Abstract
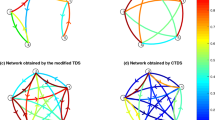
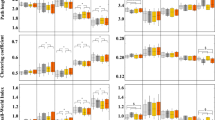
In this study we illustrate a methodology able to follow and study concurrent and simultaneous brain processes during cooperation between individuals, with non invasive EEG methodologies. We collected data from fourteen pairs of subjects while they were playing a card game with EEG. Data collection was made simultaneously on all the subjects during the card game. An extension of the Granger-causality approach allows us to estimate the functional connection between signals estimated from different Regions of Interest (ROIs) in different brains during the analyzed task. Finally, with the use of graph theory, we contrast the functional connectivity patterns of the two players belonging to the same team. Statistically significant functional connectivities were obtained from signals estimated in the ROIs modeling the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) and the prefrontal areas described by the Brodmann areas 8 with the signals estimated in all the other modelled cortical areas. Results presented suggested the existence of Granger-sense causal relations between the EEG activity estimated in the prefrontal areas 8 and 9/46 of one player with the EEG activity estimated in the ACC of their companion. We illustrated the feasibility of functional connectivity methodology on the EEG hyperscannings performed on a group of subjects. These functional connectivity estimated from the couple of brains could suggest, in statistical and mathematical terms, the modelled cortical areas that are correlated in Granger-sense during the solution of a particular task. EEG hyperscannings could be used to investigate experimental paradigms where the knowledge of the simultaneous interactions between the subjects have a value.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Astolfi L, Cincotti F, Mattia D, Babiloni C, Carducci F, Basilisco A et al (2005) Assessing cortical functional connectivity by linear inverse estimation and directed transfer function: simulations and application to real data. Clin Neurophysiol 116(4):920–932
Astolfi L, Cincotti F, Mattia D, Marciani MG, Baccala L, de Vico Fallani F et al (2007a) Comparison of different cortical connectivity estimators for high-resolution EEG recordings. Hum Brain Mapp 28(2):143–157
Astolfi L, de Vico Fallani F, Cincotti F, Mattia D, Marciani MG, Bufalari S et al (2007b) Imaging functional brain connectivity patterns from high-resolution EEG and fMRI via graph theory. Psychophysology 44(6):880–893
Astolfi L, Cincotti F, Mattia D, de Vico Fallani F, Tocci A, Colosimo A et al (2008) Tracking the time-varying cortical connectivity patterns by adaptive multivariate estimators. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 55(3):902–913
Babiloni C, Babiloni F, Carducci F, Cincotti F, Rosciarelli F, Rossini PM et al (2001) Mapping of early and late human somatosensory evoked brain potentials to phasic galvanic painful stimulation. Hum Brain Mapp 12(3):168–179
Babiloni F, Cincotti F, Babiloni C, Carducci F, Mattia D, Astolfi L et al (2005) Estimation of the cortical functional connectivity with the multimodal integration of high resolution EEG and fMRI data by Directed Transfer Function. Neuroimage 24(1):118–131
Baccalà LA, Sameshima K (2001) Partial directed coherence: a new concept in neural structure determination. Biol Cybern 84:463–474
Bechara A, Damasio H, Damasio AR (2000) Emotion, decision-making and the orbitofrontal cortex. Cereb Cortex 10:295–307
Bendat JS, Piersol AG (1993) Engineering applications of correlation and spectral analysis. Wiley, New York
Botvinick M, Cohen JD, Carter CS (2004) Conflict monitoring and anterior ingulate cortex: an update. Trends Cogn Sci 8:539–546
De Vico Fallani F, Astolfi L, Cincotti F, Mattia D, Tocci A, Marciani MG et al (2007a) Extracting information from cortical connectivity patterns estimated from high resolution EEG recordings: a theoretical graph approach. Brain Topogr 19(3):125–136
De Vico Fallani F, Astolfi L, Cincotti F, Mattia D, Marciani MG, Salinari S et al (2007b) Cortical functional connectivity networks in normal and spinal cord injured patients: evaluation by graph analysis. Hum Brain Mapp 28(12):1334–1346
Ding M, Bressler SL, Yang W, Liang Ding H (2000) Short-window spectral analysis of cortical event-related potentials by adaptive multivariate autoregressive modeling: data preprocessing, model validation, and variability assessment. Biol Cybern 83:35–45
Escudero J, Hornero R, Abásolo D, Fernández A, López-Coronado M (2007) Artifact removal in magnetoencephalogram background activity with independent component analysis. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 54(11):1965–1973
Formisano E, Esposito F, Di Salle F, Goebel R (2004) Cortex-based independent component analysis of fMRI time series. Magn Reson Imaging 22(10):1493–1504
Granger CWJ (1969) Investigating causal relations by econometric models and cross-spectral methods. Econometrica 37:424–438
Grave de Peralta Menendez R, Gonzalez Andino SL (1999) Distributed source models: standard solutions and new developments. In: Uhl C (ed) Analysis of neurophysiological brain functioning. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 176–201
Hansen PC (1992) Analysis of discrete ill-posed problems by means of L-curve. SIAM Rev 43:561–580
Hasson U, Nir Y, Levy I, Fuhrmann G, Malach R (2004) Intersubject synchronization of cortical activity during natural vision. Science 303:1634–1640
