Abstract
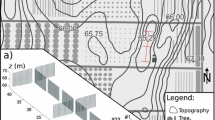
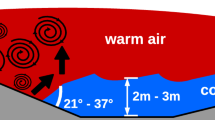
We present a novel approach based on fibre-optic distributed temperature sensing (DTS) to measure the two-dimensional thermal structure of the surface layer at high resolution (0.25 m, ≈0.5 Hz). Air temperature observations obtained from a vertically-oriented fibre-optics array of approximate dimensions 8 m × 8 m and sonic anemometer data from two levels were collected over a short grass field located in the flat bottom of a wide valley with moderate surface heterogeneity. The objectives of the study were to evaluate the potential of the DTS technique to study small-scale processes in the surface layer over a wide range of atmospheric stability, and to analyze the space–time dynamics of transient cold-air pools in the calm boundary layer. The time response and precision of the fibre-based temperatures were adequate to resolve individual sub-metre sized turbulent and non-turbulent structures, of time scales of seconds, in the convective, neutral, and stable surface layer. Meaningful sensible heat fluxes were computed using the eddy-covariance technique when combined with vertical wind observations. We present a framework that determines the optimal environmental conditions for applying the fibre-optics technique in the surface layer and identifies areas for potentially significant improvements of the DTS performance. The top of the transient cold-air pool was highly non-stationary indicating a superposition of perturbations of different time and length scales. Vertical eddy scales in the strongly stratified transient cold-air pool derived from the DTS data agreed well with the buoyancy length scale computed using the vertical velocity variance and the Brunt–Vaisala frequency, while scales for weak stratification disagreed. The high-resolution DTS technique opens a new window into spatially sampling geophysical fluid flows including turbulent energy exchange.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Anfossi D, Oettl D, Degrazia G, Goulart A (2005) An analysis of sonic anemometer observations in low wind speed conditions. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 114(1): 179–203
Bejan A (2004) Convection heat transfer, 3rd edn. Wiley, Hoboken, p 694
Belusic D, Mahrt L (2008) Estimation of length scales from mesoscale networks. Tellus Ser A Dyn Meteorol Oceanogr 60(4): 706–715. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0870.2008.00328.x
Bergström H, Högström U (1989) Turbulent exchange above a pine forest. II. Organized structures. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 49: 231–263
Bohrer G, Katul GG, Walko RL, Avissar R (2009) Exploring the effects of microscale structural heterogeneity of forest canopies using large-eddy simulations. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 132(3): 351–382. doi:10.1007/s10546-009-9404-4
Brost RA, Wyngaard JC (1978) Model study of stably stratified planetary boundary-layer. J Atmos Sci 35(8): 1427–1440
Fritts DC, Goldstein D, Lund T (2010) High-resolution numerical studies of stable boundary layer flows in a closed basin: evolution of steady and oscillatory flows in an axisymmetric Arizona Meteor Crater. J Geophys Res Atmos 115. doi:10.1029/2009jd013359
Howell JF, Mahrt L (1997) Multiresolution flux decomposition. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 83: 117–137
Keller CA, Huwald H, Vollmer MK, Wenger A, Hill M, Parlange MB, Reimann S (2011) Fiber optic distributed temperature sensing for the determination of the nocturnal atmospheric boundary layer height. Atmos Meas Tech 4(2): 143–149. doi:10.5194/amt-4-143-2011
King L (1914) On the convection of heat from small cylinders in a stream of fluid: determination of the convection constants of small platinum wires, with applications to hot-wire anemometry. Philos Trans Roy Soc Lond Ser A 214: 373–432
Lundquist JD, Pepin N, Rochford C (2008) Automated algorithm for mapping regions of cold-air pooling in complex terrain. J Geophys Res-Atmos 113, doi:10.1029/2008jd009879
Mahrt L (2008) Mesoscale wind direction shifts in the stable boundary-layer. Tellus A 60(4): 700–705. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0870.2008.00324.x
Mahrt L, Thomas C, Prueger J (2009) Space–time structure of mesoscale modes in the stable boundary layer. Q J Roy Meteorol Soc 135: 67–75
Mahrt L, Richardson S, Seaman N, Stauffer D (2010) Non-stationary drainage flows and motions in the cold pool. Tellus Ser A Dyn Meteorol Oceanogr 62(5): 698–705. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0870.2010.00473.x
