Abstract
Valine is one of the three branched-chain amino acids which undergoes oxidation within mitochondria. In this paper, we describe the current state of knowledge with respect to the enzymology of the valine oxidation pathway and the different disorders affecting oxidation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
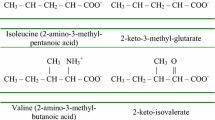
The three branched-chain amino acids (BCAA) leucine, isoleucine, and valine are neutral amino acids, each with a methyl-branch in the side chain. The human body is unable to synthesize these amino acids de novo which implies that the BCAAs are essential nutrients. Although they are present in all protein-containing foods, the most prominent sources are dairy products, red meat, whey and egg protein. Most diets provide adequate amounts of these amino acids amounting to 25–65 mg per kg body weight per day (Young and Pellett 1985; Zello et al 1995).
Amino acid homeostasis in the human body is fundamentally different as compared to carbohydrate and lipid homeostasis because carbohydrates can be stored in the form of polysaccharides notably glycogen and lipids as triglycerides. There is no separate storage form of amino acids except as present in endogenous proteins. As a consequence amino acid levels are the balanced result of (1) dietary intake in the form of free amino acids and proteins, (2) proteolysis of endogenous proteins, (3) de novo synthesis, and (4) degradation. Since BCAAs cannot be synthesized de novo, their homeostasis is maintained by degradation and dietary intake only. Since BCAAs can be degraded in multiple organs including skeletal muscle, liver, kidney, heart, brain and adipose tissue, they can be used as energy source, or utilized for biosynthetic purposes. This includes the synthesis of lipids, since all three catabolic pathways ultimately generate propionyl-CoA and/or acetyl-CoA.
In humans, the BCAAs are metabolized in the mitochondrion via the concerted action of a series of enzymes. The starting point is the transport of BCAAs via a sodium-dependent L-amino acid transporter across the plasma membrane into the cells. Once in the cytoplasm, the BCAAs can enter the mitochondrion in two ways. First, the BCAAs can be transaminated in the cytosol by the cytosolic branched-chain aminotransferase followed by the subsequent transport of the resulting 2-oxo-acids across the mitochondrial inner membrane via a specific transporter protein. Alternatively, the BCAAs can enter the mitochondrion as such via a neutral amino acid carrier protein, and are then converted into the different 2-oxo-acids by a mitochondrial aminotransferase. The contribution of the two different pathways has remained ill-defined until now and may differ between organs although the latter route appears to be preferred. Branched-chain 2-oxo-acids generated via either of these two pathways then undergo oxidative decarboxylation by the branched-chain 2-oxo-acid dehydrogenase complex (BCKADH) to form the different branched-chain acyl-CoA esters. This reaction is irreversible, similar to the pyruvate dehydrogenase and 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase reactions.
Following these common steps, the degradative pathways for each of the different BCAAs diverge and require the active participation of different enzymes which are specific for each of the BCAAs. Remarkably, the catabolic pathways of leucine, valine, and isoleucine show analogy to the fatty acid oxidation pathway, especially in the case of isoleucine which is degraded via a 4-step mechanism involving subsequent steps of dehydrogenation (via SBCAD), hydration (via crotonase), a second step of dehydrogenation catalyzed by the enzyme 3-hydroxy-2-methylbutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase, alternatively named SCHMAD, MHBD, or ERAB, as encoded by the HSD17B10 gene, and finally, thiolytic cleavage via the K+-dependent 2-methylacetoacetyl-CoA specific thiolase. Oxidation of the isovaleryl-CoA derived from leucine is completely different from that of the beta-oxidation of acyl-CoAs except that the first step involves the dehydrogenation of the substrate isovaleryl-CoA to 3-methylcrotonyl-CoA via one of the acyl-CoA dehydrogenases (ACADs) named isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase (IVD).
