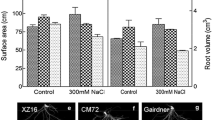
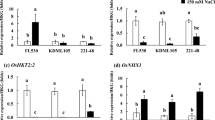
Abstract
Salt stress imposes a major environmental threat to agriculture, therefore, understanding the basic physiology and genetics of cell under salt stress is crucial for developing any breeding strategy. In the present study, the expression profile of genes involved in ion homeostasis including salt overly sensitive (HvSOS1, HvSOS2, HvSOS3), vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter (HvNHX1), and H+-ATPase (HVA) along with ion content measurement were investigated in two genotypes of Hordeum vulgare under 300 mM NaCl. The gene expressions were measured in the roots and shoots of a salt-tolerant mutant genotype M4-73-30 and in its wild-type cv. Zarjou by real-time qPCR technique. The critical differences between the salt-tolerant mutant and its wild-type were observed in the expressions of HvSOS1 (105-fold), HvSOS2 (24-fold), HvSOS3 (31-fold), and HVA (202-fold) genes in roots after 6-h exposure to NaCl. The parallel early up-regulation of these genes in root samples of the salt-tolerant mutant genotype indicated induction of Na+/H+ antiporters activity and Na+ exclusion into apoplast and vacuole. The earlier up-regulation of HvSOS1, HVA, and HvNHX1 genes in shoot of the wild-type genotype corresponded to the relative accumulation of Na+ which was not observed in salt-tolerant mutant genotype because of efficient inhibitory role of the root in Na+ transport to the shoot. In conclusion, the lack of similarity in gene expression patterns between the two genotypes with similar genetic background may confirm the hypothesis that mutation breeding could change the ability of salt-tolerant mutant genotype for efficient ion homeostasis via salinity oversensitivity response.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CBL:
-
calcineurin B-like protein
- CIPK:
-
CBL-interacting protein kinase
- HVA:
-
H+-ATPase
- NHX1:
-
Na+/H+ exchanger1
- qPCR:
-
quantitative PCR
- SOS:
-
salt overly sensitive
References
Apse, M.P., Blumwald, E.: Engineering salt tolerance in plants. - Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 13: 146–150, 2002.
Apse, M.P., Blumwald, E.: Na+ transport in plants. - FEBS. Lett. 581: 2247–2254, 2007.
Apse, M.P., Sottosanto, J.B., Blumwald, E.: Vacuolar cation/H+ exchange, ion homeostasis, and leaf development are altered in a T-DNA insertional mutant of AtNHX1, the Arabidopsis vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter. - Plant. J. 36: 229–239, 2003.
Berthomieu, P., Conejero, G., Nublat, A., Brackenbury, W.J., Lambert, C., Savio, C., Uozumi, N., Oiki, S., Yamada, K., Cellier, F., Gosti, F., Simonneau, T., Essah, P.A., Tester, M., Véry, A.A., Sentenac, H., Casse, F.: Functional analysis of AtHKT1 in Arabidopsis shows that Na(+) recirculation by the phloem is crucial for salt tolerance. - EMBO. J. 22: 2004–2014, 2003.
Blumwald, E.: Sodium transport and salt tolerance in plants. - Curr. Opin. cell. Biol. 12: 431–434, 2000.
Blumwald, E., Aharon, G.S., Apse, M.P.: Sodium transport in plant cells. - Biochim. biophys. Acta 1465: 140–151, 2000.
Cakirlar, H., Bowling, D.F.J.: The effect of salinity on the membrane potential of sunflower roots. - J. exp. Bot. 32: 479–485, 1981.
Chen, Z.H., Pottosin, I.I., Cuin, T.A., Fuglsang, A.T., Tester, M., Jha, D., Zepeda-Jazo, I., Zhou, M., Palmgren, M.G., Newman, I.A., Shabala, S.: Root plasma membrane transporters controlling K+/Na+ homeostasis in salt stressed barley. - Plant. Physiol. 145: 1714–1725, 2007.
