Abstract
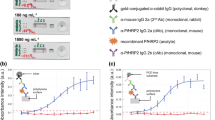
Point-of-care (POC) diagnostics are critically needed for the detection of infectious diseases, particularly in remote settings where accurate and appropriate diagnosis can save lives. However, it is difficult to implement immunoassays, and specifically immunoassays relying on signal amplification using silver staining, into POC diagnostic devices. Effective immobilization of antibodies in such devices is another challenge. Here, we present strategies for immobilizing capture antibodies (cAbs) in capillary-driven microfluidic chips and implementing a gold-catalyzed silver staining reaction. We illustrate these strategies using a species/anti-species immunoassay and the capillary assembly of fluorescent microbeads functionalized with cAbs in “bead lanes”, which are engraved in microfluidic chips. The microfluidic chips are fabricated in silicon (Si) and sealed with a dry film resist. Rabbit IgG antibodies in samples are captured on the beads and bound by detection antibodies (dAbs) conjugated to gold nanoparticles. The gold nanoparticles catalyze the formation of a metallic film of silver, which attenuates fluorescence from the beads in an analyte-concentration dependent manner. The performance of these immunoassays was found comparable to that of assays performed in 96 well microtiter plates using “classical” enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The proof-of-concept method developed here can detect 24.6 ng mL−1 of rabbit IgG antibodies in PBS within 20 min, in comparison to 17.1 ng mL−1 of the same antibodies using a ~140-min-long ELISA protocol. Furthermore, the concept presented here is flexible and necessitate volumes of samples and reagents in the range of just a few microliters.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.A. Baker, C.T. Duong, A. Grimley, M.G. Roper, Bioanalysis 1, 967 (2009)
BIO Ventures for Global Health, The Diagnostics Innovation Map: Medical Diagnostics for the Unmet Needs of the Developing World (2010)
C.D. Chin, V. Linder, S.K. Sia, Lab Chip 12, 2118 (2012)
M. A. Hayat (ed.), Immunogold-Silver Staining: Principles, Methods, and Applications (CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, 1995)
C. Holgate, P. Jackson, P. Cowen, C. Bird, J. Histochem. Cytochem. 31(7), 938-944 (1983)
H. Gai, Y. Li, E. S. Yeung, Top Curr Chem 304, 171-201 (2011)
M. Hu, J. Yan, Y. He, H. Lu, L. Weng, S. Song, C. Fan, L. Wang, ACS Nano 4, 488 (2010)
B. Hu, J. Li, L. Mou, Y. Liu, J. Deng, W. Qian, J. Sun, R. Cha, X. Jiang, Lab Chip 17, 2225 (2017)
B. Kuswandi, J.H. Nuriman, W. Verboom, Anal. Chim. Acta 601, 141 (2007)
S.W. Lin, C.H. Chang, C.H. Lin, Genomic Med. Biomarkers, Heal. Sci. 3, 27 (2011)
R. Liu, Y. Zhang, S. Zhang, W. Qiu, Y. Gao, Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 49, 121 (2014)
M. Mirasoli, M. Guardigli, E. Michelini, A. Roda, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 87, 36 (2014)
P. Novo, D.M. França Prazeres, V. Chu, J.P. Conde, Lab Chip 11, 4063 (2011)
N. Patel, B.F. Rocks, M.P. Bailey, J. Clin. Pathol. 44, 334 (1991)
R.W. Peeling, D. Mabey, Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 16, 1062 (2010)
B.F. Rocks, N. Patel, M.P. Bailey, B. Royaj, S. County, E. Road, Ann. Clin. Biochem. 28, 155 (1991)
S. Sharma, J. Zapatero-Rodríguez, P. Estrela, R. O’Kennedy, Biosensors 5, 577 (2015)
I.C. Shekarchi, J.L. Sever, L. Nerurkar, D. Fuccillo, J. Clin. Microbiol. 21, 92 (1985)
J. Sun, Y. Xianyu, X. Jiang, Chem. Soc. Rev. 43, 6239 (2014)
Y. Temiz, E. Delamarche, J. Micromech. Microeng. 24, 97001 (2014)
UNITAID, Malaria Diagnostics Technology and Market Landscape (2016), https://unitaid.eu/assets/Malaria_Diagnostics_Technology_and_Market_Landscape_3rd_Edition_April_2016-1.pdf. Accessed 14 May 2018
UNITAID, HIV Rapid Diagnostics for Self-Testing, 3rd edn. (2017), https://unitaid.eu/assets/HIV-Rapid-Diagnostic-Tests-for-Self-Testing_Landscape-Report_3rd-edition_July-2017.pdf. Accessed 14 May 2018
A. Wada, Y. Sakoda, T. Oyamada, H. Kida, J. Virol. Methods 178, 82 (2011)
H. Xu, X. Mao, Q. Zeng, W. Shengfu, A.-N. Kawde, G. Liu, Anal. Chem. 81, 669 (2009)
P. Yager, T. Edwards, E. Fu, K. Helton, K. Nelson, M.R. Tam, B.H. Weigl, Nature 442, 412 (2006)
F.Y. Yu, M.M. Vdovenko, J.J. Wang, I.Y. Sakharov, J. Agric. Food Chem. 59, 809 (2011)
Acknowledgements
Ngoc M. Pham is supported through the Engineering for Development doctoral scholarship by ETH Global and the Sawiris Foundation for Social Development. Walter Karlen is supported through the Swiss National Science Foundation professorship award 150640 “Intelligent point-of-care monitoring”. Yuksel Temiz, Robert D. Lovchik and Emmanuel Delamarche thank Elisa Hemmig and Onur Gökçe for discussions and Walter Riess and the IBM Research Frontiers Institute for their continuous support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pham, N.M., Rusch, S., Temiz, Y. et al. A bead-based immunogold-silver staining assay on capillary-driven microfluidics. Biomed Microdevices 20, 41 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-018-0284-6
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-018-0284-6