Summary
Background:
Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) is a potential new orphan drug for the treatment of some patients with phenylketonuria (PKU), mostly mild forms. Numerous studies have confirmed this finding and BH4-responsiveness may be predicted to some extent from the corresponding genotype.
Aim:
To investigate the response to BH4 loading test, the phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) mutations and the long-term therapeutic efficacy of BH4 in patients with PKU, and to better define BH4-responsive patients according to phenylalanine (Phe) levels and dietary phenylalanine tolerance.
Methods:
30 Italian PKU patients (age range: 6 months–24 years; 12 female, 18 male) were included in this retrospective study. Eleven out of 30 patients presented with Phe levels below 450 μmol/L and 19 patients with Phe levels between 450 and 900 μmol/L. In the second group, we investigated the effect of long-term (6 months–7 years) oral administration of BH4 on blood Phe levels and daily Phe tolerance.
Results:
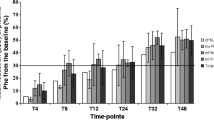
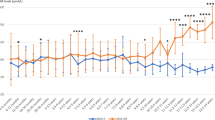
In all patients with initial blood Phe levels <450 μmol/L (n = 11), BH4 loading test was positive, but no treatment was introduced. In 12 out of 19 patients with blood Phe levels >450 μmol/L and positive at BH4 loading, the treatment with BH4 (10 mg/kg per day) was initiated. Before BH4 treatment, Phe tolerance was less than 700 mg/day in all patients except for one (patient no. 9), increasing to 2–3-fold (from 498 ± 49 to 1475 ± 155 mg/day) on BH4 treatment. In these patients the amino acid mixture supplementation was stopped and the diet was a combination of low-protein foods and natural proteins, mostly from animal sources.
Conclusion:
Long-term BH4 substitution (up to 7 years) in a group of moderate PKU patients allowed a substantial relaxation of the dietary restrictions or even replacement of the diet with BH4 without any adverse effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 6RBH4 :
-
(6R)-L-erythro-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobiopterin
- BH4:
-
tetrahydrobiopterin
- HPA:
-
hyperphenylalaninaemia
- PAH:
-
phenylalanine hydroxylase
- Phe:
-
phenylalanine
- PKU:
-
phenylketonuria
References
Bélanger-Quintana A, Garcia MJ, Castro M, et al (2005) Spanish BH4-responsive phenylalanine hydroxylase-deficient patients: evolution of seven patients on long-term treatment with tetrahydrobiopterin. Mol Genet Metab 86(Supplement 1): 61–66.
Bernegger C, Blau N (2002) High frequency of tetrahydrobiopterin-responsiveness among hyperphenylalaninemias: a study of 1919 patients observed from 1988 to 2002. Mol Genet Metab 77: 304–313.
Blau N (2008) Defining tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4)-responsiveness in PKU. J Inherit Metab Dis 31(1): 2–3.
Blau N, Erlandsen H (2004) The metabolic and molecular bases of tetrahydrobiopterin-responsive phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency. Mol Genet Metab 82: 101–111.
Boveda MD, Couce ML, Castineiras DE, et al (2007) The tetrahydrobiopterin loading test in 36 patients with hyperphenylalaninaemia: evaluation of response and subsequent treatment. J Inherit Metab Dis 30(5): 812.
Cerone R, Schiaffino MC, Fantasia AR, Perfumo M, Birk Moller L, Blau N (2004) Long-term follow-up of a patient with mild tetrahydrobiopterin-responsive phenylketonuria. Mol Genet Metab 81: 137–139.
Desviat LR, Pérez B, Bèlanger-Quintana A, et al (2004) Tetrahydrobiopterin responsiveness: results of the BH4 loading test in 31 Spanish PKU patients and correlation with their genotype. Mol Genet Metab 82: 157–162.
Dhondt JL, Ogier H, Benoist JF, Belhesme C, Giraud M (2003) The interpretation of tetrahydrobiopterin loading test in hyperphenylalaninemia. J Inherit Metab Dis 26(Supplement 2): 18.
Fiege B, Blau N (2007) Assessment of tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) responsiveness in phenylketonuria. J Pediatr 150(6): 627–630.
Fiori L, Fiege B, Riva E, Giovannini M (2005) Incidence of BH4-responsiveness in phenylalanine-hydroxylase-deficient Italian patients. Mol Genet Metab 86(Supplement 1): 67–74.
Gramer G, Burgard P, Garbade SF, Lindner M (2007) Effects and clinical significance of tetrahydrobiopterin supplementation in phenylalanine hydroxylase-deficient hyperphenylalaninaemia. J Inherit Metab Dis 30(4): 556–562.
Hennermann JB, Bührer C, Blau N, Vetter B, Mönch E (2005) Long-term treatment with tetrahydrobiopterin increases phenylalanine tolerance in classic and mild phenylketonuria. Molec Gen Metab 86(Supplement 1): 86–90.
