Summary
Objective:
To determine whether a new starch offers better short-term metabolic control than uncooked cornstarch in patients with glycogen storage diseases (GSDs).
Study design:
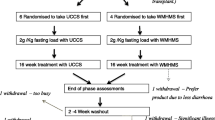
A short-term double-blind cross-over pilot study comparing uncooked physically modified cornstarch (WMHM20) with uncooked cornstarch in patients with GSD types Ia, Ib and III. Twenty-one patients (ages 3–47, 9 female) were given 2 g/kg cornstarch or WMHM20 mixed in water. Blood glucose, lactate and insulin, and breath hydrogen and 13CO2 enrichment were measured, at baseline and after each load. The hourly biochemical evaluations terminated when blood glucose was ≤3.0 mmol/L, when the study period had lasted 10 h or when the patient wished to end the test. The alternative starch was administered under similar trial conditions a median of 10 days later.
Results:
The median starch load duration was 9 h for WMHM20 versus 7 h for cornstarch. Glucose decreased more slowly (p=0.05) and lactate was suppressed faster (p=0.17) for WMHM20 compared with cornstarch. Peak hydrogen excretion was increased (p=0.05) when cornstarch was taken.
Conclusion:
These data indicate longer duration of euglycaemia and better short-term metabolic control in the majority of GSD patients with WMHM20 compared to cornstarch.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CNPF:
-
continuous nocturnal pump feed
- GSD:
-
glycogen storage disease
- IQ:
-
interquartile range
- PDB:
-
Pee Dee Belemnite
- UCCS:
-
uncooked cornstarch
- WMHM20:
-
Waxy Maize (Heat Modified) 20
References
Bodamer OA, Feillet F, Lane RE, et al (2002) Utilization of cornstarch in glycogen storage disease type Ia. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 14: 1251–1256.
Casellas F, Guarner L, Antolin M, Malagelada JR (2004) Hydrogen breath test with low-dose rice flour for assessment of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. Pancreas 29: 306–310.
Chen YT (2001) Glycogen storage diseases. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D, eds; Childs B, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, assoc, eds. The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease, 8th edn. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1521–1551.
Chen YT, Cornblath M, Sidbury JB (1984) Cornstarch therapy in type I glycogen-storage disease. N Engl J Med 310: 171–175.
Chen YT, Bazzarre CH, Lee MM, Sidbury JB, Coleman RA (1993) Type I glycogen storage disease: nine years of management with cornstarch. Eur J Pediatr 152(Suppl 1): S56–S59.
Cori GT, Cori CF (1952) Glucose-6-phosphatase of the liver in glycogen storage disease. J Biol Chem 199: 661–667.
Englyst HN, Quigley ME, Hudson GJ (1994) Determination of dietary fibre as non-starch polysaccharides with gas–liquid chromatographic, high-performance liquid chromatographic or spectrophotometric measurement of constituent sugars. The Analyst 119: 1497–1509.
Folkman J, Philippart A, Tze WJ, Crigler J Jr (1972) Portacaval shunt for glycogen storage disease: value of prolonged intravenous hyperalimentation before surgery. Surgery 72: 306–314.
Greene HL, Slonim AE, O’Neill JA Jr, Burr IM (1976) Continuous nocturnal intragastric feeding for management of type 1 glycogen-storage disease. N Engl J Med 294: 423–425.
Lee PJ, Leonard JV (1995) The hepatic glycogen storage diseases—problems beyond childhood. J Inherit Metab Dis 18: 462–472.
Lee PJ, Patel A, Hindmarsh PC, Mowat AP, Leonard JV (1995a) The prevalence of polycystic ovaries in the hepatic glycogen storage diseases: its association with hyperinsulinism. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 42: 601–606.
Lee PJ, Patel JS, Fewtrell M, Leonard JV, Bishop NJ (1995b) Bone mineralisation in type 1 glycogen storage disease. Eur J Pediatr 154: 483–487.
