Summary
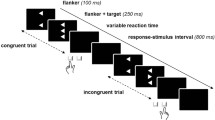
Background: The presentation rate of stimuli plays an important role in explaining the performance inefficiency in children with ADHD. In general, children with ADHD have been found to perform more poorly in conditions of relatively slow event rates as compared with fast and moderate event rates. The state regulation hypothesis states that these children have problems in correcting their energetic state necessary to counteract a performance decrement, which requires extra effort allocation. In this study, we investigated state regulation in children with ADHD and used children with early- and continuously treated phenylketonuria (PKU) as a clinical contrast group. Method: We measured the parietal P3 during a Go/No-Go task that incorporated a condition with a fast and a slow presentation rate. Results: We were able to show that children with ADHD, relative to controls, responded more slowly and more variably in the slow condition only, which was accompanied by a smaller P3, suggesting less effort allocation. In contrast, the children with PKU did not show a state regulation deficit. The PKU group showed prolonged stimulus evaluation processing, as indexed by P3 latency, compared to controls and children with ADHD. In addition, they made more errors of commission than the controls and the ADHD group. Conclusions: Our electrophysiological data support the state regulation hypothesis of ADHD. Only the children with PKU had more problems in inhibiting pre-potent responding than controls, which is in accord with the prefrontal dysfunction hypothesis of PKU.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achenbach TM, Edelbrock CS (1983) Manual for the Child Behavior Checklist and Revised Child Behavior Profile. Burlington, Vermont: University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry.
Achenbach TM, Edelbrock CS (1986) Manual for the Teacher's Report Form and Teacher Version of the Child Behavior Profile. Burlington, Vermont: University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry.
American Psychiatric Association (2000) Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th ed., text revision. Washington DC: American Psychiatic Association.
Arnold GL, Vladutiu CJ, Orlowski CC, Blakely EM, DeLuca J (2004) Prevalence of stimulant use for attentional dysfunction in children with pehylketonuria. J Inherit Metab Dis 27: 137–143.
Arnsten AFT (2000) Genetics of childhood disorders: XVIII. ADHD, Part 2: Norepinephrine has a critical modulatory influence on prefrontal cortical function. J Am Acad Child Psychiatry 39: 1201–1203.
Banich MT, Passarotti AM, White DA, Nortz MJ, Steiner RD (2000) Interhemisperic interaction during childhood: II. Children with early-treated phenylketonuria. Dev Neuropsychol 18: 53–71.
Barkley RA (1997) Behavioral inhibition, sustained attention and executive functions: constructing a unifying theory of ADHD. Psychol Bull 121: 65–94.
Barkley RA (2000) Genetics of childhood disorders: XVII. ADHD, Part 1: The executive functions and ADHD. J Am Acad Child Psychiatry 39: 1064–1068.
Bradberry CW, Karasic DH, Deutch AY, Roth RH (1989) Regionally-specific alterations in mesotelencephalic dopamine synthesis in diabetic rats: association with precursor tyrosine. J Neural Transm 78: 221–229.
Burgard P (2000) Development of intelligence in early treated phenylketonuria. Eur J Pediatr 159: S74–S79.
Burgard P, Rey F, Rupp A, Abadie V, Rey J (1997) Neuropsychologic functions of early treated patients with phenylketonuria, on and off diet: results of a cross-national and cross-sectional study. Pediatr Res 41: 368–374.
Diamond A (1994) Phenylalanine levels of 6–10 mg/dl may not be as benign as once thought. Acta Paediatr 83: 89–91.
Diamond A, Prevor MB, Callender G, Druin DP (1997) Prefrontal cortex cognitive deficits in children treated early and continuously for PKU. Monogr Soc Res Child 62.
Donchin E, Coles MGH (1988) Is the P300 component a manifestation of context updating? Behav Brain Sci 11: 355–372.
Donchin E, Kramer AF, Wickens C (1986) Applications of brain event-related potentials to problems in engineering psychology. In: Coles MGH, Donchin E, Porges S, eds. Psychophysiology: Systems, Processes and Applications, Middletown, NJ: Till & Till, 702–718.
Eimer M (1993) Effects of attention and stimulus probability on ERPs in a Go/Nogo task. Biol Psychology 35: 123–138.
