Summary
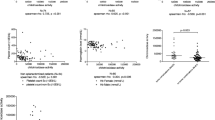
Laboratory diagnosis of lysosomal storage disorders, especially sphingomyelinase deficiency (Niemann–Pick disease type A/B) and Niemann–Pick disease type C (NPC) can be challenging. We therefore aimed to analyse the feasibility of first-step screening with specific chitotriosidase cut-off values in children ≤ 10 years of age with visceral organomegaly (hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, or hepatosplenomegaly) in whom a storage disorder was suspected. We conducted a retrospective, cross-sectional, referral, single-centre study to assess diagnostic test properties in 106 individuals. Median chitotriosidase activity was 12 655 nmol/h per ml (interquartile range 4693–20982) in Gaucher disease (GD); 780 (465–1298) in SMD (sphingomyelinase deficiency); 925 (319–1215) in NPC and 50 (29–54) in patients with miscellaneous diseases. To restrict the differential diagnosis to GD, SMD or NPC, chitotriosidase activity above 200 nmol/h per ml had a sensitivity of 96%, specificity of 100%, positive predictive value (PPV) of 100%, and negative predictive value (NPV) of 95%. For GD alone, chitotriosidase activity above 4000 nmol/h per ml had a sensitivity of 77%, specificity of 100%, PPV of 100% and NPV of 92%. Of the 44 patients analysed, 4.5% were homozygous and 36.4% heterozygous for chitotriosidase gene duplication. Adjusting for the chitotriosidase genotype, chitotriosidase activities were higher in GD type III than in GD type I. We conclude that, in the above setting, the degree of elevation of chitotriosidase activity can be applied to increase the likelihood of GD, SMD, or NPC and guide the choice of the appropriate confirmatory assay.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GD:
-
Gaucher disease
- LR:
-
likelihood ratio
- LSD:
-
lysosomal storage disorders
- NPC:
-
Niemann–Pick disease type C
- NPV:
-
negative predictive value
- OR:
-
odds ratio
- PPV:
-
positive predictive value
- ROC:
-
receiver operating characteristic
- SMD:
-
sphingomyelinase deficiency
References
Barone R, Malaguarnera L, Angius A, Musumeci S (2003a) Plasma chitotriosidase activity in patients with beta-thalassemia. Am J Hematol 72: 285–286.
Barone R, Simpore J, Malaguarnera L, Pignatelli S, Musumeci S (2003b) Plasma chitotriosidase activity in acute Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Clin Chim Acta 331: 79–85.
Barton NW, Brady RO, Dambrosia JM, et al (1991) Replacement therapy for inherited enzyme deficiency—macrophage-targeted glucocerebrosidase for Gaucher's disease. N Engl J Med 324: 1464–1470.
Boot RG, Renkema GH, Strijland A, van Zonneveld AJ, Aerts JM (1995) Cloning of a cDNA encoding chitotriosidase, a human chitinase produced by macrophages. J Biol Chem 270: 26252–26256.
Boot RG, Renkema GH, Verhoek M, et al (1998) The human chitotriosidase gene. Nature of inherited enzyme deficiency. J Biol Chem 273: 25680–25685.
Boot RG, van Achterberg TA, van Aken BE, et al (1999) Strong induction of members of the chitinase family of proteins in atherosclerosis: chitotriosidase and human cartilage gp-39 expressed in lesion macrophages. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 19: 687–694.
Brinkman J, Wijburg FA, Hollak CE, et al (2005) Plasma chitotriosidase and CCL18: early biochemical surrogate markers in type B Niemann—Pick disease. J Inherit Metab Dis 28: 13–20.
Cox T, Lachmann R, Hollak C, et al (2000) Novel oral treatment of Gaucher,s disease with N-butyldeoxynojirimycin (OGT 918) to decrease substrate biosynthesis. Lancet 355: 1481–1485.
Czartoryska B, Tylki-Szymanska A, Gorska D (1998) Serum chitotriosidase activity in Gaucher patients on enzyme replacement therapy (ERT). Clin Biochem 31: 417–420.