The catabolic route of valine has remained enigmatic not least because only a few defects in the pathway have been described. One of the reasons for doubt remaining about the true structure of the valine oxidation pathway is that part of the pathway between 3-hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA and propionyl-CoA has been claimed to proceed via free acids, thus requiring the participation of a specific hydrolase. Support for the involvement of such a hydrolase has come from work of Brown et al 1982) who identified a patient with 3-hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA hydrolase deficiency. Definitive proof that the presumed valine oxidation pathway (Fig. 1) is indeed correct has come from our own work (Loupatty et al 2007) on the identification of 3-hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA hydrolase deficiency in another patient, followed by the resolution of the molecular defect in this newly identified patient and the patient described by Brown et al (1982). Furthermore, we recently identified the first patient with 3-hydroxyisobutyric acid dehydrogenase deficiency (unpublished observations) which provides final proof that the valine degradation pathway as depicted in Fig. 1, is indeed correct.
In this paper, an update is given on the enzymology of the valine degradation pathway and the human disorders of valine degradation.
Enzymology of the valine degradation pathway
Isobutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase. Protein: IBD; Gene: ACAD8
Systematic studies by Tanaka and coworkers in the 1980s using rat liver mitochondria as starting material have led to the identification and purification of a new 2-methyl branched-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, which turned out to be reactive with both 2-methylbutyryl-CoA and isobutyryl-CoA, which are intermediates in the isoleucine and valine degradation pathways, respectively (Ikeda and Tanaka 1983a, b; Ikeda et al 1983). These data suggested the involvement of a single enzyme in the valine and isoleucine degradation pathways. More recently, the rat and human cDNAs for this enzyme have been cloned and the gene named short-branched-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (ACADSB). Recombinant rat SBCAD as produced in E.coli turned out to be reactive with both isobutyryl-CoA and 2-methylbutyryl-CoA in agreement with the results obtained with the native enzyme isolated from rat liver mitochondria by Ikeda and Tanaka (1983a). Surprisingly, however, the recombinant human enzyme was only reactive with 2-methylbutyryl-CoA and displayed little if any activity with isobutyryl-CoA. These data suggested that, at least in the human, distinct enzymes are involved in the oxidation of 2-methylbutyryl-CoA and isobutyryl-CoA, respectively. Conclusive evidence for this notion has come from the identification of patients with isolated deficiencies of 2-methylbutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase and isobutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase, respectively. Isolated 2-methylbutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency was first reported by Gibson et al (2000), followed by the resolution of the molecular defect by Andresen et al (2000) whereas isolated isobutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency was first reported in 1998 by Roe et al (1998a). Elaborating on work by Telford et al (1999), which had led to the identification of a novel cDNA coding for a new member of the ACAD-family (ACAD8), Nguyen et al (2002) expressed the ACAD8 cDNA in E.coli and established that the human recombinant enzyme had highest activity with isobutyryl-CoA (Km = 2.6 μmol/L; kcat = 2.0 ± 0.14) although (S)-2-methylbutyryl-CoA also turned out to be a relatively good substrate (Km = 18 μmol/L; kcat = 4.1 ± 0.3).
Methacrylyl-CoA hydratase
The next step in the valine degradation pathway involves the hydration of methacrylyl-CoA to 3-hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA. Although methacrylyl-CoA can apparently undergo non-enzymatic hydration to 3-hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA (Bachhawat et al 1957; Redina and Coon 1957) in aqueous solution, the generally accepted idea is that under in vivo conditions at least, the hydration of methacrylyl-CoA occurs enzymatically. Early work had already shown that the enzyme short-chain enoyl-CoA hydratase as isolated from bovine liver, which is also named crotonase (gene : ECHS1) can hydrate methacrylyl-CoA to 3-hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA (Jr and Del 1956; Steinman and Hill 1975). Studies in human liver sonicates have shown that hydration of methacrylyl-CoA occurs at a 15-fold lower rate compared with crotonyl-CoA as substrate (Brown et al 1982).
3-Hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA hydrolase (HIBCH)
Originally, it seemed paradoxical that an acyl-CoA hydrolase should be required for the degradation of valine especially since both the proximal as well as distal parts of the pathway involve coenzyme A ester intermediates. Redina and Coon (1957), however, identified an enzyme in pig heart converting 3-hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA (HIBYL-CoA) to 3-hydroxyisobutyric acid, and partially purified the enzyme. Many years later, Shimomura et al (1994) reported the purification of the enzyme from rat liver to homogeneity. The purified hydrolase had a molecular weight of 36 kDa and appeared to be a monomer. The enzyme turned out to have a very limited substrate preference only accepting 3-hydroxypropionyl-CoA as alternative substrate at 57% of the rate compared to HIBYL-CoA. The availability of the purified rat liver enzyme allowed cloning of the human enzyme. The human enzyme is made up of 352 amino acids with a 28-amino-acid mitochondrial leader sequence, reacts with S-3-hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA and 3-hydroxypropionyl-CoA with virtually no reactivity towards other acyl-CoAs, and is expressed in multiple tissues as established by immunoblot analysis. The tissue distribution is: liver = kidney > heart >> muscle = brain.