Falkenstein M, Hoormann J, Hohnsbein J (1999) ERP components in Go/Nogo tasks and their relation to inhibition. Acta Psychiatr 101: 267–291.
Faraone SV, Biederman J (1998) Neurobiology of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Biol Psychiatry 44: 951–958.
Gardiner RM (1990) Transport of amino acids across the blood–brain barrier: implications for treatment of maternal phenylketonuria. J Inherit Metab Dis 13: 627–633.
Gratton G, Coles MGH, Donchin E (1983) A new method for off-line removal of ocular artifact. Electroenceph Clin Neurophys 55: 468–484.
Henderson RM, McCulloch DL, Herbert AM, Robinson PH, Taylor MJ (2000) Visual event-related potentials in children with phenylketonuria. Acta Paediatr 89: 52–57.
Hommes FA (1989) The role of the blood-brain barrier in the aetiology of permanent brain dysfunction in hyperphenylalaninemia. J Inherit Metab Dis 12: 41–46.
Huijbregts S, De Sonneville LJM, Licht R, Sergeant JA, Van Spronsen FJ (2002) Inhibition of prepotent responding and attentional flexibility in treated phenylketonuria. Dev Neuropsych 22: 481–499.
Huijbregts SCJ, De Sonneville LMJ, Licht R, Van Spronsen FJ, Verkerk PH, Sergeant JA (2002) Sustained attention and inhibition of cognitive interference in treated phenylketonuria: associations with concurrent and lifetime phenylalanine concentrations. Neuropsych 40: 7–15.
Huijbregts SCJ, De Sonneville LMJ, Van Spronsen FJ, et al (2003) Motor function under lower and higher controlled processing demands in early and continuously treated phenylketonuria. Neuropsych 17: 369–379.
Kalverboer AF, van der Schot LW, Hendrikx MM, Huisman J, Slijper FM, Stemerdink BA (1994) Social behaviour and task orientation in early-treated PKU. Acta Paediatr Suppl 407: 104–105.
Knudsen GM, Hasselbalch S, Toft PB, Christensen E, Paulson OB, Lou H (1995) Blood-brain barrier transport of amino acids in healthy controls and in patients with phenylketonuria. J Inherit Metab Dis 18: 653–664.
Kok A (2001) On the utility of P3 amplitude as a measure of processing capacity. Psychophysiology 38: 557–577.
Kopp B, Mattler U, Goertz R, Rist F (1996) N2, P3 and the lateralized readiness potential in a go-nogo task involving selective response priming. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 99: 19–27.
Leuzzi V, Seri S, Cerquiglini A, Carducci C, Carducci C, Antonozzi I (2000) Derangement of the dopaminergic system in phenylketonuria: study of the event-related potential (P300). J Inherit Metab Dis 23: 317–320.
Leuzzi V, Pansini M, Sechi, et al (2004) Executive function impairment in early-treated PKU subjects with normal mental development. J Inherit Metab Dis 27: 115–125.
Lou HC, Lykkelund C, Gerdes A-M, Udesen H, Bruhn P (1987) Increased vigilance and dopamine synthesis by large doses of tyrosine or phenylalanine restriction in phenylketonuria. Acta Paediatr Scand 76: 560–565.
National Institutes of Health. Consensus Development Conference Statement. Phenylketonuria: Screening and Management October 16018, 2000 (online). http://odp.od.nih.gov/consensus/cons/113/113_statement.htm
Nigg JT (2001) Is ADHD a disinhibitory disorder? Psychol Bull 127: 571–598.
Oosterlaan J, Logan GD, Sergeant JA (1998) Response inhibition in AD/HD, CD, comorbid AD/HD+CD, anxious, and control children: a meta-analysis of studies with the stop task. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 39: 411–425.
Pennington BF, Ozonoff S (1996) Executive functions and developmental psychopathology. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 37: 51–87.
Pietz J, Kreis R, Rupp A, et al (1999) Large neutral amino acids block transport into brain tissue in patients with phenylketonuria. J Clin Invest 103: 1169–1178.
Plitszka SR, McCracken JT, Maas JW (1996) Catecholamines in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: current perspectives. J Am Acad Child Psychiatry 35: 264–272.
Polich J, Kok A (1995) Cognitive and biological determinants of P300: an integrative review. Biol Psychol 41: 103–146.
Quay HC (1997) Inhibition and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. J Abnorm Child Psychol 25: 7–13.
