Abstract
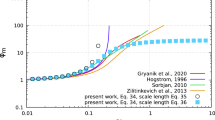
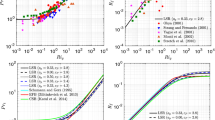
We investigate the scaling behaviour of a turbulent kinetic energy (TKE) closure model for stably stratified conditions. The mixing length scale for stable stratification is proportional to the ratio of the square root of the TKE and the local Brunt–Väisälä frequency, which is a commonly applied formulation. We analyze the scaling behaviour of our model in terms of traditional Monin–Obukov Similarity Theory and local scaling. From the model equations, we derive expressions for the stable limit behaviour of the flux–gradient relations and other scaling quantities. It turns out that the scaling behaviour depends on only a few model parameters and that the results obey local scaling theory. The analytical findings are illustrated with model simulations for the second GABLS intercomparison study. We also investigate solutions for the case in which an empirical correction function is used to express the eddy diffusivity for momentum as a function of the Richardson number (i.e. an increasing turbulent Prandtl number with stability). In this case, it seems that for certain parameter combinations the model cannot generate a steady-state solution. At the same time, its scaling behaviour becomes unrealistic. This shows that the inclusion of empirical correction functions may have large and undesired consequences for the model behaviour.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
André JC, Mahrt L (1982) The nocturnal surface inversion and influence of clear-air radiative cooling. J Atmos Sci 39: 864–878
Andreas EL (2002) Parameterizing scalar transfer over snow and ice: a review. J Hydrometeorol 3: 417–432
Baas P, Steeneveld GJ, van de Wiel BJH, Holtslag AAM (2006) Exploring self-correlation in flux–gradient relationships for stably stratified conditions. J Atmos Sci 63: 3045–3054
Basu S, Begum ZN, Rajagopal EN (1998) Impact of boundary-layer parameterization schemes on the prediction of the Asian summer monsoon. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 86: 469–485
Basu S, Porté-Agel F, Foufoula-Georgiou E, Vinuesa JF, Pahlow M (2006) Revisiting the local scaling hypothesis in stably stratified atmospheric boundary-layer turbulence: an integration of field and laboratory measurements with large-eddy simulations. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 119: 473–500
Beljaars ACM, Holtslag AAM (1991) Flux parameterization over land surfaces for atmospheric models. J Appl Meteorol 30: 327–341
Beljaars ACM, Viterbo P (1998) Role of the boundary layer in a numerical weather prediction model. In: Holtslag AAM, Duynkerke PG (eds) Clear and cloudy boundary layers. Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences, Amsterdam, pp 287–304
Bertin F, Barat J, Wilson R (1997) Energy dissipation rates, eddy-diffusivity, and the Prandtl number: an in situ experimental approach and its consequences on radar estimate of turbulent parameters. Radio Sci 32: 791–804
Bougeault P, Lacarrère P (1989) Parameterization of orography-induced turbulence in a mesobeta-scale model. Mon Wea Rev 117: 1872–1890
Brinkop S, Roeckner E (1995) Sensitivity of a general circulation model to parameterizations of cloud-turbulence interactions in the atmospheric boundary layer. Tellus 47A: 197–220
Businger JA, Wyngaard JC, Izumi Y, Bradley EF (1971) Flux profile relationships in the atmospheric surface layer. J Atmos Sci 28: 181–189
Canuto VM, Howard AM, Cheng Y, Dubovikov MS (2001) Ocean turbulence. Part I: one-point closure – momentum and heat vertical diffusivities. J Phys Oceanogr 31: 1413–1426
Cheinet S, Beljaars A, Köhler M, Morcrette JJ, Viterbo P (2005) Assessing physical processes in the ECMWF model forecasts using ARM SGP observations. In: ARM report series no. 1. ECMWF, U.K., 25 pp
Cheng Y, Canuto VM, Howard AM (2002) An improved model for the turbulent PBL. J Atmos Sci 59: 1550–1565