3-Hydroxyisobutyric acid dehydrogenase (HIBADH)
Robinson and Coon were the first to isolate and characterize a 3-hydroxyisobutyrate dehydrogenase activity from pig kidney subsequently followed by the isolation and characterization of this enzyme from various organisms (Robinson and Coon 1957; Hawes et al 1996, 2000; Rougraff et al 1988, 1989). In 1989, cloning of the rat cDNA for this enzyme was reported (Rougraff et al 1989). In 2006, we reported the successful cloning of the human HIBADH cDNA and its expression in E.coli, followed by kinetic studies to pinpoint the Km-values for (S)-3-hydroxyisobutyrate and NAD+ (Loupatty et al 2006).
Methylmalonic semialdehyde dehydrogenase (MMSDH)
The next enzyme in the valine degradation pathway converts methylmalonic semialdehyde to propionyl-CoA. The enzyme was first purified from bacteria (Bannerjee et al 1970) and subsequently purified from rat liver by Harris and coworkers (Bannerjee et al 1970). The monomer molecular mass determined by SDS-PAGE was 58 kDa whereas the native molecular mass as determined by gel filtration was 250 kDa suggesting a tetramer of four 58-kDa subunits (Gibson et al 1993; Zhang et al 1996).
The enzyme also acts on malonic semialdehyde as derived from the catabolism of uracil. Furthermore, both S-methylmalonic semialdehyde as well as R-methylmalonic semialdehyde are handled by the enzyme suggesting that a single enzyme is involved in the catabolism of valine, thymine as well as uracil. The rat liver cDNA for MMSDH has subsequently been cloned and sequenced by Kedishvili et al (1992).
The subsequent enzymes involved in the transformation of propionyl-CoA are shared with the isoleucine pathway and will not be discussed here.
Inborn errors of valine degradation
So far, relatively few patients have been identified with a defect in the valine degradation pathway. Furthermore, all the disorders in the valine degradation pathway known until now have been identified in symptomatic patients, except for IBD-deficiency for which additional patients have been identified through newborn screening. None of the other disorders have yet been identified through newborn screening and so information on the full spectrum of disease is unavailable. Moreover, most of the disorders have had inconsistent symptoms in reported patients as discussed below.
Isobutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency
Isolated isobutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency was first described by Roe et al (1998a) as “an unrecognized defect in human valine metabolism” in a 2-year-old female who was well until 12 months of age and was then found to be anemic with cardiomyopathy in addition. Acylcarnitine analyses revealed elevated C4-carnitine and a low free carnitine level (6 μmol/L) whereas urinary organic acids were normal. Subsequently, in vitro oxidation studies were done in fibroblasts using 16,16,16-2 H3-palmitate, U-13 C-L-valine, U-13 C-L-leucine and U-13 C-L-isoleucine as substrates. Oxidation of all substrates except 13 C5-valine was normal. Upon incubation with 13 C5-valine a significant increase in 13 C4-isobutyrylcarnitine was found without any incorporation of label into propionylcarnitine as observed in control cells. These results led Roe et al (1998a) to conclude that “in the human, there is a distinct isobutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase which exists as a separate enzyme serving only the valine pathway”. Subsequent studies by Nguyen et al (2002) have led to the realization that a previously uncharacterized ACAD-like sequence (ACAD8) is actually coding for a dehydrogenase with isobutyryl-CoA as preferred substrate. Mutation analysis of the cDNA prepared from the fibroblasts of the patient identified by Roe et al (1998a), revealed a homozygous single nucleotide change (c.905 G > A) causing an arginine to glutamine substitution at position 302 (Arg302Gln). The mutant enzyme was stable but turned out to be inactive when expressed in E.coli. Since the description of the first case by Roe et al (1998a) many additional cases have been reported (Koeberl et al 2003; Sass et al 2004; Pedersen et al 2006; Oglesbee et al 2007). Most cases have been identified in the extended neonatal screening programs, notably in the US. Indeed, Oglesbee et al (2007) have reported on the identification of 13 patients through neonatal screening, only 1 of whom was symptomatic. Furthermore, Oglesbee et al (2007) developed a newborn screening follow up algorithm for the diagnosis of isobutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency.