Chinnusamy, V., Zhu, J., Zhu, J.K.: Salt stress signaling and mechanisms of plant salt tolerance. - Genet. Eng. 27: 141–177, 2006.
Colmer, T.D., Munns, R., Flowers, T.J.: Improving salt tolerance of wheat and barley: future prospects. - Aust. J. exp. Agr. 45: 1425–1443, 2005.
Cuin, T.A., Shabala, S.: Potassium homeostasis in salinised plant tissues. - In: Volkov, ?. (ed.): Plant Electrophysiology? Theory and Methods. Pp. 287–317. Springer, Heidelberg 2006.
Dietz, K.J., Tavakoli, N., Kluge, C., Mimura, T., Sharma, S.S., Harris, G.C., Chardonnens, A.N., Golldack, D.: Significance of the V-type ATPase for the adaptation to stressful growth conditions and its regulation on the molecular and biochemical level. - J. exp. Bot. 52: 1969–1980, 2001.
Ding, F., Yang, J.C., Yuan, F., Wang, B.S.: Progress in mechanism of salt excretion in recretohalopytes. - Front. Biol. 5: 164–170, 2010.
Fukuda, A., Chiba, K., Maeda, M., Nakamura, A., Maeshima, M., Tanaka, Y.: Effect of salt and osmotic stresses on the expression of genes for the vacuolar H+-pyrophosphatase, H+-ATPase subunit A, and Na+/H+ antiporter from barley. - J. exp. Bot. 397: 585–594, 2004.
Garbarino, J., Dupont, F.M.: NaCl induces a Na+/H+ antiport in tonoplast vesicles from barley roots. - Plant. Physiol. 86: 231–6, 1988.
Halfter, U., Ishitani, M., Zhu, J.K.: The Arabidopsis SOS2 protein kinase physically interacts with and is activated by the calcium binding protein SOS3. - Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA 97: 3735–3740, 2000.
Harmon, A.C., Gribskov, M., Gubrium, E., Harper, J.F.: The CDPK superfamily of protein kinases. - New Phytol. 151: 175–183, 2001.
Hasegawa, P.M.: Sodium (Na+) homeostasis and salt tolerance of plants. - Environ. exp. Bot. 92: 19–31, 2013.
Hasegawa, P.M., Bressan, R.A., Zhu, J.K., Bohnert, H.J.: Plant cellular and molecular responses to high salinity. - Annu. Rev. Plant. Physiol. Plant. mol. Biol. 51: 463–499, 2000.
Hauser, F., Horie, T.: A conserved primary salt tolerance mechanism mediated by HKT transporters: a mechanism for sodium exclusion and maintenance of high K+/Na+ ratio in leaves during salinity stress. - Plant. Cell Environ. 33: 552–565, 2010.
Horie, T., Schroeder, J.I.: Sodium transporters in plants. Diverse genes and physiological functions. - Plant. Physiol. 136: 2457–2462, 2004.
Jannesar, M., Razavi, K.H., Saboora, A.: Effects of salinity on expression of the salt overly sensitive genes in Aeluropus lagopoides. - Aust. J. Crop Sci. 8: 1–8, 2014.
Kader, M.A., Lindberg, S.: Uptake of sodium in protoplasts of salt-sensitive and salt-tolerant cultivars of rice, Oryza sativa L., determined by the fluorescent dye. - J. exp. Bot. 56: 3149–3158, 2005.
Kiani, D., Soltanloo, H., Ramezanpour, S.S., Nasrolahnezhad Qumi, A.A., Yamchi, A., Zaynali Nezhad, K.H., Tavakol, E.: A barley mutant with improved salt tolerance through ion homeostasis and ROS scavenging under salt stress. - Acta Physiol. Plant. 39: 90, 2017.
Leigh, R.A.: Potassium homeostasis and membrane transport. - J. Plant. Nutr. Soil Sci. 164: 193–198, 2001.
Livak, K.J., Schmittgen, T.D.: Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. - Methods 25: 402–408, 2001.
