Abstract
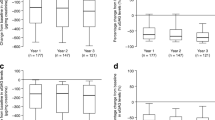
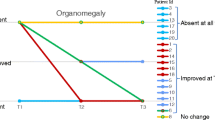
The current treatment of mucopolysaccharidosis type II (MPS II, Hunter syndrome) is enzyme replacement therapy with recombinant idursulfase (Elaprase®). The efficacy of ERT was established based primarily on reduction in urine glycosaminoglycans:creatinine (GAG:Cr) ratio and improvement in a composite score of predicted forced vital capacity (FVC% predicted) and 6-min walk-test distance (6MWT). We retrospectively reviewed these parameters in 11 boys with MPS II treated with idursulfase between April 2007 (or the time of diagnosis) and February 2010. Some results were inconsistent with published trial data, and there was only a small number of analyzable results obtained for the FVC% predicted and 6MWT. A major drawback was the high prevalence of neurological involvement and young age of patients in the study cohort compared with the clinical trials. This study emphasizes the limitations of the current tools utilized to monitor ERT efficacy and MPS II disease burden in clinical practice.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
ATS Committee on Proficiency Standards for Clinical Pulmonary Function Laboratories (2002) ATS statement: guideline for the six-minute walk test. Am J Resp Crit Care Med. 166;111-117
Bénichou B, Goyal S, Sung C, Norfleet AM, O'Brien F (2009) A retrospective analysis of the potential impact of IgG antibodies to agalsidase beta on efficacy during enzyme replacement therapy for Fabry disease. Mol Genet Metab 96:4–12
Byers S, Rozaklis T, Brumfield KL, Ranieri E, Hopwood J (1998) Glycosaminoglycan accumulation and excretion in the mucopolysaccharidosis: characterization and basis of diagnostic test for MPS. Mol Genet Metab 65:285–290
Christensen E (2008) Choosing the best endpoint. J Hepatol 49:e672–e673
Davison J, Hendriksz C, Sun Y, Davies N, Gissen P, Peet A (2010) Quantitative in vivo brain magnetic resonance spectroscopic monitoring of neurological involvement in mucopolysaccharidosis type II (Hunter Syndrome). J Inherit Metab Dis [Epub ahead of print]
Fan Z, Styner M, Muenzer J, Poe M, Escolar M (2010) Correlation of automated volumetric analysis of brain MR imaging with cognitive impairment in a natural history study of mucopolysaccharidosis II. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:1319–1323
Gallegos-Arreola MP, Machorro-Lazo MV, Flores-Martínez SE, Zúñiga-González GM, Figuera LE, González-Noriega A, Sánchez-Corona J (2000) Urinary glycosaminoglycan excretion in healthy subjects and in patients with mucopolysaccharidoses. Arch Med Res 31:505–510
Hassan J, van der Net J, Helders P, Prakken B, Takken T (2010) Six-minute walk test in children with chronic conditions. Br J Sports Med 44:270–274
International Conference on Harmonisation (1998) Harmonised tripartite guideline on statistical principles for clinical trials (E9) EMEA
Kirkby J, Welsh L, Lum S et al (2008) The EPICure study: comparison of school spirometry with that performed in the lung function laboratory. Pediatr Pulmonol 43:1233–1241
Lammers AE, Hislop AA, Flynn Y, Haworth SG (2008) The 6 minute walk test: normal values for children 4-11 years of age. Arch Dis Child 93:464–468
Mabe P, Valiente A, Soto V, Cornejo V, Raimann E (2004) Evalulation of reliability of urine mucopolysaccaridosis screening by dimethylmethylene blue and berry spot tests. Clin Chim Acta 345:135–140
Muenzer J, Wraith JE, Beck M, Giugliani R et al (2006) A Phase II/III clinical study of enzyme replacement therapy with idursulfase in mucopolysaccharidosis II (Hunter syndrome). Genet Med 8:465–473
Muenzer J, Gucsavas-Calikoglu M, McCandless SE, Schuetz TJ, Kimura A (2007) A Phase I/II clinical trial of enzyme replacement therapy in mucopolysaccharidosis II (Hunter syndrome). Mol Genet Metab 90:329–337
Rosenthal M, Bain SH, Cramer D et al (1993) Lung function in white children aged 4 to 19 years: I-Spirometry. Thorax 48:794–802
Wood M, Cleary M, Alderson L, Vellodi A (2009) Changes in gait pattern as assessed by the GAITRite walkway system in MPS II patients undergoing enzyme replacement therapy. J Inherit Metab Dis [Epub ahead of print]
Wraith JE, Beck M, Giugliani R, Clarke J, Martin R, Muenzer J, Investigators HOS (2008) Initial report from the Hunter Outcome Survey. Genet Med 10:508–516
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: Ed Wraith
Competing interest: None declared.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Glamuzina, E., Fettes, E., Bainbridge, K. et al. Treatment of mucopolysaccharidosis type II (Hunter syndrome) with idursulfase: the relevance of clinical trial end points. J Inherit Metab Dis 34, 749–754 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-011-9280-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-011-9280-1