Pedersen et al (2006) performed a comprehensive study on four patients identified by newborn screening as well as the patients described in literature by Roe et al (1998a), Nguyen et al (2002), Sass and Sperl (2001) and Battaile et al (2004). The diagnosis IBD-deficiency was substantiated by urine analysis (isobutyrylglycine), and in vitro probe analysis using 13 C5-valine but not by enzyme studies, simply because at present there is no reliable enzyme assay for isobutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase, at least in fibroblasts and lymphocytes. Molecular analysis revealed mutations in all eight patients. No common mutations were identified. Interestingly, the mutations found all produce amino acid substitutions. Expression studies in Chang cells by Pedersen et al (2006) revealed disturbed protein folding and reduced levels of correctly folded IBD tetramers, and markedly decreased enzyme activities.
Patient identification and characterization using metabolite, enzyme and molecular studies
Ideally IBD-deficiency can be diagnosed by combined analysis in plasma (acylcarnitine analysis) and urine (organic acid analysis) showing elevated C4-carnitine and marginally increased isobutyrylglycine. Indeed, increased plasma C4-carnitine and urine isobutyrylglycine have been demonstrated in most, but definitely not all patients. The first patient described by Roe et al. had elevated plasma C4-carnitine for instance, but normal urinary isobutyrylglycine. Of the four cases picked up by neonatal screening by Pedersen et al (2006), three had elevated C4-carnitine plus elevated urinary isobutyrylglycine, but one had elevated C4-carnitine only with normal urinary isobutyrylglycine. One possibility is to perform MS/MS-analysis coupled with HPLC or UPLC to separate butyryl- and isobutyryl-carnitine. Methods to achieve this have been published. As described above, there are no reports on IBD-activity measurements in fibroblasts or other readily available cells including lymphocytes. In our hands, IBD-activity in fibroblasts is too low to allow reliable measurement of IBD-activity. The absence of reliable enzymatic methods has prompted molecular analysis of the ACAD8-gene followed by expression studies in Chang cells, for instance as done by Pedersen et al (2006).
3-Hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA hydrolase deficiency
So far, only two patients with 3-hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA hydrolase deficiency as established by enzymatic and molecular methods have been identified. The first patient described by Brown et al (1982) had dysmorphic features at birth, poor feeding, failure to thrive, lack of development of motor skills, hypotonia and absence of neurologic development. The infant died at 3 months. Other findings included vertebral abnormalities, tetralogy of Fallot, and agenesis of the cingulate gyrus and corpus callosum. The biochemical basis of 3-hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA hydrolase deficiency was resolved in the early 1980s after the finding of elevated urinary levels of S-2-carboxypropyl-cysteïne and S-2-carboxypropyl-cysteamine. These derivatives are formed through the addition of cysteine and cysteamine across the carbon-carbon double bond of methacrylyl-CoA. Subsequently, the activity of 3-hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA hydrolase was measured, using a coupled enzyme assay in which methacrylyl-CoA was used in the presence of an excess of crotonase. Brown and coworkers demonstrated a 20% residual activity of 3-hydroxyisobutytyl-CoA hydrolase in cultured skin fibroblasts. Using an optimized enzyme assay, we detected no residual activity in fibroblasts from this patient, however (Loupatty et al. 2007).