Horwitz B (2003) The elusive concept of brain connectivity. Neuroimage 19(2 Pt 1):466–470
Hsu M, Bhatt M, Adolphs R, Tranel D, Camerer CF (2005) Neural systems responding to degrees of uncertainty in human decision-making. Science 310:1680–1683
Kaminski M, Blinowska K (1991) A new method of the description of the information flow in the brain structures. Biol Cybern 65:203–210
Kaminski M, Ding M, Truccolo WA, Bressler S (2001) Evaluating causal relations in neural systems: granger causality, directed transfer function and statistical assessment of significance. Biol Cybern 85:145–157
King-Casas B, Tomlin D, Anen C, Camerer CF, Quartz SR, Montague PR (2005) Getting to know you: reputation and trust in a two-person economic exchange. Science 308(5718):78–83
Knobe J (2005) Theory of mind and moral cognition: exploring the connections. Trends Cogn Sci 9(8):357–359
Kuhnen CM, Knutson B (2005) The neural basis of financial risk taking. Neuron 47:763–770
Lancaster JL, Rainey LH, Summerlin JL, Freitas CS, Fox PT, Evans AC, Toga AW, Mazziotta JC (1997) Automated labeling of the human brain: a preliminary report on the development and evaluation of a forward-transform method. Hum Brain Mapp 5:238–242
Lancaster JL, Woldorff MG, Parsons LM, Liotti M, Freitas CS, Rainey L, Kochunov PV, Nickerson D, Mikiten SA, Fox PT (2000) Automated Talairach Atlas labels for functional brain mapping. Hum Brain Mapp 10:120–131
Lee RB, DeVore I (eds) (1968) What hunters do for a living, or, how to make out on scarce resources. In: Man the hunter. Aldine, Chicago, pp 30–48
Montague PR, Berns GS, Cohen JD, McClure SM, Pagnoni G, Dhamala M et al (2002) Hyperscanning: simultaneous fMRI during linked social interactions. Neuroimage 16:1159–1164
Mulert C, Menzinger E, Leicht G, Pogarell O, Hegerl U (2005) Evidence for a close relationship between conscious effort and anterior cingulate cortex activity. Int J Psychophysiol 56:65–80
Nunez PL (1995) Neocortical dynamics and human EEG rhythms. Oxford University Press, New York
Oliveri M, Babiloni C, Filippi MM, Caltagirone C, Babiloni F, Cicinelli P et al (2003) Influence of the supplementary motor area on primary motor cortex excitability during movements triggered by neutral or emotionally unpleasant visual cues. Exp Brain Res 149(2):214–221
Preuschoff K, Bossaerts P, Quartz S (2006) Neural differentiation of expected reward and risk in human subcortical structures. Neuron 51:381–390
Raz J, Turetsky B, Fein G (1988) Confidence intervals for the signal-to-noise ratio when a signal embedded in noise is observed over repeated trials. IEEE Trans BME 35(8):646–649
Sanfey AG, Rilling JK, Aronson JA, Nystrom LE, Cohen JD (2003) The neural basis of economic decision-making in the Ultimatum Game. Science 300:1755–1758
Sato JR, Takahashi DY, Arcuri SM, Sameshima K, Morettin PA, Baccalà LA (2009) Frequency domain connectivity identification: an application of partial directed coherence in fMRI. Hum Brain Mapp 30(2):452–461
Schlögl A, Supp G (2006) Analyzing event-related EEG data with multivariate autoregressive parameters. Prog Brain Res 159:135–147 Review
Sporns O (2006) Small-world connectivity, motif composition, and complexity of fractal neuronal connections. Biosystems 85(1):55–64
Stephan KE, Riera JJ, Deco G, Horwitz B (2008) The Brain Connectivity Workshops: moving the frontiers of computational systems neuroscience. Neuroimage 42(1):1–9. Epub 2008 Apr 20
Taxidis J, Coomber B, Mason R, Owen M (2010) Assessing cortico-hippocampal functional connectivity under anesthesia and kainic acid using generalized partial directed coherence. Biol Cybern 102:327–340
Theiler J, Eubank S, Longtin A, Galdrikian B, Farmer JD (1992) Testing for nonlinearity in time series: the method of surrogate data. Physica D 58:77–94
Tobler PN, Fiorillo CD, Schultz W (2005) Adaptive coding of reward value by dopamine neurons. Science 307:1642–1645
Tononi G, Sporns O, Edelman GM (1994) A measure for brain complexity: relating functional segregation and integration in the nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:5033–5037
Urbano A, Babiloni F, Babiloni C, Ambrosini A, Onorati P, Rossini PM (1997) Human short-latency cortical responses to somatosensory stimulation. A high resolution study. NeuroReport 8(15):3239–3243
Urbano A, Babiloni C, Carducci F, Fattorini L, Onorati P, Babiloni F (1998) Dynamic functional coupling of high resolution EEG potentials related to unilateral internally triggered one-digit movements. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 106:477–487
Varela F, Lachaux JP, Rodriguez E, Martinerie J (2001) Thebrainweb: phase synchronization and large-scale integration. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:229–239
Walton ME, Bannerman DM, Rushworth MF (2002) The role of rat medial frontal cortex in effort-based decision making. J Neurosci 22:10996–11003
Whiten A, Byrne RW (1988) Tactical deception in primates. Behav Brain Sci 11:233–273
Yook SH, Jeong H, Barabási A, Tu Y (2001) Weighted evolving networks. Phys Rev Lett 86(25):5835–5838
Zar J (1984) Biostatistical analysis. Prentice Hall, New York
Acknowledgments
This study was performed with the support of the COST EU project NEUROMATH (BM 0601).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Astolfi, L., Toppi, J., De Vico Fallani, F. et al. Neuroelectrical Hyperscanning Measures Simultaneous Brain Activity in Humans. Brain Topogr 23, 243–256 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-010-0147-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-010-0147-9