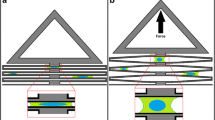
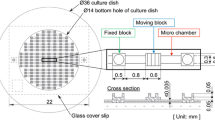
Abstract
Micromechanical systems are increasingly being used as tools in biological applications, since their characteristic dimensions permit to operate at the same length scale of the structures under investigation. Here, we present a methodology for the design, fabrication and operation of a tool for the assessment of mechanical properties of single cells. In particular, we describe a microsystems platform to study bio-mechanical response of single living cells to in-plane biaxial stretching. The proposed device employs a new linkage design in order to obtain the displacement of the quadrants of a sliced circular plate in mutually-orthogonal directions using just one linear actuator. With this linkage geometry, the whole device has only one degree of freedom. This results in a very predictable and reliable mechanical behaviour, thereby allowing use a simple and easily available control electronics. Results of this study have relevance for the design of a powerful yet simple BioMEMS platform for the characterization of living cells as in-plane bi-axial loading simulated the conditions experienced by cells in vivo more realistically than a uniaxial stretching.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.L. Andersen and L.A. Norton, Journal of Biomechanics 24, 649–654 (1991).
G. Bao and S. Suresh, Nature Materials 21, 715–725 (2003).
K.A. Barbee and L.E. Thibault LE, IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society - llth Annual International Conference (1989).
M. Bottlang, M. Simnacher, H. Schmitt, R.A. Brand, and L. Claes, Biomedizinische Technik 42, 305–309 (1997).
C.T. Brighton, B. Strafford, S.B. Gross, D.F. Leatherwood, J.L. Williams, and S.R. Pollack, Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery 73A, 320–331 (1991).
C.T. Brighton, B.J. Sennett, J.C. Farmer, J.P. Iannotti, C.A. Hansen, J.L. Williams, and J. Williamson, Journal of Orthopaedic Research 10, 385–393 (1992).
M.J. Bucklely, A.J. Banes, L.G. Lewin, B.E. Sumpio, M. Sato, R. Jordan, J. Gilbert, G.W. Link, and R. Tran Son Tay, Bone and Mineral 4, 225–236 (1988).
J. Deutsch, D. Motlagh, B. Russell, and T.A. Desai, Journal of Biomedical Materials Research 53, 3:267–275 (2000).
Y.C. Fung, Biomechanics: Motion, Flow, Stress and growth (Springer, NY, 1990).
Y.C. Fung, Biomechanics: mechanical properties of living tissues (2nd ed., Springer, NY, 1993).
Y.C. Fung, Biomechanics: circulation (2nd ed., Springer NY, 1997).
J.M. Gere and S. P. Timoshenko, Mechanics of Materials (Chapman & Hall, 1991).
J. Guck, H. Mahmood, T.J. Moon, C.C. Cunningham, and J. Käs, Biophysical Journal 81, 767–784 (2001).
A. Harell, S. Dekel, and I. Binderman, Calcified Tissue Research 22, 202–207 (1977).
M.A. Horton, Biophysical Journal 82, 2970–2981 (2002).
C.T. Hung and J.L. Williams, Journal of Biomechanics 27, 227–232 (1994).
V.P. Jaecklin, N.F. de Rooij, and J.M. Moret, Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering 2, 250–255 (1992).
D.B. Jones, H. Nolte, J.G. Scholuebbers, E. Turner, and D. Veltel, Biomaterials 12, 101–110 (1991).
D. Koester, R. Mahadevan, M. Stonefiled, and B. Hardy, Polymumps Design Handbook (2003).
G. Lin and K.P. Roos, Journal of Microelectromechanical Systems 9, 9–17 (2000).
C. Neidlinger-Wilke, H.J. Wilke, and L. Claes., Journal of Orthopaedic Research 12, 70–78 (1994).
H.V. Panchawagh, D. Serrell, D.S. Finch, T. Oreskovic, and R.L. Mahajan, 2005 ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition (2005).
D. Sameoto, T. Hubbard, and M. Kujath, Journal of Micromechanichs and Microengineering 14, 1359–1366 (2004).
D. Somjen, I. Binderman, E. Berger, and A. Harrel, Biochimica and Biophisica Acta 627, 91–100 (1980).
M. Sotoudeh, S. Jalali, S. Usami, JY-J. Shyy, and S. Chien, Annals of Biomedical Engineering 26, 181–189 (1998).
T.L. Sounart, T.A. Michalske, and K.R. Zavadil, Journal of Microelectromechanical Systems 14, 125–133 (2005).
K.J. Van Vliet, G. Bao, and S. Suresh, Acta Materialia 51, 5881–5905 (2003).
S. Yang and T. Saif, International Conference on Microelectromechanical systems (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scuor, N., Gallina, P., Panchawagh, H.V. et al. Design of a novel MEMS platform for the biaxial stimulation of living cells. Biomed Microdevices 8, 239–246 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-006-8268-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-006-8268-3