Abstract
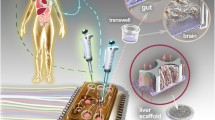
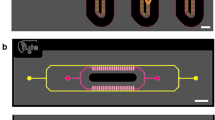
In the area of drug discovery, high-speed synthesis has increased the number of drug candidates produced. These potential drugs need to be evaluated for their adsorption, distribution, metabolism, elimination, and toxicology (ADMET) properties as early in the drug development stage as possible. Previously, a potential drug’s ADMET properties have been found out by using monolayer cell cultures and live animals. These methods can be costly, time-intensive, and impractical for screening the large amount of potential drugs created by combinatorial chemistry. A quick, small, inexpensive, and highly parallel device would be desirable to determine a drug candidate’s properties (i.e., metabolism of the drug). Here we fabricate a microfluidic device entrapping human microsomes within poly(ethylene) glycol hydrogels thereby generating an in situ microreactor to assess a drug candidate’s metabolic properties that can be coupled to analysis equipment. We show that microsomes can be entrapped without the loss of enzymatic activity during photopolymerization. Additionally, a microreactor utilizing hepatocytes was also created for comparison with the microsome microreactor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
N.A. Alcantar, E.S. Aydil et al., “Polyethylene glycol-coated biocompatible surfaces,” J Biomed Mater Res 51(3), 343–351 (2000).
S. Benetton, J. Kameoka et al., “Chip-based P450 drug metabolism coupled to electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry detection,” Analytical Chemistry: A-G. (2003).
J. Berger, M. Reist et al., “Structure and interactions in covalently and ionically crosslinked chitosan hydrogels for biomedical applications,” European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics (57), 19–34 (2003).
E.F.A. Brandon, C.D. Raap et al., “An update on in vitro test methods in human hepatic drug biotransformation research: Pros and cons.” Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology (189), 233–246 (2003).
E.F.A. Brandon, C.D. Raap, I.B. Meijerman, H. Jos, and Jan H.M. Schellens, “An update on in vitro test methods in human hepatic drug biotransformation research: Pros and cons,” Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 189, 233–246 (2003).
M. Brivio, R.H. Fokkens et al., “Integrated microfluidic systems enabling (Bio)chemical reactions with on-line MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry,” Anal Chem 74(16), 3972–3976 (2002).
J.A. Burdick and K.S. Anseth, “Photoencapsulation of osteoblasts in injectable RGD-modified PEG hydrogels for bone tissue engineering,” Biomaterials 23(22), 4315–4323 (2002).
J.T. Buters, C.D. Schiller et al., “A highly sensitive tool for the assay of cyctochrome P450 enzyme activity in rat, dog and man,” Biochemical Pharmacology 46(9), 1577–1584 (1993).
N. Chauret, N. Tremblay et al., “Description of a 96-well plate assay to measure cytochrome p4503a inhibition in human liver microsomes using a selective fluorescent probe,” Analytical Biochemistry 276, 215–226 (1999).
C.-H. Chiou, G.-B. Lee et al., “Micro devices integrated with microchannels and electrospray nozzles using PDMS casting techniques,” Sensors and Actuators B 86, 280–286 (2002).
P.R. Contag, “Whole-animal cellular and molecular imaging to accelerate drug development,” Drug Discovery Today 7(10), 555–562 (2002).
C.L. Crespi, V.P. Miller et al., “Microtiter plate assays for inhibition of human, drug-metabolizing cyctochromes P450,” Analytical Biochemistry 248, 188–190 (1997).
G.M. Cruise, D.S. Scharp et al., “Characterization of permeability and network structure of interfacially photopolymerized poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate hydrogels,” Biomaterials 19(14), 1287–1294 (1998).
I.A.M. DeGraaf, C.E. Van Meijeren et al., “Comparison of in vitro preparations for semi-quantitative prediction of in vivo drug metabolism,” Drug Metabolism and Disposition 30(10), 1129–1136 (2003).
J.G. DeLuca, G.R. Dysart et al., “A direct, highly sensitive assay for cytochrome P-450 catalyzed O-Deethylation using a novel coumarin analog,” Biochemical Pharmacology 37(9), 1731–1739 (1988).
J. Elisseeff, W. McIntosh et al., “Photoencapsulation of chondrocytes in poly(ethylene oxide)-based semi-interpenetrating networks,” J Biomed Mater Res 51(2), 164–171 (2000).
M. Gustafsson, D. Hirschberg et al., “Integrated sample prepartation and MALDI mass spectrometry on a microfluidic compact disk,” Anal Chem 76, 345–350 (2004).
J. Hodgson, “ADMET—Turning chemicals into drugs,” Nature Biotechnology 19, 722–726 (2001).
J. Honiger, P. Balladur et al., “Permeability and biocompatibility of a new hydrogel used for encapsulation of hepatocytes,” Biomaterials 16(10), 753–759 (1995).