The second patient, described by us, was the first child of healthy non-consanguineous Caucasian parents and was born at term, following an uneventful pregnancy. Initially, he fed poorly, but otherwise appeared well until 4 months of age when his parents noted head bobbing. This was followed by a delay in motor milestones, then ataxia and a loss of skills. He was able to roll over at 5 months but lost this ability at 10 months. He was reaching out and grasping objects at 4 months, but gradually lost this skill at 13 months. From the age of 9 months, he started to have transient absences and episodes of eye rolling. At the age of 10 months, he had a febrile illness during which he became irritable and more wobbly. He lost the ability to finger feed. Examination at 11 months revealed an alert interactive child with no nystagmus but constant titubation of the head. He had marked truncal ataxia and was unable to sit unsupported. Tone, power and reflexes were normal in the upper limbs. Tone was reduced, particularly distally in the lower limbs. He had marked dysmetria and tremor on reaching out. At the age of 14 months, following 2 days of coryza and lethargy, he became acutely unwell with a reduced level of consciousness and metabolic acidosis, which required intubation and ventilatory support. Blood pH was 7.29 with a base deficit of 15.8 mmol/L. Blood lactate and ammonia were normal. Echocardiography demonstrated no abnormalities. Examination following recovery from this illness showed drowsiness, variable nystagmus, sluggish papillary responses, pooling of secretions in the mouth, fasciculation of the tongue, titubation of the head, and upper and lower limb hypotonia with preservation of reflexes. He showed no improvement on treatment with thiamine or a combination of vitamin C, vitamin E and ubiquinone. As he recovered from this episode of acute encephalopathy he developed dystonia predominantly affecting the right arm and leg. A CT scan, performed during the episode of acute encephalopathy, revealed generalized edema of the brain with loss of gray/white differentiation in the basal ganglia. In addition, an MRI scan revealed signal abnormalities in the globus pallidus and the midbrain with asymmetrical involvement of the cerebral peduncles (right greater than left). No structural abnormalities of the brain were observed. As the neuroimaging was reminiscent of Leigh’s disease, initial investigations were performed focused on pyruvate dehydrogenase, pyruvate carboxylase, and the respiratory chain, which revealed no abnormalities, except for a marked reduction of complex I and a borderline reduction in complex IV. Remarkably, elevated levels of hydroxy-C4 carnitine were found in blood spots of the patient, ranging between 0.45 and 1.73 μmol/L (controls <0.4 μmol/L). Based on the elevation of hydroxy-C4 carnitine the activity of short-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase was measured, which was normal. Subsequently, the activity of 3-hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA hydrolase was measured which revealed a full deficiency (see Loupatty et al 2007)). Molecular studies in the two patients described by Brown et al (1982) and Loupatty et al (2007), respectively, revealed clear-cut mutations in the gene coding for 3-hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA hydrolase.
Except for these two patients, no additional patients with this defect have been described.
3-Hydroxyisobutyrate-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency
3-Hydroxyisobutyric aciduria is a rare organic aciduria and to date only some ten patients have been described in the literature (Ko et al 1991; Chitayat et al 1992; Boulat et al 1995; Sasaki et al 1998, 2001; Shield et al 2001). These patients usually present with dysmorphic features including a small triangular face, low set ears, long philtum and microcephaly. Patients may show widely different phenotypes ranging from mild vomiting attacks with normal brain and cognitive development, to delayed motor development, profound mental retardation and early death. Patients with 3-hydroxyisobutyric aciduria usually excrete elevated amounts of 3-hydroxyisobutyric acid in urine ranging from 60 to 390 mmol/mol creatinine (normal <40 mmol/mol creatinine). In half of the reported cases, elevated lactate levels have been observed. We have studied these patients as well as two novel patients with 3-hydroxyisobutyric aciduria. Enzyme activity measurements revealed no abnormalities in fibroblasts from these patients. In addition to that, molecular analysis of the human gene coding for 3-hydroxyisobutyrate dehydrogenase revealed no abnormalities as well. Very recently we identified the first case of 3-hydroxyisobutyrate dehydrogenase deficiency in a patient with 3-hydroxyisobutyric aciduria.
Methylmalonic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency
Although several patients with presumed methylmalonic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency have been described in the literature (Gibson et al 1993; Ko et al 1991; Gray et al 1987; Pollitt et al 1985; Roe et al 1998b), only a single patient with genetically proven methylmalonic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency has been described in the literature so far (Gray et al 1987; Pollitt et al 1985; Chambliss et al 2000). Routine newborn screening demonstrated a marked hypermethioninemia. The male patient was hospitalized at the age of 3 weeks with an unexplained episode of diarrhea and vomiting. Subsequent urinary organic acid analysis revealed extremely elevated levels of 3-hydroxyisobutyric acid. Further investigations also demonstrated increased urinary excretion of beta-alanine, 3-hydroxypropionic acid, and both isomers of 3-aminoisobutyric acid, suggesting methylmalonic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency. Molecular analysis of the human MMSDH gene revealed homozygosity for a missense mutation (c.1336 G >A; G446R) (Pollitt et al 1985). No expression studies were performed with the mutant cDNA.
