Abstract
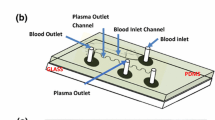
In recent years, microfluidic chips have proven ideal tools for biochemical analysis, which, however, demands a unique and compatible plasma separation scheme. Various research groups have established continuous flow separation methods in microfluidic devices; however, they have worked with relatively small dimension microchannels (similar to the blood cell diameter). The present work demonstrates separation of plasma by utilizing the hydrodynamic separation techniques in microchannels with size of the order of mm. The separation process exploits the phenomenon, which is very similar to that of plasma skimming explained under Zweifach-Fung bifurcation law. The present experiments demonstrates for, the first time, that applicability of the Zweifach-Fung bifurcation law can be extended to dimensions much higher than the suspended particle size. The T-microchannel device (comprising perpendicularly connected blood and plasma channels) were micro-fabricated using conventional PDMS micro-molding techniques. Three variables (feed hematocrit, main channel width, and flow rate distributions) were identified as the important parameters which define the device’s efficiency for the blood plasma separation. A plasma separation efficiency of 99.7 % was achieved at a high flow ratio. Novel concepts of 2-stage or multiple plasma channel designs are also proposed to yield high separation efficiency with undiluted blood. The possible underlying principle causing plasma separation (viz. aggregation and shear thinning) are investigated in detail as part of this work. The results are significant because they show nearly 100 % separations in microchannels which are much easier to fabricate than previously designed devices.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.H. Barbee, G.R. Cokelet, Microvas. Res. 3, 6–16 (1971)
G. Blankensteinand, U.D. Larsen, Biosens Bioelectron 13, 427 (1998)
C. Blattert, R. Jurischka, I. Tahhan, A. Schoth, P. Kerth, W. Menz, Conf Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 4, 2627–2630 (2004)
E. Brunet, G. Degré, F. Okkels, P. Tabeling, J. Colloid Interf Sci 282, 58–68 (2005)
X. Chen, D.F. Cui, C.C. Lui, H. Li, J. Chen, Anal Chem 584, 237–243 (2007)
R. Fahraeus, The suspension stability of the blood. Physiol. Rev., vol. ix, (no. 2), 241–274 (1929)
R. Fahraeus, T. Lindqvist, Am J Physiol 96, 562–568 (1931)
M. Faivre, M. Abkarial, Biorheology 43(2), 147–159 (2006)
B.M. Fenton, R.T. Carr, G.R. Cokelet, Microvasc Res 29, 103–126 (1985)
Y.C. Fung, Microvasc Res 5, 34–48 (1973)
Y.C. Fung, Biomechanics– Mechanical properties of living tissues (Springer – Verlag, New York, 1981)
T. Gudipaty, L.S.L. Cheung, L. Jiang, Y. Zohar, Twelfth International Conference on Miniaturized Systems for Chemistry and Life Sciences, October 12 - 16, San Diego, California, USA (2008)
J.W. Hong, S.R. Quake, Nat Biotechnol 21, 1179–1183 (2003)
D. Huh, J.H. Bahng, Y.B. Ling, H.H. Wei, O.D. Kripfgans, J.B. Fowlkes, J.B. Grotberg, S. Takayama, Anal Chem 79, 1369 (2007)
D.W. Inglis, J.A. Davis, R.H. Austin, J.C. Sturm, Lab Chip 6, 655 (2006)
R.D. Jaggi, R. Sandoz, C.S. Effenhauser, Microfluid. Nanofluid 3, 47–53 (2007)
D. Janasek, J. Franzke, A. Manz, Nature 442, 374–380 (2006)
M.K. Kerhoas, D.M. Kavanagh, R.S. Dhariwal, C.J. Campbelland, M.P.Y. Desmulliez, Lab Chip 10, 1587–1595 (2010)
J.G. Kralj, M.T.W. Lis, M.A. Schmidt, K.F. Jensen, Anal Chem 78, 5019–5025 (2006)
T. Laurell, F. Peterssonand, A. Nilsson, Chem Soc Rev 36, 492 (2007)
H.H. Lipowsky, S. Kovalcheck, B.W. Zweifach, Circ Res 43, 738–749 (1978)
H.H. Lipowsky, S. Usami, S. Chien, Microvasc Res 19, 297–319 (1980)
M.P. MacDonald, G.C. Spalding, K. Dholakia, Nature 426, 421 (2003)
A. Manz, J.C.T. Eijkel, Pure Appl. Chem. 73, 1555–1561 (2001)
J. Moorthy, D.J. Beebe, Lab Chip 3, 62–66 (2003)
N. Pamme, Lab Chip 7, 1644–1659 (2007)
C.W. Park, S.H. Shin, G.M. Kim, J.H. Jang, Y.H. Gu, Key Eng. Mater 326–328, 863–866 (2006)
A. Prabhakar, S. Mukherji, Lab Chip 10, 748–754 (2010a)
A. Prabhakar, S. Mukherji, Lab Chip 10, 3422–3425 (2010b)
A.R. Pries, T.W. Secomb, P. Gaehtgens, Cardiovasc Res 32, 654–667 (1996)
G.W. Schmid-Schonbein, R. Skalak, S. Usami, S. Chien, Microvasc Res 19, 18–44 (1980)
S. Shin, J.X. Houand, J.S. Suh, Korea Aust Rheol J 19(2), 61–66 (2007)
E. Sollier, H. Rostaing, P. Pouteau, Y. Fouillet, L. Achard, Sens. Actuators B 141, 617–624 (2009)
Y. Sugii, R. Okuda, K. Okamoto, H. Madarame, Meas Sci Technol 16, 1126 (2005)
K. Svanes, B.W. Zweifach, Microvasc Res 1, 210–220 (1968)
A.I.R. Villarreal, M. Arundell, M. Carmona, J. Samitier, Lab Chip 10, 211–219 (2010)
M. Yamada, M. Seki, Lab Chip 5, 1233 (2005)
M. Yamada, M. Nakashimaand, M. Seki, Anal Chem 76, 5465–5471 (2004)
S. Yang, A. Undar, J.D. Zahn, Lab Chip 6, 871–880 (2006)
R.T. Yen, Y.C. Fung, Amer. J. Physiol. 235(2), H251–H257 (1978)
Acknowledgements
Thanks are due to Professor Ramgopal Rao for suggesting us this problem. The authors also wish to acknowledge CEN, IIT Bombay (supported by the Department of Information Technology, MCIT, Government of India) for fabrication facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tripathi, S., Prabhakar, A., Kumar, N. et al. Blood plasma separation in elevated dimension T-shaped microchannel. Biomed Microdevices 15, 415–425 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-013-9738-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-013-9738-z