Abstract
Background
Alpha-mannosidosis (OMIM 248500) is a rare lysosomal storage disease (LSD) caused by alpha-mannosidase deficiency. Manifestations include intellectual disabilities, facial characteristics and hearing impairment. A recombinant human alpha-mannosidase (rhLAMAN) has been developed for weekly intravenous enzyme replacement therapy (ERT). We present the preliminary data after 12 months of treatment.
Methods
This is a phase I-II study to evaluate safety and efficacy of rhLAMAN. Ten patients (7–17 y) were treated. We investigated efficacy by testing motor function (6-minutes-Walk-Test (6-MWT), 3-min-Stair-Climb-Test (3-MSCT), The Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency (BOT2), cognitive function (Leiter-R), oligosaccharides in serum, urine and CSF and Tau- and GFA-protein in CSF.
Results
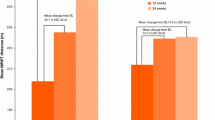
Oligosaccharides: S-, U- and CSF-oligosaccharides decreased 88.6 % (CI −92.0 −85.2, p < 0.001), 54.1 % (CI −69.5- −38.7, p < 0,001), and 25.7 % (CI −44.3- −7.1, p < 0.05), respectively. Biomarkers: CSF-Tau- and GFA-protein decreased 15 %, p < 0.009) and 32.5, p < 0.001 respectively. Motor function: Improvements in 3MSCT (31 steps (CI 6.8-40.5, p < 0.01) and in 6MWT (60.4 m (CI −8.9 −51.1, NS) were achieved. Cognitive function: Improvement in the total Equivalence Age of 4 months (0.34) was achieved in the Leiter R test (CI −0.2-0.8, NS).
Conclusions
These data suggest that rhLAMAN may be an encouraging new treatment for patients with alpha-mannosidosis.The study is designed to continue for a total of 18 months. Longer-term follow-up of patients in this study and the future placebo-controlled phase 3 trial are needed to provide greater support for the findings in this study.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
ATS committee on profiency standards for clinical pulmonary function laboratories (2002) ATS statement: guidelines for the six-minute walk test. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 166(1):111–117
Balfour-Lynn IM, Prasad SA, Laverty A, Whitehead BF, Dinwiddie R (1998) A step in the right direction: assessing exercise tolerance in cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol 25(4):278–284
Beydon N, Davis SD, Lombardi E et al (2007) An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: pulmonary function testing in preschool children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 175(12):1304–1345
Blanz J, Stroobants S, Lullmann-Rauch R et al (2008) Reversal of peripheral and central neural storage and ataxia after recombinant enzyme replacement therapy in alpha-mannosidosis mice. Hum Mol Genet 17(22):3437–3445
Blennow K, Wallin A, Agren H, Spenger C, Siegfried J, Vanmechelen E (1995) Tau protein in cerebrospinal fluid: a biochemical marker for axonal degeneration in Alzheimer disease? Mol Chem Neuropathol 26(3):231–245
Bolton JW, Weiman DS, Haynes JL, Hornung CA, Olsen GN, Almond CH (1987) Stair climbing as an indicator of pulmonary function. Chest 92(5):783–788
Buee L, Bussiere T, Buee-Scherrer V, Delacourte A, Hof PR (2000) Tau protein isoforms, phosphorylation and role in neurodegenerative disorders. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 33(1):95–130
Colletti L, Zoccante L (2008) Nonverbal cognitive abilities and auditory performance in children fitted with auditory brainstem implants: preliminary report. Laryngoscope 118(8):1443–1448
Crawley AC, Walkley SU (2007) Developmental analysis of CNS pathology in the lysosomal storage disease alpha-mannosidosis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 66(8):687–697
