Abstract
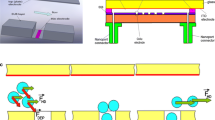
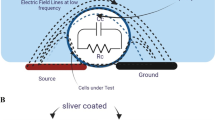
The manipulation of biological cells is essential to many biomedical applications. Insulator-based dielectrophoresis (iDEP) trapping consists of insulating structures which squeeze the electric field in a conductive solution to create a non-uniform electric field. The iDEP trapping microchip with the open-top microstructures was designed and fabricated in this work. For retaining the merit of microfabrication, the microelectrodes were deposited on the substrate to reduce the voltage required, due to the shortened spacing between them. The dielectrophoretic responses of both live and dead HeLa cells under different frequencies (100 Hz, 1 kHz and 1 MHz) have been investigated herein. The live cells exhibited negative dielectrophoresis at low frequencies of 100 Hz and 1 kHz, but a positive dielectrophoretic response with the frequency at 1 MHz. As for dead cells, positive dielectrophoretic responses were shown at all the frequencies applied. Therefore, selective trapping of dead HeLa cells from live cells was achieved experimentally at the frequency of 1 kHz. The open-top microstructures are suitable for trapping cells or biological samples, and easily proceeding to further treatment for cells, such as culturing or contact detection. The intensity of the emitted light during fluorescent detection will not suffer interference by a cover, as it does not exist herein.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Asami, Y. Takahashit, S. Takashima, Frequency domain analysis of membrane capacitance of cultured cells (HeLa and myeloma) using the micropipette technique Biophys. J. 58, 143–148 (1990)
I. Barbulovic-Nad, X. Xuan, J.S.H. Lee, D. Li, DC-dielectrophoresis separation of microparticles using an oil droplet obstacle Lab Chip 6, 274–279 (2006) doi:10.1039/b513183a
M. Berger, J. Castelino, R. Huang, M. Shah, R.H. Austin, Design of a microfabricated magnetic cell separator Electrophoresis 22, 3883–3892 (2001). doi:10.1002/1522-2683(200110)22:18<3883::AID-ELPS3883>3.0.CO;2-4
J.P.H. Burt, T.A.K. Al-Ameen, R. Pethig, An optical dielectrophoresis spectrometer for low-frequency measurements on colloidal suspensions J. Phys. E Sci. Instrum. 22, 952–957 (1989) doi:10.1088/0022-3735/22/11/011
J.P.H. Burt, R. Pethig, P.R.C. Gascoyne, F.F. Fecker, Dielectrophoretic characterisation of Friend murine erythroleukaemic cells as a measure of induced differentiation Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1034, 93–101 (1990)
W.H. Chan, Y.J. Chang, Dosage effects of resveratrol on ethanol-induced cell death in the human K562 cell line Toxicol. Lett. 161(1), 1–9 (2006) doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2005.07.010
P.Y. Chiou, A.T. Ohta, M.C. Wu, Massively parallel manipulation of single cells and microparticles using optical images Nature 436, 370–372 (2005) doi:10.1038/nature03831
C.F. Chou, Z. Frederic, Electrodeless dielectrophoresis for micro total analysis systems IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 22(6), 62–67 (2003) doi:10.1109/MEMB.2003.1266048
C.F. Chou, J.O. Tegenfeldt, O. Bakajin, S.S. Chan, E.C. Cox, N. Darnton, T. Duke, R.H. Austin, Electrodeless dielectrophoresis of single-and double-stranded DNA Biophys. J. 83, 2170–2179 (2002)
N. Chronis, L.P. Lee, Electrothermally activated SU-8 microgripper for single cell manipulation in solution J. Microelectromech. Syst. 14(4), 857–863 (2005) doi:10.1109/JMEMS.2005.845445
J.J. Hawkes, R.W. Barber, D.R. Emerson, W.T. Coakley, Continuous cell washing and mixing driven by an ultrasound standing wave within a microfluidic channel Lab Chip 4, 446–452 (2004) doi:10.1039/b408045a
T. Heida, W.L.C. Rutten, E. Marani, Dielectrophoretic trapping of dissociated fetal cortical rat neurons IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 48(8), 921–930 (2001) doi:10.1109/10.936368
Y. Huang, R. Pethig, Electrode design for negative dielectrophoresis Meas. Sci. Technol. 2, 1142–1146 (1991) doi:10.1088/0957-0233/2/12/005
Y. Huang, R. Holzel, R. Pethig, X.B. Wang, Differences in the AC electrodynamics of viable and non-viable yeast cells determined through combined dielectrophoresis and electrorotation studies Phys. Med. Biol. 37, 1499–1517 (1992) doi:10.1088/0031-9155/37/7/003