Valine degradation disorders and newborn screening
In various countries around the world, at least some of the valine degradation disorders have been included in neonatal screening programs. For some of these disorders algorithms have been developed to be used in the follow-up of cases picked up by newborn screening as described by Oglesbee et al (2007) for isobutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. Most, if not all the enzymes involved in the valine oxidation pathway are also expressed in blood cells, including lymphocytes, which indicates that there might also be a place for enzymatic analysis in the follow-up of cases picked up by newborn screening. We are currently studying the feasibility of using enzymatic methods for this purpose.
References
Andresen BS, Christensen E, Corydon TJ, Bross P, Pilgaard B, Wanders RJA, Ruiter JPN, Simonsen H, Winter V, Knudsen I, Schroeder LD, Gregersen N, Skovby F (2000) Isolated 2-Methylbutyrylglycinuria Caused by Short/Branched-Chain Acyl- CoA Dehydrogenase Deficiency: Identification of a New Enzyme Defect, Resolution of Its Molecular Basis, and Evidence for Distinct Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenases in Isoleucine And Valine Metabolism. Am J Hum Genet 67:1095–1103
Bachhawat BK, Coon MJ, Kupiecki FP, Nagle R, Robinson WG (1957) Coenzyme A thiol esters of isobutyric, methacrylic, and beta-hydroxyisobutyric acids as intermediates in the enzymatic degradation of valine. J Biol Chem 224:1–11
Bannerjee D, Sanders LE, Sokatch JR (1970) Properties of purified methylmalonate semialdehyde dehydrogenase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Biol Chem 245:1828–1835
Battaile KP, Nguyen TV, Vockley J, Kim JJ (2004) Structures of isobutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase and enzyme-product complex: comparison with isovaleryl- and short-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenases. J Biol Chem 279:16526–16534
Boulat O, Benador N, Girardin E, Bachmann C (1995) 3-hydroxyisobutyric aciduria with a mild clinical course. J Inherit Metab Dis 18:204–206
Brown GK, Hunt SM, Scholem R, Fowler K, Grimes A, Mercer JF, Truscott RM, Cotton RG, Rogers JG, Danks DM (1982) Beta-hydroxyisobutyryl coenzyme A deacylase deficiency: a defect in valine metabolism associated with physical malformations. Pediatrics 70:532–538
Chambliss KL, Gray RG, Rylance G, Pollitt RJ, Gibson KM (2000) Molecular characterization of methylmalonate semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency. J Inherit Metab Dis 23:497–504
Chitayat D, Meagher-Villemure K, Mamer OA, O'Gorman A, Hoar DI, Silver K, Scriver CR (1992) Brain dysgenesis and congenital intracerebral calcification associated with 3-hydroxyisobutyric aciduria. J Pediatr 121:86–89
Gibson KM, Lee CF, Bennett MJ, Holmes B, Nyhan WL (1993) Combined malonic, methylmalonic and ethylmalonic acid semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiencies: an inborn error of beta-alanine, L-valine and L-alloisoleucine metabolism? J Inherit Metab Dis 16:563–567
Gibson KM, Burlingame TG, Hogema B, Jakobs C, Schutgens RBH, Millington D, Roe CR, Roe DS, Sweetman L, Steiner RD, Linck L, Pohowalla P, Sacks M, Kiss D, Rinaldo P, Vockley J (2000) 2-Methylbutyryl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency: a new inborn error of L-isoleucine metabolism. Pediatr Res 47:830–833
Gray RG, Pollitt RJ, Webley J (1987) Methylmalonic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency: demonstration of defective valine and beta-alanine metabolism and reduced malonic semialdehyde dehydrogenase activity in cultured fibroblasts. Biochem Med Metab Biol 38:121–124
Hawes JW, Harper ET, Crabb DW, Harris RA (1996) Structural and mechanistic similarities of 6-phosphogluconate and 3-hydroxyisobutyrate dehydrogenases reveal a new enzyme family, the 3-hydroxyacid dehydrogenases. FEBS Lett 389:263–267