Crawley AC, Jones MZ, Bonning LE, Finnie JW, Hopwood JJ (1999) Alpha-mannosidosis in the guinea pig: a new animal model for lysosomal storage disorders. Pediatr Res 46(5):501–509
Deitz JC, Kartin D, Kopp K (2007) Review of the Bruininks-Oseretsky test of motor proficiency, second edition (BOT-2). Phys Occup Ther Pediatr 27(4):87–102
Eng CM, Banikazemi M, Gordon RE et al (2001a) A phase 1/2 clinical trial of enzyme replacement in fabry disease: pharmacokinetic, substrate clearance, and safety studies. Am J Hum Genet 68(3):711–722
Eng CM, Guffon N, Wilcox WR et al (2001b) Safety and efficacy of recombinant human alpha-galactosidase A–replacement therapy in Fabry’s disease. N Engl J Med 345(1):9–16
Giovannoni G, Nath A (2011) After the storm: neurofilament levels as a surrogate endpoint for neuroaxonal damage. Neurology 76(14):1200–1201
Grubb JH, Vogler C, Levy B, Galvin N, Tan Y, Sly WS (2008) Chemically modified beta-glucuronidase crosses blood–brain barrier and clears neuronal storage in murine mucopolysaccharidosis VII. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(7):2616–2621
Harmatz P, Giugliani R, Schwartz IV et al (2008) Long-term follow-up of endurance and safety outcomes during enzyme replacement therapy for mucopolysaccharidosis VI: Final results of three clinical studies of recombinant human N-acetylgalactosamine 4-sulfatase. Mol Genet Metab 94(4):469–475
Hessl D, Nguyen DV, Green C et al (2009) A solution to limitations of cognitive testing in children with intellectual disabilities: the case of fragile X syndrome. J Neurodev Disord 1(1):33–45
Holden DA, Rice TW, Stelmach K, Meeker DP (1992) Exercise testing, 6-min walk, and stair climb in the evaluation of patients at high risk for pulmonary resection. Chest 102(6):1774–1779
Malm D, Nilssen O (2008) Alpha-mannosidosis. Orphanet J Rare Dis doi:10.1186/1750-1172-3-21
Malm D, Nilssen O (2010) Alpha-Mannosidosis—GeneReviews—NCBI Bookshelf. University of Washington, Seattle
Malm D, Tollersrud OK, Tranebjaerg L, Mansson JE (1995) Alpha-mannosidosis. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen 115(5):594–597
Malm D, Pantel J, Linaker OM (2005) Psychiatric symptoms in alpha-mannosidosis. J Intellect Disabil Res 49(Pt 11):865–871
Mattsson N, Savman K, Osterlundh G, Blennow K, Zetterberg H (2010) Converging molecular pathways in human neural development and degeneration. Neurosci Res 66(3):330–332
Mattsson N, Portelius E, Rolstad S et al (2012) Longitudinal cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers over four years in mild cognitive impairment. J Alzheimers Dis 30(4):767–778
Meikle PJ, Hopwood JJ, Clague AE, Carey WF (1999) Prevalence of lysosomal storage disorders. JAMA 281(3):249–254
Mynarek M, Tolar J, Albert MH et al (2012) Allogeneic hematopoietic SCT for alpha-mannosidosis: an analysis of 17 patients. Bone Marrow Transplant 47(3):352–359
Myrelid A, Bergman S, Elfvik SM et al (2010) Late effects of early growth hormone treatment in Down syndrome. Acta Paediatr 99(5):763–769
Nilssen O, Berg T, Riise HM et al (1997) alpha-Mannosidosis: functional cloning of the lysosomal alpha-mannosidase cDNA and identification of a mutation in two affected siblings. Hum Mol Genet 6(5):717–726
Pastores GM (2008) Laronidase (Aldurazyme): enzyme replacement therapy for mucopolysaccharidosis type I. Expert Opin Biol Ther 8(7):1003–1009
Pastores GM, Boyd E, Crandall K, Whelan A, Piersall L, Barnett N (2007) Safety and pharmacokinetics of agalsidase alfa in patients with Fabry disease and end-stage renal disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 22(7):1920–1925
Roces DP, Lullmann-Rauch R, Peng J et al (2004) Efficacy of enzyme replacement therapy in alpha-mannosidosis mice: a preclinical animal study. Hum Mol Genet 13(18):1979–1988
