Abstract
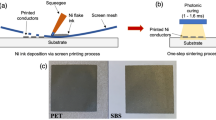
This study reports on the fabrication of biocompatible organic devices by means of inkjet printing with a novel combination of materials. The devices were fabricated on Parylene C (PaC), a biocompatible and flexible polymer substrate. The contact tracks were inkjet-printed using a silver nanoparticle ink, while the active sites were inkjet-printed using a poly (3,4ethylenedioxythiophene)/polystyrene sulfonate (PEDOT:PSS) solution. To insulate the final device, a polyimide ink was used to print a thick film, leaving small open windows upon the active sites. Electrical characterization of the final device revealed conductivities in the order of 103 and 102 S.cm−1 for Ag and PEDOT based inks, respectively. Cell adhesion assays performed with PC-12 cells after 96 h of culture, and B16F10 cells after 24 h of culture, demonstrated that the cells adhered on top of the inks and cell differentiation occurred, which indicates Polyimide and PEDOT:PSS inks are non-toxic to these cells. The results indicate that PaC, along with its surface-treated variants, is a potentially useful material for fabricating cell-based microdevices.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Abdulghani, P.G. Morouço, Biofabrication for osteochondral tissue regeneration: Bioink printability requirements. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 30, 1–13 (2019)
M.R. Abidian, J.M. Corey, D.R. Kipke, D.C. Martin, Conducting-polymer nanotubes improve electrical properties mechanical adhesion neural attachment and neurite outgrowth of neural electrodes. Small 6(3), 421–429 (2010)
M.R. Abidian, D.C. Martin, Experimental and theoretical characterization of implantable neural microelectrodes modified with conducting polymer nanotubes. Biomaterials 29, 1273–1283 (2008)
Adly N, Weidlich S, Seyock S, Brings F, Yakushenko A, Offenhäusser A, Wolfrum B. Printed microelectrode arrays on soft materials: from PDMS to hydrogels. npj Flex. Electron. 2018;2:15
M. Asplund, T. Nyberg, O. Inganäs, Electroactive polymers for neural interfaces. Polym. Chem. 1, 1374–1391 (2010)
A. Blau, A. Murr, S. Wolff, E. Sernagor, P. Medini, G. Iurilli, C. Ziegler, F. Benfenati, Flexible all-polymer microelectrode arrays for the capture of cardiac and neuronal signals. Biomaterials 32, 1778–1786 (2011)
E. Bystrenova, M. Jelitai, I. Tonazzini, A.N. Lazar, M. Huth, P. Stoliar, C. Dionigi, M.G. Cacace, B. Nickel, E. Madarasz, F. Biscarini, Neural networks grown on organic semiconductors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 18(12), 1751–1756 (2008)
T.Y. Chang, V.G. Yadav, S.D. Leo, A. Mohedas, B. Rajalingam, C.-L. Chen, S. Selvarasah, M.R. Dokmeci, A. Khademhosseini, Cell and protein compatibility of Parylene-C surfaces. Langmuir 23(23), 11718–11725 (2007)
X. Cui, D.C. Martin, Electrochemical deposition and characterization of poly(3,4- ethylenedioxythiophene) on neural microelectrode arrays. Sensors Actuators B 89, 92–102 (2003)
N. De la Oliva, M. Mueller, T. Stieglitz, X. Navarro, J. del Valle, On the use of Parylene C polymer as substrate for peripheral nerve electrodes. Sci. Rep. 8, 5965 (2018)
R.D. Deegan, Pattern formation in drying drops. Phys. Rev. E Stat .Phys. Plasmas Fluids Relat. Interdiscip. Topics 61, 475–485 (2000)
M.C. Demirel, E. So, T.M. Ritty, S.H. Naidu, A. Lakhtakia, Fibroblast cell attachment and growth on nanoengineered sculptured thin films. J Biomed Mater Res Part B 81(1), 219–223 (2007)
A. Denneulin, A. Blayo, C. Neuman, J. Bras, Infra-red assisted sintering of inkjet printed silver tracks on paper substrates. J. Nanopart. Res. 13, 3815–3823 (2011)
M. ElMahmoudy, A.M. Charrier, G.G. Malliaras, S. Sanaur, Facile nanopatterning of PEDOT:PSS thin films. Adv. Mater. Technol. 3, 1700344 (2018)