Luttge, U., Fischer-Schliebs, E., Ratajczak, R.: The H+ pumping V-ATPase of higher plants: a versatile “ecoenzyme” in response to environmental stress. - Cell. Biol. Mol. Lett. 6: 356–361, 2001.
Maathuis, F.J.M., Amtmann, A.: K+ nutrition and Na+ toxicity: the basis of cellular K+/Na+ ratios. - Ann. Bot. 84: 123–133, 1999.
Mahluji, M., Mal Verdi, Q., Afyuni, D., Jafari, A., DorchehI, M.A., Sadeqi, D., Yusefi, A.: Introducing and comparing of salinity tolerant barley lines (4 and 5) to local cultivar in onfarm trial. - https://doi.org/agris.fao.org/agrissearch/search.do?recordID=IR2008000425, 2007.
Martinez-Atienza, J., Jiang, X., Garciadeblas, B., Mendoza, I., Zhu, J.K., Pardo, J.M., Quintero, F.J.: Conservation of the salt overly sensitive pathway in rice. - Plant Physiol. 143: 1001–1012, 2007.
Maser, P., Eckelman, B., Vaidyanathan, R., Fairbain, D.J., Kubo, M., Yamagami, M., Yamaguchi, K., Nishimura, M., Uozumi, N., Robertson, W., Sussman, M.R., Schroeder, J.I.: Altered shoot/root Na+ distribution and bifurcating salt sensitivity in Arabidopsis by genetic disruption of the Na+ transporter AtHKT1. - FEBS Lett. 531: 157–161, 2002.
Maughan, P.J., Turner, T.B., Coleman, C.E., Elzinga, D.B., Jellen, E.N., Morales, J.A., Udall, J.A., Fairbanks, D.J., Bonifacio, A.: Characterization of Salt Overly Sensitive 1 (SOS1) gene homoeologs in quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd). - Genome 52: 647–657, 2009.
Munns, R., Tester, M.: Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. - Annu. Rev. Plant. Biol. 59: 651–681, 2008.
Oh, D.H., Gong, Q., Ulanov, A., Zhang, Q., Li, Y., Ma, W., Yun, D.J., Bressan, R.A., Bohnert, H.J.: Sodium stress in the halophyte the Tellungiella halophyla and transcriptional changes in a ThSOS-RNA interference line. - J. integr. Plant Biol. 49: 1484–1496, 2007.
Palmgren, M.G.: Plant plasmembrane H+-ATPases: powerhouses for nutrient uptake. - Annu. Rev. Plant. Physiol. Plant. mol. Biol. 52: 817–845, 2001.
Pfaffl, M.W., Hegeleit, M.: Validities of mRNA quantification using recombinant RNA and recombinant DNA external calibration curves in real-time RT-PCR. - Biotechnol. Lett. 23: 275–282, 2001.
Pfaffl, M.W., Horgan, G.W., Dempfle, L.: Relative expression software tool (REST©) for group-wise comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results in real-time PCR. - Nucl. Acids Res. 30: e36, 2002.
Qiu, Q.S., Barkla, B.J., Vera-Estrella, R., Zhu, J.K., Schumaker, K.S.: Na+/H+ exchange activity in the plasma membrane of Arabidopsis. - Plant Physiol. 132: 1041–1052, 2003.
Qiu, Q.S., Guo, Y., Quintero, F.J., Pardo, J.M., Schumaker, K.S., Zhu, J.K.: Regulation of vacuolar Na+/H+ exchange in Arabidopsis thaliana by the salt-overly-sensitive (SOS) pathway. - J. biol. Chem. 279: 207–215, 2004.
Rezaei Moshaei, M., Nematzadeh, G.H.A., Askari, H., Mozaffari Nejad, A.S., Pakdin, A.: Quantitative gene expression analysis of some sodium ion transporters under salinity stress in Aeluropus littoralis. - Saudi. J. biol. Sci. 21: 394–399, 2014.