Lee PJ, Dalton RN, Shah V, Hindmarsh PC, Leonard JV (1995c) Glomerular and tubular function in glycogen storage disease. Pediatr Nephrol 9: 705–710.
Lee PJ, Dixon MA, Leonard JV (1996) Uncooked cornstarch—efficacy in type I glycogenosis. Arch Dis Child 74: 546–547.
Leonard JV, Dunger DB (1978) Hypoglycaemia complicating feeding regimens for glycogen storage disease. Lancet 312: 1203–1204.
Metz G, Jenkins DJ, Peters TJ, Newman A, Blendis LM (1975) Breath hydrogen as a diagnostic method for hypolactasia Lancet (7917): 1155–1157.
Moses SW (2002) Historical highlights and unsolved problems in glycogen storage disease type I. Eur J Pediatr 161(Suppl 1): S2–S9.
Rake JP, Visser G, Labrune P, Leonard JV, Ullrich K, Smit GP (2002a) Glycogen storage disease type I: diagnosis, management, clinical course and outcome. Results of the European Study on Glycogen Storage Disease Type I (ESGSD I). Eur J Pediatr 161(Suppl 1): S20–S34.
Rake JP, Visser G, Labrune P, Leonard JV, Ullrich K, Smit GP (2002b) Guidelines for management of glycogen storage disease type I—European Study on Glycogen Storage Disease Type I (ESGSD I). Eur J Pediatr 161(Suppl 1): S112–S119.
Sanderson IR, Bisset WM, Milla PJ, Leonard JV (1991) Chronic inflammatory bowel disease in glycogen storage disease type IB. J Inherit Metab Dis 14: 771–776.
Sidbury JB, Chen YT, Roe CR (1986) The role of raw starches in the treatment of type I glycogenosis. Arch Intern Med 146: 370–373.
Smit GP, Berger R, Potasnick R, Moses SW, Fernandes J (1984) The dietary treatment of children with type I glycogen storage disease with slow release carbohydrate. Pediatr Res 18: 879–881.
Smit GP, Ververs MT, Belderok B, Van Rijn M, Berger R, Fernandes J (1988) Complex carbohydrates in the dietary management of patients with glycogenosis caused by glucose-6-phosphatase deficiency. Am J Clin Nutr 48: 95–97.
Starzl TE, Marchioro TL, Sexton AW, et al (1965) The effect of portocaval transposition on carbohydrate metabolism: experimental and clinical observations. Surgery 57: 687–697.
Tester RF, Karkalas J, Qi X (2004) Starch structure and digestibility enzyme–substrate relationship. World’s Poultry Science Journal 60: 186–195.
Visser G, Rake JP, Kokke FT, Nikkels PG, Sauer PJ, Smit GP (2002) Intestinal function in glycogen storage disease type I. J Inherit Metab Dis 25: 261–267.
Weinstein DA, Wolfsdorf JI (2002) Effect of continuous glucose therapy with uncooked cornstarch on the long-term clinical course of type 1a glycogen storage disease. Eur J Pediatr 161(Suppl 1): S35–S39.
Wolfsdorf JI, Crigler JF Jr (1997) Cornstarch regimens for nocturnal treatment of young adults with type I glycogen storage disease. Am J Clin Nutr 65: 1507–1511.
Wolfsdorf JI, Crigler JF Jr (1999) Effect of continuous glucose therapy begun in infancy on the long-term clinical course of patients with type I glycogen storage disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 29: 136–143.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicating editor: René Santer
Competing interests: None declared
References to electronic databases: Glycogen storage disease I, OMIM 232200. Glycogen storage disease III, OMIM 232400. Glucose-6-phosphatase, EC 3.1.3.9. Amylo-1,6-glucosidase, EC 3.2.1.33. Oligo-1,4-1,4-glucanotransferase, EC 2.4.1.25
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhattacharya, K., Orton, R.C., Qi, X. et al. A novel starch for the treatment of glycogen storage diseases. J Inherit Metab Dis 30, 350–357 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-007-0479-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-007-0479-0