M. ElMahmoudy, V.F. Curto, M. Ferro, A. Hama, G.G. Malliaras, R.P. O'Connor, S. Sanaur, Electrically controlled cellular migration on a periodically micropatterned PEDOT:PSS conducting polymer platform. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 136, 47029 (2019)
F. Fallegger, G. Schiavone, Lacour. SP. Conformable Hybrid Systems for Implantable Bioelectronic Interfaces. Adv. Mater. 32, 1903904 (2020)
I.J. Fernandes, A.F. Aroche, A. Schuck, P. Lamberty, C.R. Peter, W. Hasenkamp, T.L.A.C. Rocha, Silver nanoparticle conductive inks: Synthesis, characterization, and fabrication of inkjet-printed flexible electrodes. Sci. Rep. 10, 878 (2020)
S.R. Forrest, The path to ubiquitous and low-cost organic electronic appliances on plastic. Nature 428, 911–918 (2004)
A.P. Gerratt, H.O. Michaud, S.P. Lacour, Elastomeric electronic skin for prosthetic tactile sensation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 25, 2287–2295 (2015)
R.A. Green, N.H. Lovell, L.A. Poole-Warren, Cell attachment functionality of bioactive conducting polymers for neural interfaces. Biomaterials 30, 3637–3644 (2009)
N.K. Guimard, N. Gomez, C.E. Schmidt, Conducting polymers in biomedical engineering. Prog. Polym. Sci. 32, 876–921 (2007)
F.K. Hansen, The Measurement of Surface Energy of Polymers by Means of Contact Angles of Liquids on Solid Surfaces - a Short Overview of Frequently Used Methods (University of Oslo, 2004)
T.J.J. Hondrich, B. Lenyk, P. Shokoohimehr, D. Kireev, V. Maybeck, D. Mayer, A. Offenhäusser, MEA recordings and cell–substrate investigations with Plasmonic and transparent, tunable holey gold. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 11, 46451–46461 (2019)
J. Isaksson, P. Kjall, D. Nilsson, N.D. Robinson, M. Berggren, A. Richter-Dahlfors, Electronic control of Ca2+ signalling in neuronal cells using an organic electronic ion pump. Nat. Mater. 6(9), 673–679 (2007)
J. Kettle, T. Lamminmäki, P. Gane, A review of modified surfaces for high speed inkjet coating. Surf. Coat. Tech. 204, 2103–2109 (2010)
D. Khodagholy, T. Doublet, M. Gurfinkel, P. Quilichini, E. Ismailova, P. Leleux, T. Herve, S. Sanaur, C. Bernard, G.G. Malliaras, Highly conformable conducting polymer electrodes for In Vivo recordings. Adv. Mater. 23, H268–H272 (2011)
D. Khodagholy, T. Doublet, P. Quilichini, M. Gurfinkel, P. Leleux, A. Ghestem, E. Ismailova, T. Hervé, S. Sanaur, C. Bernard, G.G. Malliaras, In vivo recordings of brain activity using organic transistors. Nat. Commun. 4, 1575 (2013)
B.J. Kim, E. Meng, Micromachining of Parylene C for bioMEMS. Polym. Adv. Technol. 27, 564–576 (2016)
D.-H. Kim, S. Richardson-Burns, L. Povlich, M.R. Abidian, S. Spanninga, J. Hendricks, D.C. Martin, in Indwelling Neural Implants: Strategies for Contending with the In-Vivo Environment, ed. by W. M. Reichert. (CRC Press Taylor Francis, Boca Raton FL, 2008), p. 271
S. Lacour, G. Courtine, J. Guck, Materials and technologies for soft implantable neuroprostheses. Nat. Rev. Mater. 1, 16063 (2016)
J. Lai, B. Sunderland, J. Xue, S. Yan, W. Zhao, M. Folkard, B.D. Michael, Y. Wang, Study on hydrophilicity of polymer surfaces improved by plasma treatment. Appl Surf Science 252(10), 3375–3379 (2006)
Z. Liu, Y. Su, K. Varahramyan, Inkjet-printed silver conductors using silver nitrate ink and their electrical contacts with conducting polymers. Thin Solid Films 478(1–2), 275–279 (2005)
K.A. Ludwig, J.D. Uram, J. Yang, D.C. Martin, D.R. Kipke, Chronic neural recordings using silicon microelectrode arrays electrochemically deposited with a poly(3,4- ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) film. J. Neural Eng. 3, 59–70 (2006)
G.G. Malliaras, R.H. Friend, An organic electronics primer. Phys. Today 58, 53–58 (2005)
