Abstract
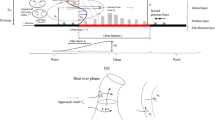
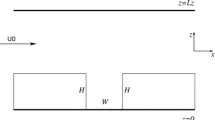
The turbulent exchange of momentum between a two-dimensional cavity and the overlying boundary layer has been studied experimentally, using hot-wire anemometry and particle image velocimetry (PIV). Conditions within the boundary layer were varied by changing the width of the canyons upstream of the test canyon, whilst maintaining the square geometry of the test canyon. The results show that turbulent transfer is due to the coupling between the instabilities generated in the shear layer above the canyons and the turbulent structures in the oncoming boundary layer. As a result, there is no single, unique velocity scale that correctly characterizes all the processes involved in the turbulent exchange of momentum across the boundary layer. Similarly, there is no single velocity scale that can characterize the different properties of the turbulent flow within the canyon, which depends strongly on the way in which turbulence from the outer flow is entrained into the cavity and carried round by the mean flow. The results from this study will be useful in developing simple parametrizations for momentum exchange in the urban canopy, in situations where the street geometry consists principally of relatively long, uniform streets arranged in grid-like patterns; they are unlikely to be applicable to sparse geometries composed of isolated three-dimensional obstacles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bearman P (1972) Some measurements of the distortion of turbulence approaching a two-dimensional bluff body. J Fluid Mech 53(3): 451–467
Belcher SE (2005) Mixing and transport in urban areas. Philos Trans Roy Soc 363: 2947–2963
Castelain T (2006) Contrôle de jet par microjets impactants. Ph.D. thesis, Ecole Centrale de Lyon, 173 pp
Caton F, Britter R, Dalziel S (2003) Dispersion mechanism in a street canyon. Atmos Environ 37: 693–702
Coceal O, Belcher SE (2004) A canopy model of mean winds through urban areas. Q J Roy Meteorol Soc 130: 1349–1372
Coceal O, Thomas TG, Castro IP, Belcher SE (2006) Mean flow and turbulence statistics over groups of urban-like obstacles. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 121: 491–519
Coceal O, Dobre A, Thomas TG (2007) Unsteady dynamics and organized structures from DNS over an idealized building canopy. Int J Climatol 27: 1943–1953
Finnigan JJ (1985) Turbulent transport in flexible plant canopies. In: Hutchinson B, Hicks B (eds) The forest–atmosphere interaction. D. Reidel Publishing Co., Dordrecht, pp 443–480
Finnigan JJ (2000) Turbulence in plant canopies. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 32: 519–572
Fouras A, Soria J (1998) Accuracy of out-of-plane vorticity measurements derived from in-plane velocity field data. Exp Fluids 25: 409–430
Garbero V, Salizzoni P, Soulhac L (2010) Experimental study of pollutant dispersion within a network of streets. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 136: 457–487
Grimmond CSB, Oke TR (1999) Aerodynamic properties of urban areas derived from analysis of surface form. J Appl Meteorol 38: 1262–1292
Hamlyn D, Hilderman T, Britter R (2007) A simple network approach to modelling dispersion among large groups of obstacles. Atmos Environ 41(28): 5848–5862
Harman IN, Belcher SE (2006) The surface energy balance and boundary layer over urban street canyons. Q J Roy Meteorol Soc 132: 2749–2768
Hunt J, Kawai H, Ramsay S, Pedrizetti G, Perkins R (1990) A review of velocity and pressure fluctuations in turbulent flows around bluff bodies. J Wind Eng Ind Aerodyn 35: 49–85
Huq P, Carrillo A, White LA, Redondo J, Dharmavaram S, Hanna SR (2007) The shear layer above and in urban canopies. J Appl Meteorol Climatol 46: 368–376
Irwin HP (1981) The design of spires for wind simulation. J Wind Eng Ind Aerodyn 7: 361–366
Jimènez J (2004) Turbulent flows over rough wall. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 36: 96–173
Kaimal J, Finnigan J (1994) Atmospheric boundary layer flow. Oxford University Press, New York, p 289
Kim J, Baik J (2003) Effects of inflow turbulence intensity on flow and pollutant dispersion in an urban street canyon. J Wind Eng Ind Aerodyn 91: 309–329
Leonardi S, Orlandi P, Antonia R (2007) Properties of d- and k-type roughness in a turbulent channel. Phys Fluids 19: 125101
Louka P, Belcher SE, Harrison RG (2000) Coupling between air flow in streets and the well-developed boundary-layer aloft. Atmos Environ 34(16): 2613–2622
Perry A, Shofield WH, Joubert PN (1969) Rough wall turbulent boundary layers. J Fluid Mech 37: 383–413
Poggi D, Katul GC (2007) Turbulent flows on forested hilly terrain: the recirculation region. Q J Roy Meteorol Soc 133: 1027–1039
Raupach MR, Antonia R, Rajagopalan S (1991) Rough-wall turbulent boundary layers. Appl Mech Rev 44(1): 1–25
Salizzoni P, Soulhac L, Mejean P, Perkins R (2008) Influence of a two scale surface roughness on a turbulent boundary layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 127(1): 97–110
Salizzoni P, Soulhac L, Mejean P (2009a) Street canyon ventilation and atmospheric turbulence. Atmos Environ 43: 5056–5067
Salizzoni P, Van Liefferinge R, Soulhac L, Mejean P, Perkins RJ (2009b) Influence of wall roughness on the dispersion of a passive scalar in a turbulent boundary layer. Atmos Environ 43(3): 734–748
Salizzoni P, Van Liefferinge R, Mejean P, Soulhac L, Perkins RJ (2010) Scaling of the vertical spreading of a plume of a passive tracer in a rough-wall neutral boundary-layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 135: 455–467
Simoëns S, Ayrault M, Wallace JM (2007) The flow across a street canyon with variable width—part 1: kinematic description. Atmos Environ 41: 9002–9017
Soulhac L (2000) Modélisation de la dispersion atmosphérique à l’intérieur de la canopée urbaine. Ph.D. thesis, Ecole Centrale de Lyon, 345 pp
Soulhac L, Puel C, Duclaux O, Perkins R (2003) Simulations of atmospheric pollution in Greater Lyon an example of the use of nested models. Atmos Environ 37: 5147–5156
Soulhac L, Perkins R, Salizzoni P (2008) Flow in a street canyon for any external wind direction. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 126: 365–388
Soulhac L, Garbero V, Salizzoni P, Mejean P, Perkins R (2009) Flow and dispersion in street intersections. Atmos Environ 43: 2981–2996
Stanislas M, Carlier J, Foucaut J, Dupont P (1998) Experimental study of a high Reynolds number turbulent boundary layer using DPIV. In: 9th International symposium on application of laser technology to fluid mechanics, Lisbon, Portugal
Townsend AA (1976) The structure of turbulent shear flows. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p 444
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salizzoni, P., Marro, M., Soulhac, L. et al. Turbulent Transfer Between Street Canyons and the Overlying Atmospheric Boundary Layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 141, 393–414 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-011-9641-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-011-9641-1