Summary
Background
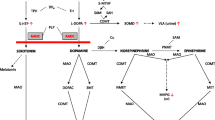
Aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC) deficiency is a disorder of biogenic amine metabolism resulting in generalized combined deficiency of serotonin, dopamine and catecholamines. Main clinical features are developmental delay, muscular hypotonia, dystonia, oculogyric crises and additional extraneurological symptoms. Response to therapy has been variable and unsatisfactory; the overall prognosis is guarded.
Methods
To gain more insight into this rare disorder we collected clinical and laboratory data of nine German patients. All patients were clinically examined by one investigator, and their responses to different drug regimes were evaluated by the patients’ charts.
Results
Symptoms were obvious from early infancy. Later, main neurological features were truncal muscular hypotonia, hypokinesia, oculogyric crises and rigor. Three patients had single seizures. All patients presented distinct extraneurological symptoms, such as hypersalivation, hyperhidrosis, nasal congestion, sleep disturbances and hypoglycaemia. In CSF all patients revealed the pattern typical of AADC with decreased concentrations of homovanillic and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid and elevated concentration of 3-ortho-methyldopa. Diagnosis was confirmed by measurement of AADC activity in plasma in all patients. Drug regimes consisted of vitamin B6, dopamine agonists, MAO inhibitors and anticholinergics in different combinations. No patient achieved a complete recovery from neurological symptoms, but partial improvement of mobility and mood could be achieved in some.
Conclusion
AADC deficiency is a severe neurometabolic disorder, characterized by muscular hypotonia, dystonia, oculogyric crises and additional extraneurological symptoms. Medical treatment is challenging, but a systematic trial of the different drugs is worthwhile.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 3-OMD:
-
3-ortho-methyldopa
- 5-HIAA:
-
5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid
- 5-MTHF:
-
5-methyltetrahydrofolate
- AADC:
-
aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase
- CSF:
-
cerebrospinal fluid
- HVA:
-
homovanillic acid
- MAO:
-
monoamine oxidase
References
Abdenur JE, Abeling NG, Specola N, etal (2006) Aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency: unusual neonatal presentation and additional findings in organic acid analysis. Mol Gen Metab 87: 48–53. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2005.09.007.
Abeling NG, van Gennip AH, Barth PG, van Cruchten A, Westra M, Wijburg FA (1998) Aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency: a new case with a mild clinical presentation and unexpected laboratory findings. J Inherit Metab Dis 21: 240–242. doi:10.1023/A:1005307919767.
Anselm IA, Darras BT (2006) Catecholamine toxicity in aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency. Pediatr Neurol 35(2): 142–144. doi:10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2006.01.008.
Brautigam C, Wevers R, Hyland K, etal (2000) The influence of l-dopa on methylation capacity in aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency. J Inherit Metab Dis 23: 321–324. doi:10.1023/A:1005698223186.
Brautigam C, Hyland K, Wevers R, etal (2002) Clinical and laboratory findings in twins with neonatal epileptic encephalopathy mimicking aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency. Neuropediatrics 33: 113–117. doi:10.1055/s-2002-33673.
Burlina AB, Burlina AP, Hyland K, Bonafe L, Blau N (2001) Autistic syndrome and aromatic l-aminoacid decarboxylase deficiency. J Inherit Metab Dis 24(Supplement 1): 34. doi:10.1023/A:1012471928628.
Chang YT, Mues G, McPherson JD, etal (1998) Mutations in the human aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase gene. JInherit Metab Dis 21: 4. doi:10.1023/A:1005467830063.
Chang YT, Radhakant S, Marsh JL, etal (2004) Levodopa-responsive aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency. Ann Neurol 55: 435–438. doi:10.1002/ana.20055.
Fiumara A, Bräutigam C, Hyland K (2002) Aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency with hyperdopaminuria. Clinical and laboratory findings in response to different therapies. Neuropediatrics 33: 203–208. doi:10.1055/s-2002-34497.
Hyland K, Clayton PT (1990) Aromatic amino acid decarboxylase deficiency in twins. J Inherit Metab Dis 13: 301–304. doi:10.1007/BF01799380.
Hyland K, Clayton PT (1992) Aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency: diagnostic methodology. Clin Chem 38: 2405–2410.
Hyland K, Surtees RAH, Rodeck C, Clayton PT (1992) Aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase: deficiency: clinical features, diagnosis and treatment of a new inborn error of neurotransmitter amine synthesis. Neurology 42: 1980–1988.
Ito S, Nakayama T, Die S, etal (2008) Aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency associated with epilepsy mimicking non-epileptic involuntary movements. Dev Med Child Neurol 50(11): 876–878.
Korenke GC, Christen HJ, Hyland K, Hunnemann D, Hanefeld F (1997) Aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency: an extrapyramidal movement disorder with oculogyric crisis. Eur J Pediatr Neurol 1: 67–71.
Lee HF, Tsai CR, Chi CS, Chang TM, Lee HJ (2008) Aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency in Taiwan. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. Jun 20. [Epub ahead of print].
Malller A, Hyland K, Milstien S, Biaggioni I, Butler IJ (1997) Aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency: clinical features, diagnosis and treatment of a second family. J Child Neurol 12: 349–354.
Mills PB, Surtees RA, Champion MP, etal (2005) Neonatal epileptic encephalopathy caused by mutations in the PNPO gene encoding pyridox(am)ine 5′-phosphate oxidase. Hum Mol Genet 14: 1077–1086.
Pons R, Ford B, Chiriboga CA, etal (2004) Aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency: clinical features, treatment and prognosis. Neurology 62: 1058–1065.
Swoboda KJ, Hyland K, Goldstein DS, etal (1999) Clinical and therapeutic observations in aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency. Neurology 53: 1205–1211.
Swoboda KJ, Saul JP, McKenna C, Speller NB, Hyland K (2003) Aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency: overview of clinical features and outcome. Ann Neurol 54(Supplement 6): 49–55.
Tay SK, Poh KS, Hyland K, etal (2007) Unusually mild phenotype of AADC deficiency in 2 siblings. Mol Genet Metab 91(4): 374–378.
Acknowledgement
The authors thank Professor Keith Hyland (Horizon Molecular Medicine, Atlanta, GA, USA) and Dr Rüdiger Kläs and Dr Friedrich W. Cremer (Zentrum für Humangenetik, Mannheim, Germany) for performing molecular genetic investigations of the AADC gene.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicating editor: Michael Gibson
Competing interests: None declared
References to electronic databases: Aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency: OMIM #608643. Aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase: EC 4.1.1.28.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manegold, C., Hoffmann, G.F., Degen, I. et al. Aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency: clinical features, drug therapy and follow-up. J Inherit Metab Dis 32, 371–380 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-009-1076-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-009-1076-1