Rosengren LE, Ahlsen G, Belfrage M, Gillberg C, Haglid KG, Hamberger A (1992) A sensitive ELISA for glial fibrillary acidic protein: application in CSF of children. J Neurosci Methods 44(2–3):113–119
Rosengren LE, Karlsson JE, Karlsson JO, Persson LI, Wikkelso C (1996) Patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and other neurodegenerative diseases have increased levels of neurofilament protein in CSF. J Neurochem 67(5):2013–2018
Salzer J, Svenningsson A, Sundstrom P (2010) Neurofilament light as a prognostic marker in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 16(3):287–292
Scarpa M, Bird T, Pagon R, Dolan C, Stephens K & Adam M (1993) Mucopolysaccharidosis type II. GeneReviews. University of Washington, Seattle
Thomas GH (2001) Disorder of glycoprotein degradation, the metabolic & molecular bases of inherited disease, 8th edn
Tsatsanis KD, Dartnall N, Cicchetti D, Sparrow SS, Klin A, Volkmar FR (2003) Concurrent validity and classification accuracy of the Leiter and Leiter-R in low-functioning children with autism. J Autism Dev Disord 33(1):23–30
Yoon DY, Scott K, Hill MN, Levitt NS, Lambert EV (2006) Review of three tests of motor proficiency in children. Percept Mot Skills 102(2):543–551
Zymenex A/S (2012) Investigator’s brochure for LAMAZYM, information for clinical investigators
Acknowledgments
We thank our study-site personnel Marianne Luiten, Sanni Mahncke, Kamille Fogh; Camilla Sørensen, Anne Sylvest Olsen, Kirsten Glarborg, Department of Clinical Genetics; Birgitte Hanel, Paediatric Pulmonary Service, Department of Paediatrics and Adolescent Medicine, Rigshospitalet, Denmark; Pia Ringholm and Susanne Rodholm, Lene Skammelsen Zymenex A/S, Hillerød, Denmark; Elisabeth Jameson, St. Mary’s hospital, Manchester, UK; Laila Arash, Yasmina Amraoui, Johannes Gutenberg University Hospital, Mainz, Germany; Dorthe Grønnegaard Mejer, Jesper Nelby Kristiansen, Maike Dideriksen, Larix A/S, Skovlunde, Denmark, EU-framework 7 program for supporting the ALPHA-MAN project economically.
Special thanks to the patients and families for their participation and dedicated efforts in the study.
Funding
The study is funded by the EU in the “ALPHA-MAN” project through a Framework 7 grant of 5,887,150 Euro for a period of 36 months. The entire grant covers both scientific programs and clinical programs. The clinical program of the funding covers all clinical trials (phases 1, 2a, 2b and 3) and all the support for the clinical trial such as transport of patients, monitoring of the trial procedures, data management and analysis etc.
Conflict of interest
Zymenex provides the investigational recombinant human enzyme Lamazym (rhLAMAN) for the clinical trials. The investigators or any other study-site personnel are not employed by Zymenex.
Dr. Line Borgwardt has received travel expenses for a scientific meeting by Zymenex. No other reimbursements/fees/funds/salaries have been accepted.
The authors; expect Fogh J who is employed at Zymenex; confirms independence from the sponsors; the content of the article has not been influenced by the sponsors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by:Maurizio Scarpa
EudraCT number: 2010-022084-36 and 2010-022085-26
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borgwardt, L., Dali, C.I., Fogh, J. et al. Enzyme replacement therapy for alpha-mannosidosis: 12 months follow-up of a single centre, randomised, multiple dose study. J Inherit Metab Dis 36, 1015–1024 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-013-9595-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-013-9595-1