Abstract
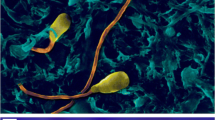
Swimming microrobots are envisioned to impact minimally invasive diagnosis, localized treatment of diseases, and environmental monitoring. Dynamics of micro-scale swimming robots falls in the realm of low Reynolds number, where viscous forces exerted on the robots are dominant over inertia. Viscous forces developed at the interface of the swimming microrobots and the surrounding fluid are a strong function of the body geometry. In this work, a collection of bacteria-powered micro-robots (BacteriaBots) with prolate spheroid, barrel, and bullet-shaped bodies is fabricated and the influence of body shape on the dynamics of the BacteriaBots is investigated. We have experimentally demonstrated that using non-spherical geometries increases the mean directionality of the motion of the BacteriaBots but does not significantly affect their average speed compared with their spherical counterparts. We have also demonstrated that directionality of non-spherical BacteriaBots depends on the aspect ratio of the body and for the case of prolate spheroid, a higher aspect ratio of two led to a larger directionality compared to their low aspect ratio counterparts.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Akin, J. Sturgis, K. Ragheb, D. Sherman, K. Burkholder, J.P. Robinson, A.K. Bhunia, S. Mohammed, R. Bashir, Bacteria-mediated delivery of nanoparticles and cargo into cells. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2, 441–449 (2007)
C.S. Barker, B.M. Prüß, P. Matsumura, Increased motility of Escherichia coli by insertion sequence element integration into the regulatory region of the flhD operon. J. Bacteriol. 186, 7529–7537 (2004)
B. Behkam, M. Sitti, Bacterial flagella-based propulsion and on/off motion control of microscale objects. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 023902 (2007)
B. Behkam, M. Sitti, Effect of quantity and configuration of attached bacteria on bacterial propulsion of microbeads. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 223901 (2008)
B. Behkam, M. Sitti, Bacteria integrated swimming microrobots. 50 years of artificial intelligence 154–163 (2007a)
H.C. Berg, D.A. Brown, Chemotaxis in Escherichia coli analysed by three-dimensional tracking. Nature 239, 500 (1972)
H.C. Berg, Random walks in biology: Princeton Univ Pr. (1993)
J.A. Champion, Y.K. Katare, S. Mitragotri, Making polymeric micro-and nanoparticles of complex shapes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 104, 11901 (2007)
A. Darji, C.A. Guzmán, B. Gerstel, P. Wachholz, K.N. Timmis, J. Wehland, T. Chakraborty, S. Weiss, Oral somatic transgene vaccination using attenuated S. typhimurium. Cell 91, 765–775 (1997)
N. Darnton, L. Turner, K. Breuer, H.C. Berg, Moving fluid with bacterial carpets. Biophys. J. 86, 1863–1870 (2004)
R. Dreyfus, J. Baudry, M.L. Roper, M. Fermigier, H.A. Stone, J. Bibette, Microscopic artificial swimmers. Nature 437, 862–865 (2005)
R. Fernandes, M. Zuniga, F.R. Sassine, M. Karakoy, D.H. Gracias, Enabling Cargo–Carrying Bacteria via Surface Attachment and Triggered Release. Small 7, 588–592 (2011)
Y. Geng, P. Dalhaimer, S. Cai, R. Tsai, M. Tewari, T. Minko, D.E. Discher, Shape effects of filaments versus spherical particles in flow and drug delivery. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2, 249–255 (2007)
S.E.A. Gratton, P.A. Ropp, P.D. Pohlhaus, J.C. Luft, V.J. Madden, M.E. Napier, J.M. DeSimone, The effect of particle design on cellular internalization pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 105, 11613 (2008)
Y. Han, A. Alsayed, M. Nobili, A.G. Yodh, Quasi-two-dimensional diffusion of single ellipsoids: Aspect ratio and confinement effects. Phys. Rev. E 80, 011403 (2009)
J. Happel, H. Brenner, L.R.N. Hydrodynamics Nijhoff. Dordrecht, The Netherlands (1983)
D.M. Heimann, S.A. Rosenberg, Continuous intravenous administration of live genetically modified Salmonella typhimurium in patients with metastatic melanoma. J. Immunother. (Hagerstown, Md: 1997) 26, 179 (2003)
C. Ho, A. Keller, J. Odell, R. Ottewill, Preparation of monodisperse ellipsoidal polystyrene particles. Colloid Polym. Sci. 271, 469–479 (1993)
S. Martel, C.C. Tremblay, S. Ngakeng, G. Langlois, Controlled manipulation and actuation of micro-objects with magnetotactic bacteria. Applied Physics Letters 89:233904-233904-233903 (2006)
