Abstract
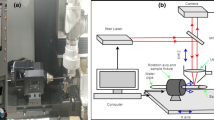
Atherosclerosis is a major cardiovascular disease involving accumulations of lipids, white blood cells, and other materials on the inside of artery walls. Since the calcification found in the advanced stage of atherosclerosis dramatically enhances the mechanical properties of the plaque, restoring the original lumen of the artery remains a challenge. High-speed rotational atherectomy, when performed with an ablating grinder to remove the plaque, produces much better results in the treatment of calcified plaque compared to other methods. However, the high-speed rotation of the Rotablator commercial rotational atherectomy device produces microcavitation, which should be avoided because of the serious complications it can cause. This research involves the development of a high-speed rotational ablation tool that does not generate microcavitation. It relies on surface modification to achieve the required surface roughness. The surface roughness of the tool for differential cutting was designed based on lubrication theory, and the surface of the tool was modified using Nd:YAG laser beam engraving. Electron microscope images and profiles indicated that the engraved surface of the tool had approximately 1 μm of root mean square surface roughness. The ablation experiment was performed on hydroxyapatite/polylactide composite with an elastic modulus similar to that of calcified plaque. In addition, differential cutting was verified on silicone rubber with an elastic modulus similar to that of a normal artery. The tool performance and reliability were evaluated by measuring the ablation force exerted, the size of the debris generated during ablation, and through visual inspection of the silicone rubber surface.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.M. Abbo, M. Dooris, S. Glazier, W.W. O’neill, D. Byrd, C.L. Grines, R.D. Safian, The Am. J. Cardiol. 75, 12 (1995)
S.S. Ahn, D. Auth, D.R. Marcus, W.S. Moore, J. Vasc. Surg. 7, 2 (1988)
R.M. Bersin, C.A. Simonton, Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 58, 4 (2003)
O.F. Bertrand, R. Sipehia, R. Mongrain, J. Rodes, J.-C. Tardif, L. Bilodeau, G. Cote, M.G. Bourassa, J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 32, 3 (1998)
C. Bredlau, G. Roubin, P. Leimgruber, J. Douglas Jr., S. King 3d, A. Gruentzig, Circ. 72, 5 (1985)
E. Cavusoglu, A.S. Kini, J.D. Marmur, S.K. Sharma, Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 62, 4 (2004)
R.W. Culbert, J. Biol. Chem. 109, 2 (1935)
D.M. Ebenstein, Diss., Bioengneering, Univ. of California, Berkeley, with Univ. of California, San Francisco, (2002)
D.M. Ebenstein, L.A. Pruitt, Nano Today 1, 3 (2006)
E. Eeckhout, M.J. Kern, Eur. Heart J. 22, 9 (2001)
S. Ellis, J. Popma, M. Buchbinder, I. Franco, M. Leon, K. Kent, A. Pichard, L. Satler, E. Topol, P. Whitlow, Circ. 89, 2 (1994)
A.C. Fischer-Cripps, Nanoindentation, 2nd edn. (Springer, New York, 2004)
B.J. Hamrock, D. Dowson, J. Lubr. Technol. 100, 2 (1978)
B.J. Hamrock, S.R. Schmid, B.O. Jacobson, Fundamentals of fluid film lubrication (Marcel Dekker, New York, 2004)
N. Ignjatovic, S. Tomic, M. Dakic, M. Miljkovic, M. Plavsic, D. Uskokovic, Biomater. 20, 9 (1999)
N. Ignjatovic, D. Uskokovic, Appl. Surf. Sci. 238, 1–4 (2004)
H. Im, K.H. Oh, S.G. Kim, S. Jeong, Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 10, 4 (2009)
S.A. Johnson, M.J. Adams, A. Arvanitaki, B.J. Briscoe, Tribol. Ser. 32 (1997)
G.D. Kim, J.T. Rundel, B.K. Paul, Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 11, 5 (2010)
A. Kini, J.D. Marmur, S. Duvvuri, G. Dangas, S. Choudhary, S.K. Sharma, Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 46, 3 (1999)
A.A. Lubrecht, C.H. Venner, Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. - Part J - J. Eng. Tribol. 213 (1999)
G. Mayer, Can. Méd. Assoc. J. 91, 18 (1964)
M. Nakao, K. Tsuchiya, W. Maeda, D. Iijima, CIRP Ann. - Manuf. Technol. 54, 1 (2005)
W.C. Oliver, G.M. Pharr, J. Mater. Res. 7, 6 (1992)
T.J. Romer, J.F. Brennan III, M. Fitzmaurice, M.L. Feldstein, G. Deinum, J.L. Myles, J.R. Kramer, R.S. Lees, M.S. Feld, Circ. 97, 9 (1998)
R.D. Safian, K.A. Niazi, M. Strzelecki, A. Lichtenberg, M.A. May, N. Juran, M. Freed, R. Ramos, V. Gangadharan, C.L. Grines, Circ. 88, 3 (1993)
R. Stribeck, Zeitschrift des Vereines Deutscher Ingenieure. 46 (1902)
Smooth-on, Technical overview, (2009), http://www.smooth-on.com/tb/files/Mold_Max_Series_TB.pdf. Accessed 12 July 2009
R.J. Zotz, R. Erbel, A. Philipp, A. Judt, H. Wagner, W. Lauterborn, J. Meyer, Catheter. Cardiovasc. Diagn. 26, 2 (1992)
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Strategy Technology Development Programs from the Korea Ministry of Knowledge Economy (No.10030046), a grant from the Seoul R&BD Program (TR080578), and second stage of Brain Korea 21 of Seoul National University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, MH., Kim, HJ., Kim, N.N. et al. A rotational ablation tool for calcified atherosclerotic plaque removal. Biomed Microdevices 13, 963–971 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-011-9566-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-011-9566-y