D. Müller, C.R. Rambo, D.O.S. Recouvreux, L.M. Porto, G.M.O. Barra, Chemical in situ polymerization of polypyrrole on bacterial cellulose nanofibers. Synth. Met. 161, 106–111 (2011)
T. Nyberg, A. Shimada, K. Torimitsu, Ion conducting polymer microelectrodes for interfacing with neural networks. J Neurosci Meth. 160, 16–25 (2007)
R. Owens, G. Malliaras, Organic electronics at the Interface with biology. MRS Bull. 35, 449–456 (2010)
B.D. Paulsen, K. Tybrandt, E. Stavrinidou, et al., Organic mixed ionic–electronic conductors. Nat. Mater. 19, 13–26 (2020)
L. Poole-Warren, N. Lovell, S. Baek, R. Green, Development of bioactive conducting polymers for neural interfaces. Expert Rev Med Devices 7(1), 35–49 (2010)
T. Roberts, J.B. De Graaf, C. Nicol, T. Hervé, M. Fiocchi, S. Sanaur, Flexible inkjet-printed multielectrode arrays for neuromuscular cartography. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 5, 1462–1470 (2016)
M. Shur, F. Fallegger, E. Pirondini, A. Roux, A. Bichat, Q. Barraud, G. Courtine, S.P. Lacour, Soft printable electrode coating for neural interfaces. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 3, 4388–4397 (2020)
M. Singh, H.M. Haverinen, P. Dhagat, G.E. Jabbour, Inkjet printing – Process and its applications. Adv. Mater. 21, 1–13 (2009)
T. Someya, Z. Bao, G. Malliaras, The rise of plastic bioelectronics. Nature 540, 379–385 (2016)
S. Staufert, H. Torlakcik, S. Pané, C. Hierold, Highly adherent Parylene-C coatings with Nanostructuring for enhanced cell adhesion and growth. IEEE Transactions on NanoBioscience 18(2), 230–233 (2019)
E. Tekin, B. De Gans, U.S. Schubert, Ink-jet printing of polymers – From single dots to thin film libraries. J. Mater. Chem. 14, 2627–2632 (2004)
G.G. Wallace, S.E. Moulton, G.M. Clark, Electrode-cellular interface. Science 324, 185–186 (2009)
L. Wei, A. Lakhtakia, A.P. Roopnariane, T.M. Ritty, Human fibroblast attachment on fibrous parylene-C thin-film substrates. Mater Sci Eng C 30(8), 1252–1259 (2010)
B.A. Weisenberg, D.L. Mooradian, Hemocompatibility of materials used in microelectromechanical systems: Platelet adhesion and morphology in vitro. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 60(2), 283–291 (2002)
D. Wright, B. Rajalingam, J. Karp, S. Selvarasah, Y. Ling, J. Yeh, R. Langer, M.R. Dokmeci, A. Khademhosseini, Reusable reversibly sealable parylene membranes for cell and protein patterning. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 85A(2), 530–538 (2008)
D. Wright, B. Rajalingam, S. Selvarasah, M.R. Dokmeci, A. Khademhosseini, Generation of static and dynamic patterned co-cultures using microfabricated parylene-C stencils. Lab Chip 7(10), 1272–1279 (2007)
S. Wu, Calculation of interfacial tension in polymer systems. J. Polym. Sci., C Polym Symp. 34, 19–30 (1971)
F. Xue, Z. Liu, Y. Su, K. Varahramyan, Inkjet printed silver source/drain electrodes for low-cost polymer thin film transistors. Microelectron. Eng. 83, 298–302 (2006)
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa e Inovação do Estado de Santa Catarina (FAPESC, Brazil) under contract number 9307/2009-3, National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq/Brazil) and Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Level Personnel (CAPES/Brazil), Finance Code 001. The authors thank the Central Laboratory of Electronic Microscopy (LCME-UFSC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mandelli, J.S., Koepp, J., Hama, A. et al. Cell viability and cytotoxicity of inkjet-printed flexible organic electrodes on parylene C. Biomed Microdevices 23, 2 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-020-00542-z
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-020-00542-z