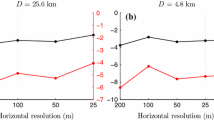
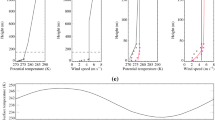
Abstract
The analysis of momentum and heat fluxes from the Cooperative Atmosphere-Surface Exchange Study 1999 (CASES-99) field experiment is extended throughout the diurnal cycle following the investigation of nighttime turbulence by Sun et al. (J Atmos Sci 69:338–351, 2012). Based on the observations, limitations of Monin–Obukhov similarity theory (MOST) are examined in detail. The analysis suggests that strong turbulent mixing is dominated by relatively large coherent eddies that are not related to local vertical gradients as assumed in MOST. The HOckey-Stick Transition (HOST) hypothesis is developed to explain the generation of observed large coherent eddies over a finite depth and the contribution of these eddies to vertical variations of turbulence intensity and atmospheric stratification throughout the diurnal cycle. The HOST hypothesis emphasizes the connection between dominant turbulent eddies and turbulence generation scales, and the coupling between the turbulence kinetic energy and the turbulence potential energy within the turbulence generation layer in determining turbulence intensity. For turbulence generation directly influenced by the surface, the HOST hypothesis recognizes the role of the surface both in the vertical variation of momentum and heat fluxes and its boundary effect on the size of the dominant turbulence eddies.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acevedo OC, Fitzjarrald DR (2003) In the core of the night-effects of intermittent mixing on a horizontally heterogeneous surfaces. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 106:1–33
Andreas EL, Hicks BB (2002) Comments on critical test of the validity of Monin-Obukhov similarity during convective conditions. J Atmos Sci 59:2605–2607
Baas P, Steeneveld GJ, van de Wiel BJH, Holtslag AAM (2006) Exploring self-correlation in flux-gradient relationships for stably stratified conditions. Q J R Meteorol Soc 63:3045–3054
Banta RM, Pichugina YL, Newsom RK (2003) Relationship between low-level jet properties and turbulence kinetic energy in the nocturnal stable boundary layer. J Atmos Sci 60:2549–2555
Banta RM (2008) Stable-boundary-layer regimes from the perspective of the low-level jet. Acta Geophys 56:58–87. doi:10.2478/s11600-007-0049-8
Beljaars ACM, Holtslag AAM (1991) Flux parameterization over land surfaces for atmospheric models. J Appl Meteorol 30:327–341
Bonin TA, Blumberg WG, Klein PM, Chilson PB (2015) Thermodynamic and turbulence characteristics of the Southern Great Plains nocturnal boundary layer under differing turbulent regimes. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 157:1–2
Boussinesq J (1877) Essai sur la théorie des eaux courantes. Mémoires présentés par divers savants à l’Académie des Sciences 23(1):1–680
Caulfield CP, Kerswell RR (2001) Maximal mixing rate in turbulent stably stratified Coutte flow. Phys Fluids 13:894–900
Etling D, Brown R (1993) Roll vortices in the planetary boundary layer: a review. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 65:215–248
Garratt JR (1992) The atmospheric boundary layer. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 316 pp
Hamba F (2005) Nonlocal analysis of the Reynolds stress in turbulent shear flow. Phys Fluids 17(11):102–115
Hicks BB (1978) Some limitations of dimensional analysis and power laws. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 14:567–569
Högström U (1996) Review of some basic characteristics of the atmospheric surface layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 78(3–4):215–246
Högström U, Hunt JCR, Smedman AS (2002) Theory and measurements for turbulence spectra and variances in the atmospheric neutral surface layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 103:101–124
Holliday D, McIntyre ME (1981) On potential energy density in an incompressible, stratified fluid. J Fluid Mech 107:221–225
Hopfinger EJ (1987) Turbulence in stratified fluids: a review. J Geophys Res 92(C5):5287–5303