Dodelson de Kremer R, Paschini de Capra A, Angaroni CJ, Giner de Ayala A (1997) [Plasma chitotriosidase activity in Argentinian patients with Gaucher disease, various lysosomal diseases and other inherited metabolic disorders]. Medicina (B Aires) 57: 677–684.
Gal AE, Brady RO, Hibbert SR, Pentchev PG (1975) A practical chromogenic procedure for the detection of homozygotes and heterozygous carriers of Niemann—Pick disease. N Engl J Med 293: 632–636.
Giraldo P, Cenarro A, Alfonso P, et al (2001) Chitotriosidase genotype and plasma activity in patients with type 1 Gaucher's disease and their relatives (carriers and non carriers). Haematologica 86: 977–984.
Guo Y, He W, Boer AM, et al (1995) Elevated plasma chitotriosidase activity in various lysosomal storage disorders. J Inherit Metab Dis 18: 717–722.
Harzer K, Rolfs A, Bauer P, et al (2003) Niemann—Pick disease type A and B are clinically but also enzymatically heterogeneous: pitfall in the laboratory diagnosis of sphingomyelinase deficiency associated with the mutation Q292K. Neuropediatrics 34: 301–306.
Hollak CE, van Weely S, van Oers MH, Aerts JM (1994) Marked elevation of plasma chitotriosidase activity. A novel hallmark of Gaucher disease. J Clin Invest 93: 1288–1292.
Imrie J, Wraith JE (2001) Isolated splenomegaly as the presenting feature of Niemann—Pick disease type C. Arch Dis Child 84: 427–429.
Imrie J, Vijayaraghaven S, Whitehouse C, et al (2002) Niemann—Pick disease type C in adults. J Inherit Metab Dis 25: 491–500.
Korolenko TA, Zhanaeva SY, Falameeva OV, et al (2000) Chitotriosidase as a marker of macrophage stimulation. Bull Exp Biol Med 130: 948–950.
Malaguarnera L, Simpore J, Prodi DA, et al (2003) A 24-bp duplication in exon 10 of human chitotriosidase gene from the sub-Saharan to the Mediterranean area: role of parasitic diseases and environmental conditions. Genes Immun 4: 570–574.
Michelakakis H, Dimitriou E, Labadaridis I (2004) The expanding spectrum of disorders with elevated plasma chitotriosidase activity: an update. J Inherit Metab Dis 27: 705–706.
Peters SP, Coyle P, Glew RH (1976) Differentiation of beta-glucocerebrosidase from beta-glucosidase in human tissues using sodium taurocholate. Arch Biochem Biophys 175: 569–582.
Ries M, Gupta S, FitzGibbon EJ, Hertle RW, Schiffmann R (2003) Assessment of saccadic eye movement in chronic neuronopathic Gaucher disease. J Inherit Metab Dis 26: 168.
Rodrigues MR, Sa Miranda MC, Amaral O (2004) Allelic frequency determination of the 24-bp chitotriosidase duplication in the Portuguese population by real-time PCR. Blood Cells Mol Dis 33: 362–364.
Vanier MT, Revol A, Fichet M (1980) Sphingomyelinase activities of various human tissues in control subjects and in Niemann—Pick disease—development and evaluation of a microprocedure. Clin Chim Acta 106: 257–267.
Vanier MT, Rodriguez-Lafrasse C, Rousson R, et al (1991) Type C Niemann—Pick disease: spectrum of phenotypic variation in disruption of intracellular LDL-derived cholesterol processing. Biochim Biophys Acta 1096: 328–337.
Wajner A, Michelin K, Burin MG, et al (2004) Biochemical characterization of chitotriosidase enzyme: comparison between normal individuals and patients with Gaucher and with Niemann—Pick diseases. Clin Biochem 37: 893–897.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicating editor: Irene Maire
Competing interests: None declared
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ries, M., Schaefer, E., Lührs, T. et al. Critical assessment of chitotriosidase analysis in the rational laboratory diagnosis of children with Gaucher disease and Niemann–Pick disease type A/B and C. J Inherit Metab Dis 29, 647–652 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-006-0363-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-006-0363-3