2002) ArticleTitleDeath and anti-death: tumour resistance to apoptosis Nat Rev Cancer 2 277–288 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nrc776 Occurrence Handle12001989
H Mueller N Flury R Liu S Scheidegger U Eppenberger (1996) ArticleTitleTumor necrosis factor and interferon are selectively cytostatic in vitro for hormone-dependent and hormone-independent human breast cancer cells Eur J Cancer 32A 2312–2318 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0959-8049(96)00273-0 Occurrence Handle9038615
ME Burow CB Weldon Y Tang GL Navar S Krajewski JC Reed TG Hammond S Clejan BS Beckman (1998) ArticleTitleDifferences in susceptability to tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced apoptosis among MCF-7 cancer cell variants Cancer Res 58 4940–4946 Occurrence Handle9810003
C Ruiz-Ruiz C Munoz-Pinedo A Lopez-Rivas (2000) ArticleTitleInterferon- gamma treatment elevates caspase-8 expression and sensitises human breast cancer cells to a death receptor-induced mitochondria-operated apoptotic program Cancer Res 60 5673–5680
ME Burow CB Weldon Y Tang JA McLachlan BS Beckman (2001) ArticleTitleEstrogen-mediated suppression of tumour necrosis factorα-induced apoptosis in MCF-7 cells: subversion of Bcl-2 by antiestrogens J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 78 409–418 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0960-0760(01)00117-0 Occurrence Handle11738551
EM Gibson ES Henson N Haney J Villanueva SB Gibson (2002) ArticleTitleEpidermal growth factor protects epithelial-derived cells from tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis by inhibiting cytochrome c release Cancer Res 62 488–496 Occurrence Handle11809700
SW Tobin MK Brown K Douville DC Payne A Eastman BA Arrick (2001) ArticleTitleInhibition of transforming growth factor beta signalling in MCF-7 cells results in resistance to tumor necrosis factor alpha: a role for Bcl-2 Cell Growth Differ 12 109–117 Occurrence Handle11243465
A Almasan A Ashkenazi (2003) ArticleTitleApo2L/TRAIL: apoptosis signalling, biology and potential for cancer therapy Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 14 337–348 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1359-6101(03)00029-7 Occurrence Handle12787570
XD Zhang T Nguyen WD Thomas JE Sanders P Hersey (2000) ArticleTitleMechanisms of resistance of normal cells to TRAIL induced apoptosis vary between different cell types FEBS Lett 482 193–199 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0014-5793(00)02042-1 Occurrence Handle11024459
G Pan K O’Rourke AM Chinnaiyan R Gentz R Ebner J Ni VM Dixit (1997) ArticleTitleThe receptor for the cytotoxic ligand TRAIL Science 276 111–113 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.276.5309.111 Occurrence Handle9082980
H Walczak MA Degli-Esposti RS Johnson PM Smolak JY Waugh N Boiani (1997) ArticleTitleTRAIL-R2: a novel apoptosis-mediating receptor for TRAIL EMBO J 16 5386–5397 Occurrence Handle10.1093/emboj/16.17.5386 Occurrence Handle9311998
MM Noesel Particlevan S Bezouw Particlevan GS Salomons PA Voute R Pieters SB Baylin (2002) ArticleTitleTumor-specific down-regulation of the tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand decoy receptors DcR1 and DcR2 is associated with dense promoter hypermethylation Cancer Res 62 2157–2161 Occurrence Handle11929838
JG Emery P McDonnell MB Burke KC Deen S Lyn C Silverman (1998) ArticleTitleOsteoprotegerin is a receptor for the cytotoxic ligand TRAIL J Biol Chem 273 14363–14367 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.273.23.14363 Occurrence Handle9603945
AC Spalding RM Jotte RI Scheinman MW Geraci P Clarke KL Tyler GL Johnson (2002) ArticleTitleTRAIL and inhibitors of apoptosis are opposing determinants for NF-kappaB-dependent, genotoxin-induced apoptosis of cancer cells Oncogene 21 260–271 Occurrence Handle10.1038/sj.onc.1205048 Occurrence Handle11803469
RJ Thomas TA Guise JJ Yin J Elliott NJ Horwood TJ Martin MT Gillespie (1999) ArticleTitleBreast cancer cells interact with osteoblasts to support osteoclast formation Endocrinology 140 4451–4458 Occurrence Handle10.1210/en.140.10.4451 Occurrence Handle10499498