Cheng Y, Parlange MB, Brutsaert W (2005) Pathology of Monin–Obukhov similarity in the stable boundary layer. J Geophys Res 110: D06101
Chimonas C, Nappo CJ (1989) Wave drag in the planetary boundary layer over complex terrain. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 47: 217–232
Cuxart J, Bougeault P, Redelsperger JL (2000) A turbulence scheme allowing for mesoscale and large-eddy simulations. Quart J Roy Meteorol Soc 126: 1–30
Cuxart J, Morales G, Terradellas E, Yagüe C (2002) Study of coherent structures and estimation of the pressure transport terms for the nocturnal stable boundary layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 105: 305–328
Cuxart J, Holtslag AAM, Beare RJ, Bazile E, Beljaars A, Cheng A, Conangla L, Ek MB, Freedman F, Hamdi R, Kerstein A, Kitagawa H, Lenderink G, Lewellen D, Mailhot J, Mauritsen T, Perov V, Schayes G, Steeneveld GJ, Svensson G, Taylor P, Weng W, Wunsch S, Xu KM (2006) Single-column model intercomparison for a stably stratified atmospheric boundary layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 118: 273–303
Deardorff JW (1980) Stratocumulus-capped mixed layers derived from a three-dimensional model. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 18: 495–527
Duynkerke PG (1991) Radiation fog: a comparison of model simulations with detailed observations. Mon Wea Rev 119: 324–341
Duynkerke PG, de Roode SR (2001) Surface energy balance and turbulence characteristics observed at the SHEBA ice camp during FIRE III. J Geophys Res 106: 15313–15322
Dyer AJ (1974) A review of flux-profile relationships. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 7: 363–372
Högström U (1988) Nondimensional wind and temperature profiles in the atmospheric boundary layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 42: 55–78
Holtslag AAM (1998) Modelling of atmospheric boundary layers. In: Holtslag AAM, Duynkerke PG (eds) Clear and cloudy boundary layers. Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences, Amsterdam, pp 287–304
Holtslag AAM (2006) GEWEX atmospheric boundary layer study (GABLS) on stable boundary layers. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 118: 85–110
Howell JF, Sun J (1999) Surface-layer fluxes in stable conditions. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 90: 495–520
Jones CG, Lenderink G, Ivarsson LI (2003) Representing subgrid scale mixing under stable conditions: importance for overall model synoptic development. Hirlam Newslett 43: 125–134
Kim J, Mahrt L (1992) Simple formulation of mixing in the stable free atmosphere and nocturnal boundary layer. Tellus 44A: 381–394
Kondo J, Kanechika O, Yasuda N (1978) Heat and momentum transfer under strong stability in the atmospheric surface layer. J Atmos Sci 35: 1012–1021
Lenderink G, Holtslag AAM (2000) Evaluation of the kinetic energy approach for modeling turbulent fluxes in stratocumulus. Mon Wea Rev 128: 244–258
Lenderink G, Holtslag AAM (2004) An updated length scale formulation for turbulent mixing in clear and cloudy boundary layers. Quart J Roy Meteorol Soc 130: 3405–3427
Lenderink G, van den Hurk B, van Meijgaard E, van Ulden A, Cuijpers H (2003) Simulation of present-day climate in RACMO2: first results and model development. In: TR-252. KNMI, The Netherlands, 24 pp
Lenderink G, Siebesma AP, Cheinet S, Irons S, Jones CG, Marquet P, Mueller F, Olmeda D, Calvo J, Sanchez E, Soares PMM (2004) The diurnal cycle of shallow cumulus clouds over land: A single column model intercomparison study. Quart J Roy Meteorol Soc 130: 3339–3364
Lock A, Mailhot J (2006) Combining non-local scalings with a TKE closure for mixing in boundary layer clouds. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 121: 313–338
Louis JF, Tiedtke M, Geleyn JF (1982) A short history of the PBL parameterization at ECMWF. In: Workshop on boundary layer parameterization. ECMWF, UK, pp 59–79