Hawes JW, Crabb DW, Chan RJ, Rougraff PM, Paxton R, Harris RA (2000) Mammalian 3-hydroxyisobutyrate dehydrogenase. Meth Enzymol 324:218–228
Ikeda Y, Tanaka K (1983a) Purification and characterization of 2-methyl-branched chain acyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase, an enzyme involved in the isoleucine and valine metabolism, from rat liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem 258:9477–9487
Ikeda Y, Tanaka K (1983b) Purification and characterization of isovaleryl coenzyme A dehydrogenase from rat liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem 258:1077–1085
Ikeda Y, Dabrowski C, Tanaka K (1983) Separation and properties of five distinct acyl-CoA dehydrogenases from rat liver mitochondria. Identification of a new 2-methyl branched chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem 258:1066–1076
Jr S, Del CA (1956) Enzymes of fatty acid metabolism. II. Properties of crystalline crotonase. J Biol Chem 218:985–1002
Kedishvili NY, Popov KM, Rougraff PM, Zhao Y, Crabb DW, Harris RA (1992) CoA-dependent methylmalonate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase, a unique member of the aldehyde dehydrogenase superfamily. cDNA cloning, evolutionary relationships, and tissue distribution. J Biol Chem 267:19724–19729
Ko FJ, Nyhan WL, Wolff J, Barshop B, Sweetman L (1991) 3-Hydroxyisobutyric aciduria: an inborn error of valine metabolism. Pediatr Res 30:322–326
Koeberl DD, Young SP, Gregersen NS, Vockley J, Smith WE, Benjamin DK Jr, An Y, Weavil SD, Chaing SH, Bali D, McDonald MT, Kishnani PS, Chen YT, Millington DS (2003) Rare disorders of metabolism with elevated butyryl- and isobutyryl-carnitine detected by tandem mass spectrometry newborn screening. Pediatr Res 54:219–223
Loupatty FJ, van der Steen A, IJlst L, Ruiter JPN, Ofman R, Baumgartner MR, Ballhausen D, Yamaguchi S, Duran M, Wanders RJA (2006) Clinical, biochemical, and molecular findings in three patients with 3-hydroxyisobutyric aciduria. Mol Genet Metab 87:243–248
Loupatty FJ, Clayton PT, Ruiter JPN, Ofman R, IJlst L, Brown GK, Thorburn DR, Harris RA, Duran M, Desousa C, Krywawych S, Heales SJ, Wanders RJA (2007) Mutations in the Gene Encoding 3-Hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA Hydrolase Results in Progressive Infantile Neurodegeneration. Am J Hum Genet 80:195–199
Nguyen TV, Andresen BS, Corydon TJ, Ghisla S, bd-El RN, Mohsen AW, Cederbaum SD, Roe DS, Roe CR, Lench NJ, Vockley J (2002) Identification of isobutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase and its deficiency in humans. Mol Genet Metab 77:68–79
Oglesbee D, He M, Majumder N, Vockley J, Ahmad A, Angle B, Burton B, Charrow J, Ensenauer R, Ficicioglu CH, Keppen LD, Marsden D, Tortorelli S, Hahn SH, Matern D (2007) Development of a newborn screening follow-up algorithm for the diagnosis of isobutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. Genet Med 9:108–116
Pedersen CB, Bischoff C, Christensen E, Simonsen H, Lund AM, Young SP, Koeberl DD, Millington DS, Roe CR, Roe DS, Wanders RJA, Ruiter JPN, Keppen LD, Stein Q, Knudsen I, Gregersen N, Andresen BS (2006) Variations in IBD (ACAD8) in children with elevated C4-carnitine detected by tandem mass spectrometry newborn screening. Pediatr Res 60:315–320
Pollitt RJ, Green A, Smith R (1985) Excessive excretion of beta-alanine and of 3-hydroxypropionic, R- and S-3-aminoisobutyric, R- and S-3-hydroxyisobutyric and S-2-(hydroxymethyl)butyric acids probably due to a defect in the metabolism of the corresponding malonic semialdehydes. J Inherit Metab Dis 8:75–79
Redina G, Coon MJ (1957) Enzymatic hydrolysis of the coenzyme a thiol esters of beta-hydroxypropionic and beta-hydroxyisobutyric acids. J Biol Chem 225:523–534