I Holen PI Croucher FC Hamdy CL Eaton (2002) ArticleTitleOsteoprotegerin (OPG) is a survival factor for human prostate cancer cells Cancer Res 62 1619–1623 Occurrence Handle11912131
CM Shipman PI Croucher (2003) ArticleTitleOsteoprotegerin is a soluble decoy receptor for tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand/Apo2 ligand and can function as a paracrine survival factor for human myeloma cells Cancer Res 63 IssueID5 912–916 Occurrence Handle12615702
R Nyambo N Cross J Lippitt I Holen G Bryden FC Hamdy CL Eaton (2004) ArticleTitleHuman bone marrow stromal cells protect prostate cancer cells from TRAIL-induced apoptosis J Bone Miner Res 10 1712–1721
HL Neville-Webbe NA Cross CL Eaton R Nyambo CA Evans RE Coleman I Holen (2004) ArticleTitleOsteoprotegerin (OPG) produced by bone␣marrow stromal cells protects breast cancer cells from TRAIL-induced apoptosis Breast Cancer Res Treat 86 269–279 Occurrence Handle10.1023/B:BREA.0000036900.48763.b3 Occurrence Handle15567943
WS Simonet DL Lacey C Dunstan M Kelley M-S Chang R Luthy (1997) ArticleTitleOsteoprotegerin: a novel secreted protein involved in the regulation of bone density Cell 89 309–319 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80209-3 Occurrence Handle9108485
E Tsuda M Goto S Mochizuki K Yano F Kobayashi T Morinaga (1997) ArticleTitleIsolation of a novel cytokine from human fibroblasts that specifically inhibits osteoclastogenesis Biochem Biophys Res Comm 234 137–142 Occurrence Handle10.1006/bbrc.1997.6603 Occurrence Handle9168977
R Ito H Nakayama K Yoshida (2003) ArticleTitleExpression of osteoprotegerin correlates with aggressiveness and poor prognosis of gastric carcinoma Virchows Arch 443 146–151 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00428-003-0845-8 Occurrence Handle12838418
MM Reinholz SJ Iturria PC Roche (2002) ArticleTitleDifferential gene expression of TGF-beta family members and osteopontin in breast tumour tissue: analysis by real-time quantitative PCR Breast Cancer Res Treat 74 IssueID3 255–269 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1016339120506 Occurrence Handle12206515
LC Hofbauer AE Heufelder (2000) ArticleTitleThe role of receptor activator of nuclear factor κB ligand and osteoprotegerin in the pathogenesis and treatment of metabolic bone disease J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85 2355–2363 Occurrence Handle10.1210/jc.85.7.2355 Occurrence Handle10902778
M MacFarlane W Merrison D Dinsdale GM Cohen (2000) ArticleTitleActive caspases and cleaved cytokeratins are sequestered into cytoplasmic inclusions in TRAIL-induced apoptosis J Cell Biol 148 IssueID6 1239–1254 Occurrence Handle10.1083/jcb.148.6.1239 Occurrence Handle10725337
YJ Lee CJ Froelich N Fujita T Tsuruo JH Kim (2004) ArticleTitleReconstitution of caspase-3 confers low glucose-enhanced tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand cytotoxicity and Akt cleavage Clin Cancer Res 10 IssueID6 1894–1900 Occurrence Handle15041704
Oba T, Sun X, Grubbs B, Cui Y, Kakonen, Guise TA, Chirgwin JM: Effects of tumor secretion on recombinant osteoprotegerin (OPG) on osteolytic metastases. ASBMR 23rd annual meeting, Abstract F066, 2001.
Fischer JL, Thomas RJ, Elloitt J, Dunstan CR, Choong PFM, Martin TJ, Gillespie MT: Over-expression of native OPG by breast cancer cells enhances tumour growth in bone. ASBMR 24th annual meeting, Abstract SA081, 2002.
A Truneh S Sharma C Silverman S Khandekar MP Reddy KC Deen MM McLaughlin SM Srinivasula GP Livi LA Marshall ES Alnemri WV Williams ML Doyle (2000) ArticleTitleTemperature-sensitive differential affinity of TRAIL for its receptors DR5 is the highest affinity receptor J Biol Chem 275 IssueID30 23319–23325 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.M910438199 Occurrence Handle10770955
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holen, I., Cross, S.S., Neville-Webbe, H.L. et al. Osteoprotegerin (OPG) Expression by Breast Cancer Cells in vitro and Breast Tumours in vivo – A Role in Tumour Cell Survival?. Breast Cancer Res Treat 92, 207–215 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-005-2419-8
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-005-2419-8