Summary
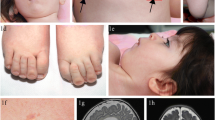
Congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDG) represent a group of inherited multiorgan diseases caused by defects in the biosynthesis of glycoproteins. We report on two dysmorphic siblings with severe liver disease who died at the age of a few weeks. Increased activities of lysosomal enzymes in plasma were found, though total sialic acid in plasma was strongly decreased. Isoelectric focusing of serum sialotransferrins showed a type 2-like CDG pattern. Some of the known CDG subtypes were excluded. O-Glycosylation was investigated by isoelectric focusing of apolipoprotein C-III, which showed increased fractions of hyposialylated isoforms. In a consecutive study a defect in the conserved oligomeric Golgi complex was established at the level of subunit COG-7, leading to disruption of multiple glycosylation functions of the Golgi. This report on patients with a new variant of CDG, due to a multiple Golgi defect, emphasizes in addition to sialotransferrins the importance of analysis of a serum O-linked glycoprotein, e.g. apolipoprotein C-III, in unclassified CDG-X cases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barone R, Carchon H, Jansen E, et al (1998) Lysosomal enzyme activities in serum and leukocytes from patients with carbohydrate-deficient glycoprotein syndrome type IA (phosphomannomutase deficiency). J Inherit Metab Dis 21: 167–172.
Beltran-Valero de Bernabé D, Currier S, Steinbrecher A, et al (2002) Mutations in the O-mannosyltransferase gene POMT1 give rise to the severe neuronal migration disorder Walker–Warburg syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 71: 1033–1043.
Cantor AB, Baranski TJ, Kornfeld S (1992) Lysosomal enzyme phosphorylation. II. Protein recognition determinants in either lobe of procathepsin D are sufficient for phosphorylation of both the amino and carboxyl lobe oligosaccharides. J Biol Chem 267: 23349–23356.
Chantret I, Dancourt J, Dupre T, et al (2003) A deficiency in dolichyl-P-glucose:Glc1 Man9GlcNAc2-PP-dolichyl alpha3-glucosyltransferase defines a new subtype of congenital disorders of glycosylation. J Biol Chem 278: 9962–9971.
de Koning TJ, Borland L, van Diggelen OP, et al (1998) A novel disorder of N-glycosylation due to phosphomannose isomerase deficiency. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 245: 38–42.
De Praeter CM, Gerwig GJ, Bause E, et al (2000) A novel disorder caused by defective biosynthesis of N-linked oligosaccharides due to glucosidase I deficiency. Am J Hum Genet 66: 1744–1756.
Frank CG, Grubenmann CE, Eyaid W, Berger EG, Aebi M, Hennet T (2004) Identification and functional analysis of a defect in the human ALG9 gene: definition of congenital disorder of glycosylation type IL. Am J Hum Genet 75: 146–150.
Ghosh P, Griffith J, Geuze HJ, Kornfeld S (2003) Mammalian GGAs act together to sort mannose 6-phosphate receptors. J Cell Biol 163: 755–766.
Grubenmann CE, Frank CG, Hulsmeier AJ, et al (2004) Deficiency of the first mannosylation step in the N-glycosylation pathway causes congenital disorder of glycosylation type Ik. Hum Mol Genet 13: 535–542.
Grunewald S, Imbach T, Huijben K, et al (2000) Clinical and biochemical characteristics of congenital disorder of glycosylation type Ic, the first recognized endoplasmic reticulum defect in N-glycan synthesis. Ann Neurol 47: 776–781.
Hanßke B, Thiel C, Lubke T, et al (2002) Deficiency of UDP-galactose:N-acetylglucosamine beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase I causes the congenital disorder of glycosylation type IId. J Clin Invest 109: 725–733.
Hayakawa K, De Felice C, Watanabe T (1993) Determination of free N-acetylneuraminic acid in human body fluids by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorimetric detection. J Chromatogr 620: 25–31.
Imbach T, Schenk B, Schollen E, et al (2000) Deficiency of dolichol-phosphate-mannose synthase-1 causes congenital disorder of glycosylation type Ie. Clin Invest 105: 233–239.
Jaeken J (2003) Komrower Lecture. Congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDG): It’s all in it! J Inherit Metab Dis 26: 99–118.
