Abstract
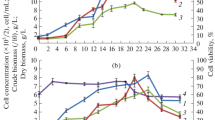
Cytophysiological and cytogenetic characteristics of cell suspension culture of Panax japonicus var. repens were studied in relation to the accumulation of ginsenosides (GSs). The minimal time of cell number doubling was 1.3 ± 0.1 d and cell number increased 7 to 8-fold during growth cycle. The cell culture can be considered as aneuploid with about tetraploid (46–60 chromosomes) modal class. Upon long-term cultivation, the total content of GSs considerably increased and maximal concentration of GSs was 2.2 %(d.m.). The ratio of seven major GSs only slightly altered both over each and different subcultures. The overall amount of GSs of Rg-group significantly exceeded that of Rb-group. Cell volume and the number of large cellular aggregates with the higher proportion (by 20 %) of parenchymal cells increased late in the subculture. In this time the population contained about 20 % of the cells with doubled amount of nuclear DNA and accompanied with elevation in the GS content. These data prompted us to suggest that biosynthesis of GSs has a link with cell differentiation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HPLC:
-
high-performance liquid chromatography
- GS:
-
ginsenoside
- PJ:
-
Panax japonicus var. repens
- SM:
-
secondary metabolite
References
Bayliss, M.V.: Chromosomal variation in plant tissue culture.-Int. Rev. Cytol. 11A(Suppl.): 113–144, 1980.
Bondarev, N., Reshetnyak, O., Nosov, A.: Peculiarities of diterpenoid steviol glycoside production in in vitro cultures of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni.-Plant Sci. 161: 155–163, 2001.
Bondarev, N.I., Sukhanova, M.A., Reshetnyak, O.V., Nosov, A.M.: Steviol glycoside content in different organs of Stevia rebaudiana and its dynamics during ontogeny.-Biol. Plant. 47: 261–264, 2003/4.
Bonfill, M., Cusidó, R.M., Palazón, J., Piñol, M.T., Morales, C.: Influence of auxins on organogenesis and ginsenoside production in Panax ginseng calluses.-Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 68: 73–78, 2002.
Briskin, D.P.: Medicinal plants and phytomedicines. Linking plant biochemistry and physiology to human health.-Plant Physiol. 124: 507–514, 2000.
Bulgakov, V.P., Zhuravlev, Yu.N., Kozyrenko, M.A., Babkina, E.N., Uvarova, N.I., Makhan’kov, V.V.: [The content of dammarane-type glycosides in different callus lines of Panax ginseng C.A. Mey.]-Rast. Resursy 27: 94–100, 1991. [In Russ.]
Butenko, R.G.: Plant Tissue Culture and Plant Morphogenesis.-Israel Program for Scientific Translations Ltd., Jerusalem 1968.
Butenko, R.G., Frolova, L.V., Lipsky, A.Kh., Reshetnyak, O.V.: Characteristics of Panax ginseng strains and growth of cell suspensions in bioreactors.-In: Proceedings of the 6th International Ginseng Symposium. Pp. 150–154. Korea Ginseng and Tobacco Research Institute, Taejon 1993.
Chaiko, A.L., Reshetnyak, O.V., Kulichenko, I.E.: [The Panax japonicus (var. repens) cell culture: callus and suspension culture production, growth optimization and analysis of ginsenosides.]-Biotekhnologiya 6: 51–55, 1999. [In Russ.]
Choi, K.-T., Ahn, I.-O., Park, J.-C.: Production of ginseng saponin in tissue culture of ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer).-Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 41: 784–789, 1994.
Craig, W.J.: Health-promoting properties of common herbs.-Amer. J. clin. Nutr. 70(Suppl.): 491S–499S, 1999.
Dixon, R.A.: Natural products and plant disease resistance.-Nature 411: 843–847, 2001.
Eeva, M., Ojala, T., Tammela, P., Galambosi, B., Vuorela, H., Hiltunen, R., Fagerstedt, K., Vuorela, P.: Propagation of Angelica archangelica plants in an air-sparged bioreactor from a novel embryogenic cell line, and their production of coumarins.-Biol. Plant. 46: 343–347, 2003.
Estévez, J.M., Cantero, A., Reindl, A., Reichler, S., León, P.: 1-Deoxy-d-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase, a limiting enzyme for plastidic isoprenoid biosynthesis in plants.-J. biol. Chem. 276: 22901–22909, 2001.
Fedorov, A.L. (ed.): Khromosomnye Chisla Tsvetkovykh Rasteniï. [Chromosomal Numbers of Phanerogamous Plants.]-Nauka, Leningrad 1969. [In Russ.]
Flores-Sánchez, I.J., Ortega-López, J., Montes-Horcasitas, M.C., Ramos-Valdivia, A.C.: Biosynthesis of sterols and triterpenes in cell suspension cultures of Uncaria tomentosa.-Plant Cell Physiol. 43: 1502–1509, 2002.