Rus, A., Lee, B.H., Munoz-Mayor, A., Sharkhuu, A., Miura, K., Zhu, J.K., Bressan, R.A., Hasegawa, P.M.: AtHKT1 facilitates Na+ homeostasis and K+ nutrition in planta. - Plant Physiol. 136: 2500–2511, 2004.
Schachtman, D.P., Lagudah, E.S., Munns, R.: The expression of salt tolerance from Triticum tauschii in hexaploid wheat. - Theor. appl. Genet. 84: 714–719, 1992.
Shabala, S.: Ionic and osmotic components of salt stress specifically modulate net ion fluxes from bean leaf mesophyll. - Plant. Cell Environ. 23: 825–837, 2000.
Shabala, S., Cuin, T.A.: Potassium transport and plant salt tolerance. - Physiol. Plant. 133: 651–669, 2008.
Shabala, S.N., Shabala, L., Van Volkenburgh, E.: Effect of calcium on root development and root ion fluxes in salinised barley seedlings. - Funct. Plant Biol. 30: 507–514, 2003.
Shabala, S., Shabala, S., Cuin, T.A., Pang, J., Percey, W., Chen, Z., Conn, S., Eing, C.H., Wegner, L.H.: Xylem ionic relations and salinity tolerance in barley. - Plant J. 61: 839–853, 2010.
Shavrukov, Y., Gupta, N.K., Miyazaki, J., Baho, M.N., Kenneth, J., Chalmers, K.J., Tester, M., Langridge, P.C., Collins, N.: HvNax3-a locus controlling shoot sodium exclusion derived from wild barley (Hordeum vulgare ssp. spontaneum). - Funct. integr. Genomics 10: 277–291, 2010.
Shi, H., Ishitani, M., Kim, C., Zhu, J.K.: The Arabidopsis thaliana salt tolerance gene SOS1 encodes a putative Na+/H+ antiporter. - Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA 97: 6896–6901, 2000.
Shi, H., Quintero, F.J., Pardo, J.M., Zhu, J.K.: The putative plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter SOS1 controls long distance Na+ transport in plants. - Plant Cell 14: 465–477, 2002.
Stevens, T.H., Forgac, M.: Structure, function and regulation of the vacuolar (H+)-ATPase. - Annu. Rev. cell. dev. Biol. 13: 779–808, 1997.
Tavakoli, F., Vazan, S., Moradi, F., Shiran, B., Sorkheh, K.: Differential response of salt-tolerant and susceptible barley genotypes to salinity stress. - J. Crop. Improvement 24: 244–260, 2010.
Tester, M., Davenport, R.: Na+ tolerance and Na+ transport in higher plants. - Ann. Bot. 91: 503–527, 2003.
Volkov, V., Amtmann, A.: Thellungiella halophyla, a salttolerant relative of Arabidopsis thaliana, has specific root ion-channel features supporting K+/Na+ homeostasis under salinity stress. - Plant J. 48: 342–353, 2006.
Volkov, V., Wang, B., Dominy, P.J., Fricke, W., Amtmann, A.: Thellungiella halophyla, a salt-tolerant relative of Arabidopsis thaliana, possesses effective mechanisms to discriminate between potassium and sodium. - Plant Cell Environ. 27: 1–14, 2004.
Walia, H., Wilson, C., Wahid, A., Condamine, P., Cui, X., Close, T.J.: Expression analysis of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) during salinity stress. - Funct. integr. Genomics 6: 143, 2006.
Wang, S., Zhang, Y.D., Perez, P.G., Deng, Y.W., Li, Z.Z., Huang, D.F.: Isolation and characterization of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene from Cucumis melo L. - Afr. J. Biotechnol. 10: 1752–1759, 2011.
Wang, P., Xue, L., Batelli, G., Lee, S., Hou, Y.J., Van Oosten, M.J., Zhang, H., Tao, W.A., Zhu, J.K.: Quantitative phosphoproteomics identifies SnRK2 protein kinase substrates and reveals the effectors of abscisic acid action. - Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA 110: 11205–11210, 2013.