Ris MD, Williams SE, Hunt MM, Berry HK, Leslie N (1994) Early-treated phenylketonuria: adult neuropsychological outcome. J Pediatr 124: 388–392.
Sanders AF (1983) Toward a model of stress and human performance. Acta Psychol 53: 61–79.
Sanders AF (1998) Elements of Human Performance: Reaction Processes and Attention in Human Skill. Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Schachar R, Logan GD (1990) Impulsivity and inhibitory control in normal development and childhood psychopathology. Dev Psychol 26: 710–720.
Sergeant JA, Oosterlaan J, van der Meere JJ (1999) Information processing and energetic factors in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. In: Quay HC, Hogan AE, eds. Handbook of Disruptive Behavior Disorders. New York: Plenum Press, 75–104.
Schmidt E, Rupp A, Burgard P, Pietz J, Weglage J, De Sonneville L (1994) Sustained attention in adult phenylketonuria: the influence of the concurrent phenylalanine blood-level. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 16: 681–688.
Scriver CR, Kaufman S, Eisensmith RC, Woo SLC (1995) The hyperpheylalaninemias. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D, eds.; Childs B, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, assoc. eds. The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1025–1075.
Shaffer D, Fisher P, Lucas CP, Dulcan MK, Schwab-Stone ME (2000) NIMH diagnostic interview schedule for children version IV (NIMH DISC-IV): description, differences from previous versions, and reliability of some common diagnoses. J Am Acad Child Psychiatr 39: 28–38.
Singhal A, Fowler B (2004) The differential effects of Sternberg short- and long-term memory scanning on the late Nd and P300 in a dual-task paradigm. Cogn Brain Res 21: 124–132.
Smith ML, Klim P, Mallozzi E, Hanley WB (1996) A test of the frontal-specificity hypothesis in the cognitive performance of adults with phenylketonuria. Dev Neuropsychol 12: 327–341.
Stemerdink NBA, van der Meere JJ, Van der Molen MW, et al (1995) Information processing in patients with early and continuously treated phenylketonuria. Eur J Pediatr 154: 739–746.
Stemerdink NBA, Van der Molen MW, Kalverboer AF, et al (1999) Prefrontal dysfunction in early and continuously treated phenylketonuria. Dev Neuropsychol 16: 29–57.
Stemerdink NBA, Kalverboer AF, van der Meere JJ, et al (2000) Behaviour and school achievement in patients with early and continuously treated phenylketonuria. J Inherit Metab Dis 23: 548–562.
Swanson J, Castellanos FX, Murias M, Lahoste G, Kennedy J (1998) Cognitive neuroscience of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and hyperkinetic disorder. Curr Opin Neurobiol 8: 263–271.
Ullrich K, Weglage J, Oberwittler C, et al (1996) Effect of L-dopa on visual evoked potentials and neuropsychological tests in adult phenylketonuria patients. Eur J Pediatr 155: S74–S77.
Ullsperger P, Freude G, Erdmann U (2001) Auditory probe sensitivity to mentalworkload changes—an event-related potential study. Int J Psychophysiol 40: 201–209.
Van der Meere JJ (2002) The role of attention. In: Sandberg S, ed. Monographs on Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. Hyperactivity Disorders, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, 162–213.
Weglage J, Pietsch M, Fűnders B, Koch HG, Ullrich K (1996) Deficits in selective and sustained attention processes in early treated children with phenylketonuria—result of impaired frontal lobe functions? Eur J Pediatr 155: 200–204.
Weglage J, Oberwittler C, Marquardt T, et al (2000) Neurological deterioration in adult phenylketonuria. J Inherit Metab Dis 23: 83–83.
Welsh MC, Pennington BF, Ozonoff S, Rouse B, McCabe ERB (1990) Neuropsychology of early treated phenylketonuria: specific executive function deficits. Child Dev 61: 1697–1713.
Wickens C, Kramer A, Vanasse L, Donchin E (1983) Performance of concurrent tasks. A psychophysiological analysis of the reciprocity of information-processing resources. Science 221: 1080–1082.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wiersema, J.R., der Meere, J.J.v. & Roeyers, H. State regulation and response inhibition in children with ADHD and children with early- and continuously treated phenylketonuria: An event-related potential comparison. J Inherit Metab Dis 28, 831–843 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-005-0110-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-005-0110-1