A. Irimajiri, T. Hanai, A. Inouye, A dielectric theory of “multi-stratified shell” model with its application to a lymphoma cell J. Theor. Biol. 78, 251–269 (1979) doi:10.1016/0022-5193(79)90268-6
T.B. Jones, Electromechanics of particles (Cambridge University Press, New York, 1995)
T.B. Jones, J.P. Kraybill, Active feedback-controlled dielectrophoretic levitation J. Appl. Phys. 60, 1247–1252 (1986) doi:10.1063/1.337345
B.H. Lapizco-Encinas, B.A. Simmons, E.B. Cummings, Y. Fintschenko, Dielectrophoretic concentration and separation of live and dead bacteria in an array of insulators Anal. Chem. 76, 1571–1579 (2004) doi:10.1021/ac034804j
H. Lee, Y. Liu, D. Ham, R.M. Westervelt, Integrated cell manipulation systems Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 1063–1065 (2004) doi:10.1063/1.1776339
H. Li, R. Bashir, Dielectrophoretic separation and manipulation of live and heat-treated cells of Listeria on microfabricated devices with interdigitated electrodes Sens. Actuators B Chem. 86, 215–221 (2002) doi:10.1016/S0925-4005(02)00172-7
P. Marszalek, J.J. Zielinski, M. Fikus, Experimental verification of a theoretical treatment of the mechanism of dielectrophoresis Bioelectrochem. Bioenerg. 22, 289–298 (1989) doi:10.1016/0302-4598(89)87046-1
S. Masuda, M. Washizu, T. Nanba, Novel method of cell-fusion in field constriction area in fluid integrated-circuit IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 25, 732–737 (1989) doi:10.1109/28.31255
G.H. Markx, M.S. Talary, R. Pethig, Separation of viable and non-viable yeast using dielectrophoresis J. Biotechnol. 32, 29–37 (1994) doi:10.1016/0168-1656(94)90117-1
K. Park, D. Akin, R. Bashir, Electrical capture and lysis of vaccinia virus particles using silicon nano-scale probe array Biomed. Microdevices 9, 877–883 (2007) doi:10.1007/s10544-007-9101-3
R. Pethig, Dielectrophoresis of biological cells. in Encyclopedia of surface and colloid science, ed. by P. Somasundaran. (CRC, Boca Raton, 2006), pp. 1719–1736.
R. Pethig, D.B. Kell, The passive electrical properties of biological systems: their significance in physiology, biophysics, and biotechnology Phys. Med. Biol. 32, 933–970 (1987) doi:10.1088/0031-9155/32/8/001
R. Pethig, X.B. Wang, Y. Huang, J.P.H. Burt, Positive and negative dielectrophoretic collection of colloidal particles using interdigitated castellated microelectrodes J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 24, 881–888 (1992) doi:10.1088/0022-3727/25/5/022
H.A. Pohl, The motion and precipitation of suspensoids in divergent electric fields J. Appl. Phys. 22, 869–871 (1951) doi:10.1063/1.1700065
H.A. Pohl, Dielectrophoresis (Cambridge University Press, New York, 1978)
H.A. Pohl, K. Pollock, Electrode geometries for various dielectrophoretic force laws J. Electrost. 5, 337–342 (1978) doi:10.1016/0304-3886(78)90028-1
C. Prinz, J.O. Tegenfeldt, R.H. Austin, E.C. Cox, J.C. Sturm, Bacterial chromosome extraction and isolation Lab Chip 2, 207–212 (2002) doi:10.1039/b208010a
A. Ramos, H. Morgan, G.N. Green, A. Castellanos, Ac electrokinetics: a review of forces in microelectrode structures J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 31, 2338–2353 (1998) doi:10.1088/0022-3727/31/18/021
E. Rubin, H. Rottenberg, Ethanol-induced injury and adaptation in biological membranes Fed. Proc. 41(8), 2465–2471 (1982)
J. Voldman, Electrical forces for microscale cell manipulation Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 8, 425–454 (2006) doi:10.1146/annurev.bioeng.8.061505.095739
J. Voldman, R.A. Braff, M. Toner, M.L. Gray, M.A. Schmidt, Holding forces of single-particle dielectrophretic traps Biophys. J. 80, 531–541 (2001)
M. Yoshida, K. Tohda, M. Gratzl, Hydrodynamic micromanipulation of individual cells onto patterned attachment sites on biomicroelectromechanical system chips Anal. Chem. 75, 4686–4690 (2003) doi:10.1021/ac030055u
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to thank the National Science Council of the Republic of China for financial support of this research under contract No. NSC-96-2221-E-194-053 and the National Center for High-performance Computing for computer time and facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jen, CP., Chen, TW. Selective trapping of live and dead mammalian cells using insulator-based dielectrophoresis within open-top microstructures. Biomed Microdevices 11, 597–607 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-008-9269-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-008-9269-1