Petrides A, Huff J, Arik A, Van de Giesen N, Kennedy A, Thomas C, Selker JS (2011) Shade estimation over streams using distributed temperature sensing. Water Resour Res 47: W07,601. doi:10.1029/2010WR009482
Pypker TG, Unsworth MH, Lamb B, Allwine E, Edburg S, Sulzman E, Mix AC, Bond BJ (2007) Cold air drainage in a forested valley: Investigating the feasibility of monitoring ecosystem metabolism. Agric For Meteorol 145(3–4): 149–166. doi:10.1016/j.agrfomret.2007.04.016
Selker J, van de Giesen N, Westhoff M, Luxemburg W, Parlange MB (2006a) Fiber optics opens window on stream dynamics. Geophys Res Lett 33(24). doi:10.1029/2006gl027979
Selker JS, Thevenaz L, Huwald H, Mallet A, Luxemburg W, de Giesen NV, Stejskal M, Zeman J, Westhoff M, Parlange MB (2006b) Distributed fiber-optic temperature sensing for hydrologic systems. Water Resourc Res 42(12). doi:10.1029/2006wr005326
Shaw RH, Schumann U (1992) Large-eddy simulation of turbulent-flow above and within a forest. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 61(1–2): 47–64
Sheridan P, Smith S, Brown A, Vosper S (2010) A simple height-based correction for temperature downscaling in complex terrain. Meteorol Appl 17(3): 329–339. doi:10.1002/met.177
Smedman AS, Bergstrom H, Hogstrom U (1995) Spectra, variances and length scales in a marine stable boundary layer dominated by a low level jet. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 76(3): 211–232
Smith SA, Brown AR, Vosper SB, Murkin PA, Veal AT (2010) Observations and simulations of cold air pooling in valleys. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 134(1): 85–108. doi:10.1007/s10546-009-9436-9
Sorbjan Z, Balsley BB (2008) Microstructure of turbulence in the stably stratified boundary layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 129(2): 191–210. doi:10.1007/s10546-008-9310-1
Sun JL, Burns SP, Lenschow DH, Banta R, Newsom R, Coulter R, Frasier S, Ince T, Nappo C, Cuxart J, Blumen W, Lee X, Hu XZ (2002) Intermittent turbulence associated with a density current passage in the stable boundary layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 105(2): 199–219
Sun JL, Lenschow DH, Burns SP, Banta RM, Newsom RK, Coulter R, Frasier S, Ince T, Nappo C, Balsley BB, Jensen M, Mahrt L, Miller D, Skelly B (2004) Atmospheric disturbances that generate intermittent turbulence in nocturnal boundary layers. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 110(2): 255–279
Taylor G (1938) The spectrum of turbulence. Proc R Soc Lond A 164: 476–490. doi:10.1098/rspa.1938.0032
Thomas C (2011) Variability of subcanopy flow, temperature, and horizontal advection in moderately complex terrain. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 139: 61–81. doi:10.1007/s10546-010-9578-9
Thomas C, Foken T (2005) Detection of long-term coherent exchange over spruce forest using wavelet analysis. Theor Appl Climatol 80: 91–104
Thorpe SA (1977) Turbulence and mixing in a Scottish loch. Philos Trans Roy Soc Lond A 286(1334): 125–181
Tyler SW, Burak SA, McNamara JP, Lamontagne A, Selker JS, Dozier J (2008) Spatially distributed temperatures at the base of two mountain snowpacks measured with fiber-optic sensors. J Glaciol 54(187): 673–679
Tyler SW, Selker JS, Hausner MB, Hatch CE, Torgersen T, Thodal CE, Schladow SG (2009) Environmental temperature sensing using raman spectra DTS fiber-optic methods. Water Resour Res 45:W00D23 doi:10.1029/2008wr007052
Westhoff MC, Savenije HHG, Luxemburg WMJ, Stelling GS, van de Giesen NC, Selker JS, Pfister L, Uhlenbrook S (2007) A distributed stream temperature model using high resolution temperature observations. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 11(4): 1469–1480
Whiteman CD, Zhong SY (2008) Downslope flows on a low-angle slope and their interactions with valley inversions. Part I: Observations. J Appl Meteorol Climatol 47(7): 2023–2038. doi:10.1175/2007jamc1669.1
Whiteman CD, Zhong S, Shaw WJ, Hubbe JM, Bian X, Mittelstadt J (2001) Cold pools in the Columbia basin. Wea Forecast 16(4): 432–447
Zhong SY, Whiteman CD, Bian XD, Shaw WJ, Hubbe JM (2001) Meterological processes affecting the evolution of a wintertime cold air pool in the Columbia basin. Mon Weather Rev 129(10): 2600–2613
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thomas, C.K., Kennedy, A.M., Selker, J.S. et al. High-Resolution Fibre-Optic Temperature Sensing: A New Tool to Study the Two-Dimensional Structure of Atmospheric Surface-Layer Flow. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 142, 177–192 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-011-9672-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-011-9672-7