Howell J (1995) Identifying sudden changes in data. Mon Weather Rev 123(4):1207–1212
Howell J, Mahrt L (1994) An adaptive multiresolution data filter: applications to turbulence and climatic time series. J Atmos Sci 51(4):2165–2178
Howell JF, Sun J (1999) Surface-layer fluxes in stable conditions. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 90:495–520
King JC, Mobbs SD, Edwards NR (1994) Surface boundary conditions in stably-stratified environmental flows. In: Castro IP, Rochliff NJ (eds) Stably stratified flows: flow and dispersion over topography. Institute of Mathematics and Its Applications, University of Surrey; Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 93–103
Klipp CL, Mahrt L (2004) Flux-gradient relationship, self-correlation and intermittency in the stable boundary layer. Q J R Meteorol Soc 130:2087–2103
Lenschow DH, Zhang SF, Stankov BB (1988) The stably stratified boundary layer over the Great Plains I: mean and turbulence structure. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 42:95–121
Lindborg E (2006) The energy cascade in a strongly stratified fluid. J Fluid Mech 550:207–242
Lin JT, Pao YH (1979) Wakes in stratified fluids. Ann Rev Fluid Mech 11:317–338
Mahrt L, Sun J, Blumen W, Delany T, Oncley S (1998) Nocturnal boundary-layer regimes. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 88:255–278
Mahrt L (2007) The influence of nonstationarity on the turbulent flux-gradient relationship for stable stratification. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 125:245–264
Mahrt L (2008) Bulk formulation of surface fluxes extended to weak-wind stable conditions. Q J R Meteorol Soc 134:1–10
Mahrt L (2009) Characteristics of submeso winds in the stable boundary layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 130:1–14
Mahrt L, Thomas C, Richardson S, Seaman N, Stauffer D, Zeeman M (2013) Non-stationary generation of weak turbulence for very stable and weak-wind conditions. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 147(2):179–199
Mahrt L, Sun J, Stauffer D (2015) Dependence of turbulent velocities on wind speed and stratification. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 155(1):55–71
Martins HS, Sá LD, Moraes OL (2013) Low level jets in the Pantanal wetland nocturnal boundary layer-case studies. Amer J Environ Eng 3(1):32–47
McNaughton K (2009) The rise and fall of Monin–Obukhov theory. AsiaFlux Newsletter 30:1–22
Monin AS, Obukhov AM (1954) Basic laws of turbulent mixing in the atmosphere near the ground. Trudy Geofiz Inst AN SSSR 24:163–187
Obukhov AM (1946) Turbulence in an atmosphere with a non-uniform temperature. Trudy Instituta Teoreticheskio Geofiziki AN SSSR 1:95–115
Ostrovsky L, Troitskaya YI (1987) A model of turbulent transfer and dynamics of turbulence in a stratified shear-flow. Izvestiya Akademii Nauk SSSR Fizika Atmosfery I Okeana 23(10):1031–1040
Peña A, Gryning SE, Mann J (2010) On the length-scale of the wind profile. Q J R Meteorol Soc 136:2119–2131
Poulos GS, Blumen W, Fritts DC, Lundquist JK, Sun J, Burns SP, Nappo C, Banta R, Newsom R, Cuxart J, Terradellas E, Balsley B, Jensen M (2002) CASES-99—a comprehensive investigation of the stable nocturnal boundary layer. Bull Amer Meteor Soc 83:555–581
Prandtl L (1925) Report on investigation of developed turbulence. Tech. rep, National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics, Technical Memorandum No 1231
Sanderse S, van der Pijl SP, Koren B (2011) Review of computational fluid dynamics for wind turbine wake aerodynamics. Wind Energy 14:799–819
Schmitt F (2007) About Boussinesq’s turbulent viscosity hypothesis: historical remarks and a direct evaluation of its validity. Comptes Rendus Mecanique 335(9/10):617–627
Starr VP (1968) Physics of negative viscosity phenomena. McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York
Stull RB (1984) Transilient turbulence theory. Part I: the concept of eddy-mixing across finite distances. J Atmos Sci 41(23):3351–3367
Sun J, Esbensen SK, Mahrt L (1995) Estimation of surface heat flux. J Atmos Sci 52(17):3162–3171