Robinson WG, Coon MJ (1957) The purification and properties of beta-hydroxyisobutyric dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem 225:511–521
Roe CR, Cederbaum SD, Roe DS, Mardach R, Galindo A, Sweetman L (1998a) Isolated isobutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency: an unrecognized defect in human valine matabolism. Mol Genet Metab 65:264–271
Roe CR, Struys E, Kok RM, Roe DS, Harris RA, Jakobs C (1998b) Methylmalonic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency: psychomotor delay and methylmalonic aciduria without metabolic decompensation. Mol Genet Metab 65:35–43
Rougraff PM, Paxton R, Kuntz MJ, Crabb DW, Harris RA (1988) Purification and characterization of 3-hydroxyisobutyrate dehydrogenase from rabbit liver. J Biol Chem 263:327–331
Rougraff PM, Zhang B, Kuntz MJ, Harris RA, Crabb DW (1989) Cloning and sequence analysis of a cDNA for 3-hydroxyisobutyrate dehydrogenase. Evidence for its evolutionary relationship to other pyridine nucleotide-dependent dehydrogenases. J Biol Chem 264:5899–5903
Sasaki M, Kimura M, Sugai K, Hashimoto T, Yamaguchi S (1998) 3-Hydroxyisobutyric aciduria in two brothers. Pediatr Neurol 18:253–255
Sasaki M, Iwata H, Sugai K, Fukumizu M, Kimura M, Yamaguchi S (2001) A severely brain-damaged case of 3-hydroxyisobutyric aciduria. Brain Dev 23:243–245
Sass JO, Sperl W (2001) 2-methyl-3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase (MHBD) deficiency versus beta-ketothiolase (MAT) deficiency. J Inherit Metab Dis 24:60
Sass JO, Sander S, Zschocke J (2004) Isobutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency: isobutyrylglycinuria and ACAD8 gene mutations in two infants. J Inherit Metab Dis 27:741–745
Shield JP, Gough R, Allen J, Newbury-Ecob R (2001) 3-Hydroxyisobutyric aciduria: phenotypic heterogeneity within a single family. Clin Dysmorphol 10:189–191
Shimomura Y, Murakami T, Fujitsuka N, Nakai N, Sato Y, Sugiyama S, Shimomura N, Irwin J, Hawes JW, Harris RA (1994) Purification and partial characterization of 3-hydroxyisobutyryl-coenzyme A hydrolase of rat liver. J Biol Chem 269:14248–14253
Steinman HM, Hill RL (1975) Bovine liver crotonase (enoyl coenzyme A hydratase). EC 4.2.1.17 L-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA hydrolyase. Meth Enzymol 35:136–151
Telford EA, Moynihan LM, Markham AF, Lench NJ (1999) Isolation and characterisation of a cDNA encoding the precursor for a novel member of the acyl-CoA dehydrogenase gene family. Biochim Biophys Acta 1446:371–376
Young VR, Pellett PL (1985) Wheat proteins in relation to protein requirements and availability of amino acids. Am J Clin Nutr 41:1077–1090
Zello GA, Wykes LJ, Ball RO, Pencharz PB (1995) Recent advances in methods of assessing dietary amino acid requirements for adult humans. J Nutr 125:2907–2915
Zhang YX, Tang L, Hutchinson CR (1996) Cloning and characterization of a gene (msdA) encoding methylmalonic acid semialdehyde dehydrogenase from Streptomyces coelicolor. J Bacteriol 178:490–495
Acknowledgement
The authors gratefully acknowledge the expert preparation of the manuscript by Mrs. Maddy Festen, and the design of the figure by Mr. Jos Ruiter.
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: Jörn Oliver Sass
Competing interest: None declared.
Presented at: the 24th Annual Meeting of the APS, Fulda, Germany, 10–12 March 2010
Rights and permissions
Open Access This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/2.0), which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
About this article
Cite this article
Wanders, R.J.A., Duran, M. & Loupatty, F.J. Enzymology of the branched-chain amino acid oxidation disorders: the valine pathway. J Inherit Metab Dis 35, 5–12 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-010-9236-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-010-9236-x