Jaeken J, De Cock P, Stibler H, et al (1993) Carbohydrate-deficient glycoprotein syndrome type II. J Inherit Metab Dis 16: 1041.
Jaeken J, Kint J, Spaapen L (1992) Serum lysosomal enzyme abnormalities in galactosaemia. Lancet 340: 1472–1473.
Jaeken J, Schachter H, Carchon H, De Cock P, Coddeville B, Spik G (1994) Carbohydrate deficient glycoprotein syndrome type II: a deficiency in Golgi localised N-acetyl-glucosaminyltransferase II. Arch Dis Child 71: 123–127.
Korner C, Knauer R, Stephani U, Marquardt T, Lehle L, von Figura K (1999). Carbohydrate deficient glycoprotein syndrome type IV: deficiency of dolichyl-P-Man:Man(5)GlcNAc(2)-PP-dolichyl mannosyltransferase. EMBO J 18: 6816–6822.
Kranz C, Denecke J, Lehrman MA, et al (2001) A mutation in the human MPDU1 gene causes congenital disorder of glycosylation type If (CDG-If). J Clin Invest 108: 1613–1619.
Lind T, Tufaro F, McCormick C, Lindahl U, Lidholt K (1998) The putative tumor suppressors EXT1 and EXT2 are glycosyltransferases required for the biosynthesis of heparan sulfate. J Biol Chem 273: 26265–26268.
Lubke T, Marquardt T, Etzioni A, Hartmann E, von Figura K, Korner C (2001) Complementation cloning identifies CDG-IIc, a new type of congenital disorders of glycosylation, as a GDP-fucose transporter deficiency. Nature Genetics 28: 73–76.
Marquardt T, Denecke J (2003) Congenital disorders of glycosylation: review of their molecular bases, clinical presentations and specific therapies. Eur J Pediatr 162: 359–379.
Quentin E, Gladen A, Roden L, Kresse H (1990) A genetic defect in the biosynthesis of dermatan sulfate proteoglycan: galactosyltransferase I deficiency in fibroblasts from a patient with a progeroid syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 1342–1346.
Thiel C, Schwarz M, Hasilik M, et al (2002) Deficiency of dolichyl-P-Man:Man7GlcNAc2-PP-dolichyl mannosyltransferase causes congenital disorder of glycosylation type Ig. Biochem J 367: 195–201.
Thiel C, Schwarz M, Peng J, et al (2003) A new type of congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDG-Ii) provides new insights into the early steps of dolichol-linked oligosaccharide biosynthesis. Biol Chem 278: 22498–22505.
Ungar D, Oka T, Brittle EE, et al (2002) Characterization of a mammalian Golgi-localized protein complex, COG, that is required for normal Golgi morphology and function. Cell Biol 157: 405–415.
Van Eijk HG, van Noort WL, Kroos MJ, van der Heul C (1982) The heterogeneity of human serum transferrin and human transferrin preparations on isoelectric focusing gels; no functional difference of the fractions in vitro. Clin Chim Acta 121: 209–216.
Van Schaftingen E, Jaeken J (1995) Phosphomannomutase deficiency is a cause of carbohydrate-deficient glycoprotein syndrome type I. FEBS Lett 377: 318–320.
Wopereis S, Grunewald S, Morava E, et al (2003) Apolipoprotein C-III isofocusing in the diagnosis of genetic defects in O-glycan biosynthesis. Clin Chem 49: 1839–1845.
Wu X, Rush JS, Karaoglu D, et al (2003) Deficiency of UDP-GlcNAc:dolichol phosphate N-acetylglucosamine-1 phosphate transferase (DPAGT1) causes a novel congenital disorder of glycosylation type Ij. Hum Mutat 22: 144–150.
Wu X, Steet RA, Bohorov O, et al (2004) Mutation of the COG complex subunit gene COG7 causes a lethal congenital disorder. Nature Medicine 10: 518–523.
Yoshida A, Kobayashi K, Manya H, et al (2001) Muscular dystrophy and neuronal migration disorder caused by mutations in a glycosyltransferase, POMGnT1. Dev Cell 1: 717–724.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spaapen, L.J.M., Bakker, J.A., van der Meer, S.B. et al. Clinical and biochemical presentation of siblings with COG-7 deficiency, a lethal multiple O- and N-glycosylation disorder. J Inherit Metab Dis 28, 707–714 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-005-0015-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-005-0015-z