Wei, W., Bilsborrow, P.E., Hooley, P., Fincham, D.A., Lombi, E., Forster, B.P.: Salinity induced differences in growth, ion distribution and partitioning in barley between the cultivar Maythorpe and its derived mutant Golden Promise. - Plant Soil 250: 183–191, 2003.
Williams, V., Twine, S.: Flame photometric method for sodium, potassium and calcium. - Modern Meth. Plant Anal. 5: 3–5, 1960.
Wu, D., Shen, Q., Qiu, L., Han, Y., Ye, L., Jabeen, Z., Shu, Q., Zhang, G.: Identification of proteins associated with ion homeostasis and salt tolerance in barley. - Proteomics 14: 1381–1392, 2014.
Xu, H.X., Jiang, X.Y., Zhan, K.H., Cheng, X.Y., Chen, X.J., Pardo, J.M., Cui, D.: Functional characterization of a wheat plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter in yeast. - Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 473: 8–15, 2008.
Yamaguchi, T., Hamamoto, S., Uozumi, N.: Sodium transport system in plant cells. - Front. Plant. Sci. 4: 410, 2013.
Yang, L., Liu, H., Fu, S.M., Ge, H.M., Tang, R.J., Yang, Y., Wang, H.H., Zhang, H.X.: Na+/H+ and K+/H+ antiporters AtNHX1 and AtNHX3 from Arabidopsis improve salt and drought tolerance in transgenic poplar. - Biol. Plant. 61: 641–650, 2017.
Yang, Q., Chen, Z.Z., Zhou, X.F., Yin, H.B., Li, X., Xin, X.F., Hong, X.H., Zhu, J.K., Gong, Z.: Over expression of SOS (salt overly sensitive) genes increases salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. - Mol. Plants 1: 22–31, 2009.
Yokoi, S., Quintero, F.J., Cubero, B., Ruiz, M.T., Bressan, R.A., Hasegawa, P.M., Pardo, J.M.: Differential expression and function of Arabidopsis thaliana NHX Na+/H+ antiporters in the salt stress response. - Plant. J. 30: 529–539, 2002.
Zhang, H.X., Blumwald, E.: Transgenic salt-tolerant tomato plants accumulate salt in foliage but not in fruit. - Nat Biotechnol. 19: 765–768, 2001.
Zhang, H.X., Hodson., J.N., Williams, J.P., Blumwald, E.: Engineering salt-tolerant Brassica plants: characterization of yield and seed oil quality in transgenic plants with increased vacuolar sodium accumulation. - Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA. 98: 12832–12836, 2001.
Zhang, G.H., Su, Q., An, L.J., Wu, S.: Characterization and expression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene from the monocot halophyte Aeluropus littoralis. - Plant. Physiol. Biochem. 46: 117–126, 2008.
Zhonghua, C., Pottosin, I.I., Tracey, A., Cuin, T.A., Fuglsang, A.T., Tester, M., Deepa, J.h., Zepeda-Jazo, I., Zhou, M., Palmgren, M.G., Newman, I.A., Shabala, S.: Root plasma transporters controlling K+/Na+ homeostasis in salt stressed barley. - Plant Physiol. 145: 1714–1725, 2007.
Zhu, J.K.: Genetic analysis of plant salt tolerance using Arabidopsis. - Plant. Physiol. 124: 941–948, 2000.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Acknowledgment: The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support received from the Faculty of Plant Production, Department of Plant Breeding and Biotechnology, Gorgan University of Agricultural Sciences and Natural Resources, Gorgan, Iran. The authors would like to thank the Seed and Plant Improvement Institute, Karaj, Iran, for the provision of seed material.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yousefirad, S., Soltanloo, H., Ramezanpour, S.S. et al. Salt oversensitivity derived from mutation breeding improves salinity tolerance in barley via ion homeostasis. Biol Plant 62, 775–785 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-018-0823-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-018-0823-2