Mahrt L (1987) Grid-averaged surface fluxes. Mon Wea Rev 115: 1550–1560
Mahrt L (2007) The influence of nonstationarity on the turbulent flux-gradient relationship for stable stratification. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 125: 245–264
Mahrt L, Sun J, Blumen W, Delany W, Oncley S (1998) Nocturnal boundary layer regimes. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 88: 255–278
Mailot J, Benoit R (1982) A finite-element model of the atmospheric boundary layer suitable for use with numerical weather prediction models. J Atmos Sci 39: 2249–2266
Mauritsen T, Svensson G (2007) Observations of stably stratified shear-driven atmospheric turbulence at low and high Richardson numbers. J Atmos Sci 64: 645–655
McCabe A, Brown AR (2007) The role of surface heterogeneity in modeling the stable boundary layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 122: 517–534
Mellor GL, Yamada T (1974) A hierarchy of turbulence closure models for planetary boundary layers. J Atmos Sci 31: 1791–1806
Nieuwstadt FTM (1984) The turbulent structure of the stable, nocturnal boundary layer. J Atmos Sci 41: 2202–2216
Poulos GS, Blumen W, Fritts DC, Lundquist JK, Sun J, Burns SP, Nappo C, Banta R, Newsom R, Cuxart J, Terradellas E, Balsley B, Jensen M (2002) CASES-99: a comprehensive investigation of the stable nocturnal boundary layer. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 83: 555–581
Schumann U, Gerz T (1995) Turbulent mixing in stably stratified shear flows. J Appl Meteorol 34: 33–48
Steeneveld GJ, van de Wiel BJH, Holtslag AAM (2006) Modeling the evolution of the atmospheric boundary layer for three contrasting nights in CASES-99. J Atmos Sci 63: 920–935
Steeneveld GJ, Mauritsen T, de Bruijn EIF, Vila-Guerau de Arellano J, Svensson G, Holtslag AAM (2007) Evaluation of limited area models for the representation of the diurnal cycle and contrasting nights in CASES99. J Appl Meteorol Clim (in press)
Stull RB (1988) An introduction to boundary layer meteorology. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, p 666
Svensson G, Holtslag AAM (2006) Single column modeling of the diurnal cycle based on CASES99 data – GABLS second intercomparison project. In: 17th symposium on boundary layers and turbulence, San Diego, CA, USA, 22–25 May 2006. Amer. Meteorol. Soc., Boston, p 8.1
Tijm ABC (2004) Tuning CBR. Hirlam Newslett 46: 18–28
Umlauf L, Burchard H (2005) Second-order turbulence closure models for geophysical boundary layers. A review of recent work. Cont Shelf Res 25: 795–827
Viterbo P, Beljaars ACM, Mahfouf JF, Teixeira J (1999) The representation of soil moisture freezing and its impact on the stable boundary layer. Quart J Roy Meteorol Soc 125: 2401–2426
Weng W, Taylor PA (2003) On modelling the one-dimensional atmospheric boundary layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 107: 371–400
Wyngaard JC, Coté OR (1974) The evolution of a convective planetary boundary layer – a higher-order-closure model study. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 7: 289–308
Zilitinkevich SS, Esau IN (2007) Similarity theory and calculation of turbulent fluxes at the surface for the stably stratified atmospheric boundary layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 125: 193–205
Zilitinkevich SS, Elperin T, Kleeorin N, Rogachevskii I (2007) Energy- and flux-budget (EFB) turbulence closure model for stably stratified flows. Part I: steady-state, homogeneous regimes. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 125: 167–191
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baas, P., de Roode, S.R. & Lenderink, G. The Scaling Behaviour of a Turbulent Kinetic Energy Closure Model for Stably Stratified Conditions. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 127, 17–36 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-007-9253-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-007-9253-y