Sun J, Burns SP, Lenschow DH, Banta R, Newsom R, Coulter R, Frasier S, Ince T, Nappo C, Cuxart J, Blumen W, Lee X, Hu XZ (2002) Intermittent turbulence associated with a density current passage in the stable boundary layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 105:199–219
Sun J, Burns SP, Delany AC, Oncley SP, Horst TW, Lenschow DH (2003) Heat balance in nocturnal boundary layers during CASES-99. J Appl Meteorol 42:1649–1666
Sun J (2007) Tilt corrections over complex terrain and their implication for CO\(_2\) transport. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 124:143–159
Sun J (2011) Vertical variations of the mixing lengths during CASES-99. J Appl Meteor Clim 50:2030–2041
Sun J, Mahrt L, Banta RM, Pichugina YL (2012) Turbulence regimes and turbulence intermittency in the stable boundary layer during CASES-99. J Atmos Sci 69:338–351
Sun J, Lenschow DH, Mahrt L, Nappo C (2013) The relationships among wind, horizontal pressure gradient, and turbulent momentum transport during CASES-99. J Atmos Sci 70:3397–3414
Sun J, Mahrt L, Nappo C, Lenschow DH (2015) Wind and temperature oscillations generated by wave-turbulence interactions in the stably stratified boundary layer. J Atmos Sci 72:1484–1503
Sun J, Mahrt L (1995) Determination of surface fluxes from the surface radiative temperature. J Atmos Sci 52(8):1096–1106
Sun J, Massman W (1999) Ozone transport during the California ozone deposition experiment. J Geophys Res 104(D10):11,939–11,948
Tennekes H, Lumley HL (1972) A first course in turbulence. The MIT Press, Cambridge
van de Wiel B, Moene A, Steeneveld G, Hartogensis O, Holtslag A (2007) Predicting the collapse of turbulence in stably stratified boundary layers. Flow Turbul Combust 79(3):251–274
van de Wiel BJH, Moene AF, Jonker HJJ, Baas P, Basu S, Donda JMM, Sun J, Holtslag AAM (2012) The minimum wind speed for sustainable turbulence in the nocturnal boundary layer. J Atmos Sci 69:3116–3127
Von Kármán T (1930) Mechanische Ähnlichkeit und turbulenz (Mechanical Similarity and Turbulence). Nachr Ges Wiss Göttingen Math Phys Klasse
Wilczak JM, Oncley SP, Stage SA (2001) Sonic anemometer tilt correction algorithms. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 99(1):127–150
Williams A, Hacker J (1992) The composite shape and structure of coherent eddies in the convective boundary layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 61(3):213–245
Zilitinkevich SS (1995) Non-local turbulent transport: pollution dispersion aspects of coherent structure of convective flows. WIT Trans Ecol Environ 6:53–60
Zilitinkevich SS, Hunt J, Esau IN, Grachev A, Lalas D, Akylas E, Tombrou M, Fairall C, Fernando H, Baklanov A et al (2006) The influence of large convective eddies on the surface-layer turbulence. Q J R Meteorol Soc 132(618):1426–1456
Zilitinkevich SS, Elperin T, Kleeorin N, Rogachevskii I (2007) Energy- and flux-budget (EFB) turbulence closure model for stably stratified flows. Part I: steady-state, homogeneous regimes. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 125:167–191
Acknowledgments
The authors thank three anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments, and acknowledge the field support from the Earth Observing Laboratory of the National Center for Atmospheric Research. Larry Mahrt received support from Grant AGS-1115011 from the National Science Foundation. The University Corporation for Atmospheric Research manages the National Center for Atmospheric Research under sponsorship by the National Science Foundation. Any opinions, findings and conclusions, or recommendations expressed in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, J., Lenschow, D.H., LeMone, M.A. et al. The Role of Large-Coherent-Eddy Transport in the Atmospheric Surface Layer Based on CASES-99 Observations. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 160, 83–111 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-016-0134-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-016-0134-0