Abstract
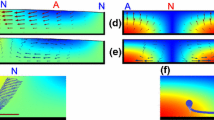
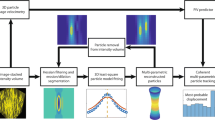
Accurate positioning of biological cells or microscopic particle without directly contacting them is a challenging task in biomedical engineering. Various trapping methods for controlling the position of a particle have been suggested. The common driving methods are based on laser and ultrasonic actuation principles. In this work we suggest a design for a hydrodynamic particle manoeuvring system. The system operates using steady streaming in a viscous fluid media induced by high frequency vibration of piezoelectric cantilevers. A particle within the workspace of the system can be trapped and manipulated to a desired position by the fairly unidirectional flow field created by the beams. In this paper, the flow field in the particle manipulation system is characterized numerically and experimentally. We find that the flow field resembles the analytical solutions of a flow field created by an oscillating sphere. Furthermore, we validate numerically the quadratic relation between the steady streaming velocity and the vibration amplitude of the beam. The calibration of the piezoelectric actuator’s oscillation amplitudes enables effective positioning of particles with a diameter of 20 um to 1 mm. We find that a 30X0.8X2 m m 3 piezoelectric beam vibrating at its first resonance frequency, 200 Hz, is able to move a particle at a typical flow velocity ranging between 0.05 mm/sec and 0.13 mm/s in 430 cSt Si oil (Re=0.2).





























Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Abadi, G. Kosa, Piezoelectric beam for intrabody propulsion controlled by embedded sensing. In print in Mechatronics, IEEE/ASME Transactions (2016)
A. Ainla, G.D.M. Jeffries, R. Brune, O. Orwar, A. Jesorka, A multifunctional pipette. Lab. Chip. 12(7), 1255–1261 (2012)
M.A. Barber, A new method of isolating micro-organisms. J. Kansas Med. Sot. 4, 489–494 (1904)
R.W. Bowman, G. M. Gibson, A. Linnenberger, D.B. Phillips, J.A. Grieve, D.M. Carberry, S. Serati, M.J. Miles, M. J. Padgett, Red tweezers: Fast, customisable hologram generation for optical tweezers. Comput. Phys. Commun. 185(1), 268–273 (2014)
J. Castillo, M. Dimaki, W. E. Svendsen, Manipulation of biological samples using micro and nano techniques. Integr. Biol. 1(1), 30–42 (2009)
K. Chong, S.D. Kelly, S. Smith, J.D. Eldredge, Inertial particle trapping in viscous streaming. Phys. Fluids. 25(3), 003622 (2013)
J. P. Desai, A. Pillarisetti, A.D. Brooks, Engineering approaches to biomanipulation. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 9, 35–53 (2007)
E. Diller, J. Giltinan, G.Z. Lum, Z. Ye, S. Metin, Six-degree-of-freedom magnetic actuation for wireless microrobotics The International Journal of Robotics Research page 0278364915583539 (2015)
T. Fukuda, F. Arai, M. Nakajima, Micro-nanorobotic manipulation systems and their applications Springer Science & Business Media (2013)
C. Gosse, V. Croquette, Magnetic tweezers: micrOmanipulation and force measurement at the molecular level. Biom. J. 82(6), 3314–3329 (2002)
D.G. Grier, Y. Roichman, Holographic optical trapping. Appl. Opt. 45(5), 880–887 (2006)
B. Hammarström, M. Evander, H. Barbeau, M. Bruzelius, J. Larsson, T. Laurell, J. Nilsson, Non-contact acoustic cell trapping in disposable glass capillaries. Lab Chip. 10(17), 2251–2257 (2010)
T. Hayakawa, S. Sakuma, F. Arai, On-chip 3d rotation of oocyte based on a vibration-induced local whirling flow. Microsystems & Nanoengineering, volume 1 (2015)
J. Holtsmark, I. Johnsen, S. To, S. Skavlem, Boundary layer flow near a cylindrical obstacle in an oscillating, incompressible fluid. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 26(1), 26–39 (1954)
T.A. House, V.H. Lieu, D.T. Schwartz, A model for inertial particle trapping locations in hydrodynamic tweezers arrays. J. Micromech. Microeng. 24(4), 045–019 (2014)
J.S. Jeong, J.W. Lee, C.Y. Lee, S.Y. Teh, A. Lee, K. Kirk Shung, Particle manipulation in a microfluidic channel using acoustic trap. Biomed. Microdevices. 13(4), 779–788 (2011)
L. Johansson, Acoustic manipulation of particles and fluids in microfluidic systems (2009)
A. Karimi, S. Yazdi, A.M. Ardekani, Hydrodynamic mechanisms of cell and particle trapping in microfluidics. Biomicrofluidics. 7(2), 021–501 (2013)
I.S.M. Khalil, V. Magdanz, S. Sanchez, O.G. Schmidt, S. Misra, E. Ben-Jacob, Wireless magnetic-based closed-loop control of self-propelled microjets. PloS one. 9(2), e83053 (2014)
I.S.M. Khalil, M.P. Pichel, L. Abelmann, S. Misra, Closed-loop control of magnetotactic bacteria. Int. J. Robot. Res. 32(6), 637–649 (2013)
K. Khoshmanesh, S. Nahavandi, S. Baratchi, A. Mitchell, K. Kalantar-zadeh, Dielectrophoretic platforms for bio-microfluidic systems. Biosensors and Bioelectronics. 26(5), 1800–1814 (2011)
S. Kim, F. Shafiei, D. Ratchford, X. Li, Controlled afm manipulation of small nanoparticles and assembly of hybrid nanostructures. Nanotechnology. 22(11), 115–301 (2011)