S. Muro, C. Garnacho, J.A. Champion, J. Leferovich, C. Gajewski, E.H. Schuchman, S. Mitragotri, V.R. Muzykantov, Control of endothelial targeting and intracellular delivery of therapeutic enzymes by modulating the size and shape of ICAM-1-targeted carriers. Mol. Ther. 16, 1450–1458 (2008)
S. Nuyts, L. Van Mellaert, J. Theys, W. Landuyt, P. Lambin, J. Anné, Clostridium spores for tumor-specific drug delivery. Anti-cancer Drugs 13, 115 (2002)
P. Paglia, E. Medina, I. Arioli, C.A. Guzman, M.P. Colombo, Gene transfer in dendritic cells, induced by oral DNA vaccination with Salmonella typhimurium, results in protective immunity against a murine fibrosarcoma. Blood 92, 3172–3176 (1998)
J.H. Park, G. von Maltzahn, L. Zhang, M.P. Schwartz, E. Ruoslahti, S.N. Bhatia, M.J. Sailor, Magnetic iron oxide nanoworms for tumor targeting and imaging. Adv. Mater. 20, 1630–1635 (2008)
J.H. Park, G. von Maltzahn, L. Zhang, A.M. Derfus, D. Simberg, T.J. Harris, E. Ruoslahti, S.N. Bhatia, M.J. Sailor, Systematic surface engineering of magnetic nanoworms for in vivo tumor targeting. Small 5, 694–700 (2009)
D.R. Sizemore, A.A. Branstrom, J.C. Sadoff, Attenuated Shigella as a DNA delivery vehicle for DNA-mediated immunization. Science 270, 299–303 (1995)
E. Steager, C.B. Kim, J. Patel, S. Bith, C. Naik, L. Reber, M.J. Kim, Control of microfabricated structures powered by flagellated bacteria using phototaxis. Applied Physics Letters 90:263901-263901-263903 (2007)
Y. Tanaka, K. Morishima, T. Shimizu, A. Kikuchi, M. Yamato, T. Okano, T. Kitamori, An actuated pump on-chip powered by cultured cardiomyocytes. Lab Chip 6, 362–368 (2006)
L. Tao, W. Hu, Y. Liu, G. Huang, B.D. Sumer, J. Gao, Shape-specific polymeric nanomedicine: emerging opportunities and challenges. Exp. Biol. Med. 236, 20–29 (2011)
B. Ten Hagen, S. Van Teeffelen, H. Löwen, Brownian motion of a self-propelled particle. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 23, 194119 (2011)
J.F. Toso, V.J. Gill, P. Hwu, F.M. Marincola, N.P. Restifo, D.J. Schwartzentruber, R.M. Sherry, S.L. Topalian, J.C. Yang, F. Stock, Phase I study of the intravenous administration of attenuated Salmonella typhimurium to patients with metastatic melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 20, 142–152 (2002)
M.A. Traoré, A. Sahari, B. Behkam, Computational and experimental study of chemotaxis of an ensemble of bacteria attached to a microbead. Phys. Rev. E 84, 061908 (2011)
G. Vassaux, J. Nitcheu, S. Jezzard, N.R. Lemoine, Bacterial gene therapy strategies. J. Pathol. 208, 290–298 (2006)
D.B. Weibel, P. Garstecki, D. Ryan, W.R. DiLuzio, M. Mayer, J.E. Seto, G.M. Whitesides, Microoxen: Microorganisms to move microscale loads. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 102, 11963 (2005)
A.Y. Yong, S. Shabahang, T.M. Timiryasova, Q. Zhang, R. Beltz, I. Gentschev, W. Goebel, A.A. Szalay, Visualization of tumors and metastases in live animals with bacteria and vaccinia virus encoding light-emitting proteins. Nat. Biotechnol. 22, 313–320 (2004)
L. Zhang, J.J. Abbott, L. Dong, B.E. Kratochvil, D. Bell, B.J. Nelson, Artificial bacterial flagella: Fabrication and magnetic control. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 064107 (2009)
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to acknowledge Birgit Scharf from the Biological Sciences Department at Virginia Tech for gifting the bacteria. Our gratitude also goes to our colleagues in the MicroN BASE laboratory at Virginia Tech especially Mehdi Kargar for helping with SEM and Meghan Canter for helping with particle stretching. We also appreciate Virginia Tech’s laboratory for interdisciplinary statistical analysis (LISA) for insightful discussions and Hamid Sahari for helping with the developing of the graphics. This work was supported by the National Science Foundation (IIS-117519).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 167 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sahari, A., Headen, D. & Behkam, B. Effect of body shape on the motile behavior of bacteria-powered swimming microrobots (BacteriaBots). Biomed Microdevices 14, 999–1007 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-012-9712-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-012-9712-1