Gundlach, H., Müller, M.J., Kutchan, T.M., Zenk M.H.: Jasmonic acid is a signal transducer in elicitor-induced plant cell cultures.-Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA 89: 2389–2393, 1992.
Hayashi, H., Huang, P., Inoue, K., Hiraoka, N., Ikeshiro, Y., Yazaki, K., Tanaka, S., Kushiro, T., Shibuya, M., Ebizuka, Y.: Molecular cloning and characterization of isomultiflorenol synthase, a new triterpene synthase from Luffa cylindrica, involved in biosynthesis of bryonolic acid.-Eur. J. Biochem. 268: 6311–6317, 2001.
Kozyrenko, M.M., Artyukova, E.V., Lauve, L.S., Zhuravlev, Yu.N., Reunova, G.D.: Genetic variability of the Panax ginseng callus lines.-Russ. J. Biotechnol. 1: 29–34, 2001.
Kubo, M., Tani, T., Katsuki, T., Ishizaki, K., Arichi, S.: Histochemistry. I. Ginsenosides in ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) root.-J. natur. Prod. 43: 278–284, 1980.
Kunakh, V.A., Mozhilevskaya, L.P., Adonin, V.I., Gubar, S.I.: [Productivity and genetic structure of Panax ginseng C.A. Mey cell populations during the in vitro cultivation.]-Biotekhnologiya 3: 25–35, 2003. [In Russ.]
Langhansová, L., Maršík, P., Vaněk, T.: Production of saponins from Panax ginseng suspension and adventitious root cultures.-Biol. Plant. 49: 463–465, 2005.
Lee, M.-H., Jeong, J.-H., Seo, J.-W., Shin, C.-G., Kim, Y.-S., In, J.-G., Yang, D.-C., Yi, J.-S., Choi, Y.-E.: Enhanced triterpene and phytosterol biosynthesis in Panax ginseng overexpressing squalene synthase gene.-Plant Cell Physiol. 45: 976–984, 2004.
Liu, S., Zhong, J.J.: Phosphate effect on production of ginseng saponin and polysaccharide by cell suspension cultures of Panax ginseng and Panax quinquefolium.-Process Biochem. 33: 69–74, 1998.
Murashige, T., Skoog, F.: A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassay with tobacco tissue culture.-Physiol. Plant. 15: 473–495, 1962.
Nosov, A.V., Globa, E.B., Kulichenko, I.E., Reshetnyak, O.V., Sobol’kova, G.I.: Effect of 5-azacytidine, a tool for epigenetic control, on saponin synthesis in cell cultures of Dioscorea deltoidea and Panax quinquefolium.-Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 47: 407–416, 2000.
Shibata, S., Tanaka, O., Shoji, J., Saito, H.: Chemistry and pharmacology of Panax.-In: Wagner, H., Hikino, H., Farnsworth, N.R. (ed.): Economic and Medicinal Plant Research. Pp. 217–284. Academic Press, London 1985.
Smith, R.G., Caswell, D., Carried, A., Zielke, B.: Variation of the ginsenoside content of American ginseng, Panax quinquefolium, roots.-Can. J. Bot. 74: 1616–1620, 1996.
Suzuki, H., Achnine, L., Xu, R., Matsuda, S.P.T., Dixon, R.A.: A genomics approach to the early stages of triterpene saponin biosynthesis in Medicago truncatula.-Plant J. 32: 1033–1048, 2002.
Świątek, A., Lenjou, M., Van Bockstaele, D., Inzé, D., Van Onckelen, H.: Differential effect of jasmonic acid and abscisic acid on cell cycle progression in tobacco BY-2 cells.-Plant Physiol. 128: 201–211, 2002.
Wang, W., Zhang, Z.-Y., Zhong, J.-J.: Enhancement of ginsenoside biosynthesis in high-density cultivation of Panax notoginseng cells by various strategies of methyl jasmonate elicitation.-Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 67: 752–758, 2005.
Zhong, J.J., Bai, Y., Wang, S.J.: Effects of plant growth regulators on cell growth and ginsenoside saponin production by suspension cultures of Panax quinquefolium.-J. Biotechnol. 45: 227–234, 1996.
Zoriniants, S.E., Nosov, A.V., Monforte-Gonzalez, M., Mendes-Zeel, M., Loyola-Vargas, V.M.: Variation of nuclear DNA content during somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration of Coffea arabica L. using cytophotometry.-Plant Sci. 164: 141–146, 2003.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
In memory of Prof. R.G. Butenko
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smolenskaya, I.N., Reshetnyak, O.V., Nosov, A.V. et al. Ginsenoside production, growth and cytogenetic characteristics of sustained Panax japonicus var. Repens cell suspension culture. Biol Plant 51, 235–241 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-007-0047-3
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-007-0047-3