V. Korzh, U. Strähle, Marshall barber and the century of microinjection: from cloning of bacteria to cloning of everything. Differentiation. 70(6), 221–226 (2002)
G. Kósa, M. Shoham, Z. Menashe, Propulsion method for swimming microrobots. IEEE Trans. Robot. 23(1), 137–150 (2007)
J.-S. Kwon, S.T. Wereley, Towards new methodologies for manipulation of colloidal particles in a miniaturized fluidic device: optoelectrokinetic manipulation technique. J. Fluids Eng. 135(2), 021–306 (2013)
J. Lee, S.-Y. Teh, A. Lee, H.H. Kim, C. Lee, K.K. Shung, Single beam acoustic trapping. Appl. Phys. Lett. 95(7), 073–701 (2009)
J. Lighthill, Acoustic streaming. J. Sound Vib. 61(3), 391–418 (1978)
B.R. Lutz, J. Chen, D.T. Schwartz, Hydrodynamic tweezers: 1. noncontact trapping of single cells using steady streaming microeddies. Anal. Chem. 78(15), 5429–5435 (2006)
V. Marx, Biophysics: using sound to move cells. Nat. Methods. 12(1), 41–44 (2015)
L. Meirovitch, R.G. Parker, Fundamentals of vibrations. Appl. Mech. Rev. 54, 100 (2001)
K.C. Neuman, A. Nagy, Single-molecule force spectroscopy: optical tweezers, magnetic tweezers and atomic force microscopy. Nat. methods. 5(6), 491–505 (2008)
P. Neuži, S. Giselbrecht, K. Länge, T.J. Huang, A. Manz, Revisiting lab-on-a-chip technology for drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 11(8), 620–632 (2012)
S. Oberti, D. Moeller, A. Neild, J. Dual, F. Beyeler, B.J. Nelson, S. Gutmann, Strategies for single particle manipulation using acoustic and flow fields. Ultrasonics. 50(2), 247–257 (2010)
C. Qian, H. Huang, L. Chen, X. Li, Z. Ge, T. Chen, Z. Yang, L. Sun, Dielectrophoresis for bioparticle manipulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 15(10), 18281–18309 (2014)
N. Riley, Oscillating viscous flows. Mathematika. 12(02), 161–175 (1965)
N. Riley, Steady streaming. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 33(1), 43–65 (2001)
P. Sajeesh, A. Kumar Sen, Particle separation and sorting in microfluidic devices: a review. Microfluidics and nanofluidics. 17(1), 1–52 (2014)
H. Schlichting, B. ebener, Berechnung ebener periodischer grenzschichtströmungen. Phys. Z. 33(1932), 327–335 (1932)
E.B. Steager, M.S. Sakar, C. Magee, M. Kennedy, A. Cowley, V Kumar, Automated biOmanipulation of single cells using magnetic microrobots. Int. J. Rob. Res. 32(3), 346–359 (2013)
J.T. Stuart, Unsteady boundary layers(unsteady boundary layer flow, considering stokes, rayleigh and heisenberg-tollmien theories application to oscillatory, fluctuating, impulsive and rotational effects). Recent research on unsteady boundary layers (1972)
E.B. Tadmor, G. Kósa, Electromechanical coupling correction for piezoelectric layered beams. J. Microelectron. Syst. 12(6), 899–906 (2003)
M. Tanyeri, C.M. Schroeder, Manipulation and confinement of single particles using fluid flow. Nano Lett. 13(6), 2357–2364 (2013)
Y. Temiz, R.D. Lovchik, G.V. Kaigala, E. Delamarche, Lab-on-a-chip devices how to close and plug the lab? Microelectron. Eng. 132, 156–175 (2015)
W. Thielicke, E. J. Stamhuis. Pivlabtime-resolved digital particle image velocimetry tool for matlab (version. 1, 35 (2014) http://pivlab.blogspot.co.il/
W. Thielicke, E. J. Stamhuis, Pivlab–towards user-friendly, affordable and accurate digital particle image velocimetry in matlab. Journal of Open Research Software. 2(1), e30 (2014)
M. Van Dyke, An album of fluid motion (1982)
C.-Y. Wang, On high-frequency oscillatory viscous flows. J. Fluid Mech. 32(01), 55–68 (1968)
J. Wang, W. Gao, Nano/microscale motors: biomedical opportunities and challenges. ACS nano. 6(7), 5745–5751 (2012)
X. Tiantian, Y. Jiangfan, X. Yan, H. Choi, L. Zhang, Magnetic actuation based motion control for microrobots An overview. Micromachines. 6(9), 1346–1364 (2015)
Y. Yalikun, A. Toshifumi, Y. Kanda, K. Morishima, in Non-contact 3d rotation and capture method for bio-object based on microfluidic stream. in Micro-NanoMechatronics and Human Science (MHS), 2014 International Symposium on, pages 1–4. IEEE, (2014)
Z. Ye, C. Edington, A.J. Russell, M. Sitti, in Versatile non-contact micro-manipulation method using rotational flows locally induced by magnetic microrobots. in Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), 2014 IEEE/ASME International Conference on, pages 26–31. IEEE, (2014)
H. Zhang, K.-K. Liu, Optical tweezers for single cells. J. R. Soc. Interface. 5(24), 671–690 (2008)
X. Zhang, L. Ma, Y. Zhang, High-resolution optical tweezers for single-molecule manipulation. Yale J. Biol. Med. 86(3), 367 (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
(WMV 8.17 MB)
(WMV 7.73 MB)
(AVI 18.3 MB )
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amit, R., Abadi, A. & Kosa, G. Characterization of steady streaming for a particle manipulation system. Biomed Microdevices 18, 39 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-016-0055-1
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-016-0055-1