U.M. Kent, L. Pascual et al., “Mechanistic studies with N-benzyl-1-aminobenzotriazole-inactivated CYP2B1: Differential effects on the metabolism of 7-ethoxy-4-(trifluoromethyl) coumarin, testosterone and benzphetamine,” Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 423, 277–287 (2004).
K.K. Khan, “Homotropic versus heterotopic cooperativity of cytochrome P450eryF: A substrate oxidation and spectral titration study,” Drug Metabolism and Disposition 31(4), 356–359 (2003).
B. Kim and N.A. Peppas, “Synthesis and characterization of pH-sensitive glycopolymer for oral drug delivery systems,” J. Biomater. Sci. Polymer Edn 13(11), 1271–1281 (2002).
J.-S. Kim and D.R. Knapp, “Microfabricated PDMS multichannel emitter for electrospray ionization mass spectrometry,” J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 12, 463–469 (2001).
W.G. Koh, L.J. Itle et al., “Molding of hydrogel microstructures to create multiphenotype cell microarrays,” Anal Chem 75(21), 5783–5789 (2003).
W.G. Koh, A. Revzin et al., “Poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogel microstructures encapsulating living cells,” Langmuir 18(7), 2459–2462 (2002).
S. LeGac, J. Carlier et al., “Monoliths for microfluidic devices in proteomics,” Journal of Chromatography B 808, 3–14 (2004).
V. Liu and S.N. Bhatia, “Three-dimensional photopatterning of hydrogels containing living cells,” Biomedical Microdevices 4(4), 257–266 (2002).
V.A. Liu, W.E. Jastromb et al., “Engineering protein and cell adhesivity using PEO-terminated triblock polymers,” J Biomed Mater Res 60(1), 126–134 (2002).
M.B., Mellott, K. Searcy et al., “Release of protein from highly cross-linked hydrogels of poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate fabricated by UV polymerization,” Biomaterials 22, 929–941 (2001).
S. Myers and A. Baker “Drug discovery—an operating model for a new era,” Nature Biotechnology 19, 727–730 (2001).
R.E. Pearce, C.J. McIntyre et al., “Effects of freezing, thawing and storing human liver microsomes on cytochrome P450 activity,” Biochemistry and Biophysics 331(2), 145–169 (1996).
N.A. Peppas, P. Bures et al., “Hydrogels in pharmaceutical formulations,” European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics (50), 27–46 (2000).
N.A. Peppas and E.W. Merrill, “Poly(vinyl Alcohol) hydrogels: Reinforcement of radiation-crosslinked networks by crystallization,” Journal of Polymer Science: Polymer Chemistry Edition 14, 441–457 (1976).
A. Revzin, R. Russell et al., “Fabrication of poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogel microstructures using photolithography,” Langmuir 17(18), 5540–5447 (2001).
A. Revzin, R.J. Russell et al., “Fabrication of poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogel microstructures using photolithography,” Langmuir 17(18), 5440–5447 (2001).
A. Revzin, R.G. Tompkins, and M. Toner, “Surface engineering with poly(ethylene glycol) photolithography to create high-density cell arrays on glass,” Langmuir 19(23), 9855–9862 (2003).
E.S. Roberts, D.P. Ballou et al., “Mechanistic studies of 9-ethynylphenanthrene-inactivated cytochrome P450 2B1,” Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 323(2), 303–312 (1995).
R. Russell, M. Pishko et al., “A fluorescence-based glucose biosensor using concanavalin A and dextran encapsulated in a poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogel,” Analytical Chemistry 71(15), 3126–3132 (1999).
R.J. Russell, A.C. Axel et al., “Mass transfer in rapidly photopolymerized poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogel used for chemical sensing,” Polymer 42, 4893–4901 (2001).
K. Sakai-Kato, M. Kato et al., “On-line drug-metabolism system using microsomes encapsulated in a capillary by the sol-gel method and integrated into capillary electrophoresis,” Analytical Biochemistry (308), 278–284 (2002).
S. Sivapathasundaram, P. Magnisali et al., “Cytochrome P450 expression and testosterone metabolism in the liver of deer,” Toxicology 187, 49–65 (2003).
M. Vondracek, Z. Xi et al., “Cytochrome P450 expression and related metabolism in human buccal mucosa,” Carcinogenesis 22(3), 481–488 (2001).
D. Wang, C.G. Williams et al., “Synthesis and characterization of a novel degradable phosphate-containing hydrogel,” Biomaterials 24, 3969–3980 (2003).
S. Wu, H. Li et al., “Modeling investigation of hydrogel volume transition,” Macromolecular Theory and Simulations 13, 13–29 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zguris, J.C., Itle, L.J., Hayes, D. et al. Microreactor Microfluidic Systems with Human Microsomes and Hepatocytes for use in Metabolite Studies. Biomed Microdevices 7, 117–125 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-005-1589-9
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-005-1589-9