Kure S, Hou DC, Ohura T, et al (1999) Tetrahydrobiopterin-responsive phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency. J Pediatr 135(3): 375–378.
Lambruschini N, Perez-Duenas B, Vilaseca MA, et al (2005) Clinical and nutritional evaluation of phenylketonuric patients on tetrahydrobiopterin monotherapy. Mol Genet Metab 86(Supplement 1): 54–60.
Lässker U, Zschocke J, Blau N, Santer R (2002) Tetrahydrobiopterin responsiveness in phenylketonuria. Two new cases and a review of molecular genetic findings. J Inherit Metab Dis 25: 65–70.
Leuzzi V, Carducci C, Carducci C, et al (2006) The spectrum of phenylalanine variations under tetrahydrobiopterin load in subjects affected by phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency. J Inherit Metab Dis 29(1): 38–46.
Levy HL, Milanowski A, Chakrapani A, et al (2007) Efficacy of sapropterin dihydrochloride (tetrahydrobiopterin, 6R-BH4) for reduction of phenylalanine concentration in patients with phenylketonuria: a phase III randomised placebo-controlled study. Lancet 370(9586): 504–510.
Lindner M, Haas D, Zschocke J, Burgard P (2001) Tetrahydrobiopterin responsiveness in phenylketonuria differs between patients with the same genotype. Mol Genet Metab 73(1): 104–106.
Lindner M, Steinfeld R, Burgard P, Schulze A, Mayatepek E, Zschocke J (2003) Tetrahydrobiopterin sensitivity in German patients with mild phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency. Hum Mutat 21(4): 400.
Lücke T, Illsinger S, Aulehla-Scholz C, Sander J, Das AM (2003) BH4-sensitive hyperphenylalaninemia: New case and review of literature. Pediatr Neurol 28(3): 228–230.
Matalon R, Koch R, Michals-Matalon K, Mosley K, Stevens R (2002) Tetrahydrobiopterin-responsive phenylalanine hydroxylase mutations. J Inherit Metab Dis 25(Supplement 1): 23.
Matalon R, Michals-Matalon K, Koch R, Grady J, Tyring S, Stevens RC (2005) Response of patients with phenylketonuria in the US to tetrahydrobiopterin. Mol Genet Metab 86(Supplement 1): S17–21.
Milstien S, Kaufman S (1975) Studies on the phenylalanine hydroxylase system in liver slices. J Biol Chem 250(12): 4777–4781.
Mitchell JJ, Wilcken B, Alexander I, et al (2005) Tetrahydrobiopterin-responsive phenylketonuria: the New South Wales experience. Mol Genet Metab 86(Supplement 1): 81–85.
Muntau AC, Roschinger W, Habich M, et al (2002) Tetrahydrobiopterin as an alternative treatment for mild phenylketonuria. N Engl J Med 347: 2122–2132.
Okano Y, Hase Y, Kawajiri M, et al (2004) In vivo studies of phenylalanine hydroxylase by phenylalanine breath test: diagnosis of tetrahydrobiopterin-responsive phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency. Pediatr Res 56: 714–719.
Perez-Duenas B, Vilaseca MA, Mas A, et al (2004) Tetrahydrobiopterin responsiveness in patients with phenylketonuria. Clin Biochem 37(12): 1083–1090.
Spaapen LJM, Bakker JA, Velter C, et al (2001) Tetrahydrobiopterin-responsive phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency in Dutch neonates. J Inherit Metab Dis 24: 325–358.
Spaapen LJ, Estela Rubio-Gozalbo M (2003) Tetrahydrobiopterin-responsive phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency, state of the art. Mol Genet Metab 78(2): 93–99.
Trefz FK, Aulehla-Scholz C, Blau N (2001) Successful treatment of phenylketonuria with tetrahydrobiopterin. Eur J Pediatr 160: 315.
Weglage J, Grenzebach M, v.Teeffelen-Heithoff A, et al (2002) Tetrahydrobiopterin responsiveness in a large series of phenylketonuria patients. J Inherit Metab Dis 25: 321–322.
Zurfluh MR, Zschocke J, Lindner M, et al (2008) Molecular genetics of tetrahydrobiopterin-responsive phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency. Hum Mutat 29(1): 167–175.
Acknowledgements
Supported by Centro Regionale Malattie Metaboliche Ereditarie, Regione Veneto and COMETA-ASMME, Italy and in part by the Swiss National Science Foundation Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicating editor: John Walter
Competing interests: None declared
References to electronic databases: Phenylalanine-4-hydroxylase: EC 1.14.16.1.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burlina, A., Blau, N. Effect of BH4 supplementation on phenylalanine tolerance. J Inherit Metab Dis 32, 40–45 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-008-0947-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-008-0947-1