Abstract
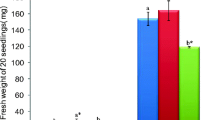
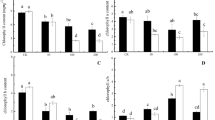
To determine whether the major influence of high salinity is caused by the osmotic component or by salinity-induced specific ion toxicity, we compared the effects of mannitol, sorbitol, NaCl and KCl (all in concentratuions corresponded to osmotic potential −1.0 MPa) on the antioxidant and anatomical responses of the apple rootstock MM 106 explants grown in the Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium. All the compounds had a significant influence on explant's mineral composition and reduced the leaf water content, whereas mannitol and salts decreased chlorophyll (Chl) content and increased proline content. Superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase (POD) and non-enzymatic antioxidant activities as well as H2O2 content were increased in the leaves and stems. In addition, in the leaves of explants exposed to NaCl an additional Mn-SOD isoform was revealed, while specific POD isoforms were detected in the leaves and stems treated with NaCl or KCl. However, catalase activity was depressed in the salt-treated leaves. At the ultrastructural level, the NaCl-treated leaves had the thickest lamina, due to an extensive increase of the size of epidermal and mesophyll cells. Also, an increase of the relative volume of the intercellular spaces in response to NaCl was observed. The results suggest that Na accumulation is the first candidate for the distinct antioxidant and anatomical responses between saline and osmotically generated stress in the MM 106 explants.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CAT:
-
catalase
- Chl:
-
chlorophyll
- FRAP:
-
ferric reducing antioxidant power
- MS medium:
-
Murashige and Skoog medium
- PAGE:
-
polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- POD:
-
peroxidase
- SOD:
-
superoxide dismutase
- WC:
-
water content
References
Al-Khayri, J.M., Al-Bahrany, A.M.: Callus growth and proline accumulation in response to sorbitol and sucrose-induced osmotic stress in rice.-Biol. Plant. 45: 609–611, 2002.
Bahaji, A., Mateu, I., Sanz, A., Cornejo, M.J.: Common and distinctive responses of rice seedlings to saline-and osmotically-generated stress.-Plant Growth Regul. 38: 83–94, 2002.
Bates, L.S., Waldren, S.P., Teare, I.D.: Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies.-Plant Soil 39: 205–207, 1973.
Beauchamp, B., Fridovich, I.: Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and applicable to acrylamide gels.-Anal. Biochem. 44: 276–287, 1971.
Benzie, I.F.F., Strain, J.J.: The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: The FRAP assay.-Anal. Biochem. 239: 70–76, 1996.
Blumwald, E., Aharon, G.S., Apse, M.P.: Sodium transport in plant cells.-Biochim. biophys. Acta 1465: 140–151, 2000.
Bradford, M.M.: A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding.-Anal. Biochem. 72: 248–254, 1976.
Cherian, S., Reddy, M.P.: Evaluation of NaCl tolerance in the callus cultures of Suaeda nudiflora Moq.-Biol. Plant. 46: 193–198, 2003.
Dash, M., Panda, S.K.: Salt stress induced changes in growth and enzyme activities in germinating Phaseolus mungo seeds.-Biol. Plant. 44: 587–589, 2001.
Grattan, S.R., Grieve, C.M.: Salinity-mineral nutrient relations in horticultural crops.-Scientia Hort. 78: 127–157, 1998.
Hsiao. T.C.: Plant responses to water stress.-Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 24: 519–570, 1973.
Kuo, J.M., Yeh, D.B., Pan, B.S.: Rapid photometric assay evaluating antioxidative activity in edible plant material.-J. Agr. Food Chem. 47: 3206–3209, 1999.
Laemmli, U.K.: Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.-Nature 227: 680–685, 1970.
Lee, D.H., Kim, T.S., Lee, C.B.: The inductive responses of the antioxidant enzymes by salt stress in the rice (Oryza sativa L.).-J. Plant Physiol. 158: 737–745, 2001.
Maathuis, F.J.M., Amtmann, A.: K+ nutrition and Na+ toxicity: the basis of cellular K+/Na+ ratios.-Ann Bot. 84: 123–133, 1999.
Mittler, R.: Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance.-Trends Plant Sci. 7: 405–410, 2002.
Murashige, T., Skoog, F.: A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassay with tobacco tissue culture.-Physiol. Plant. 15: 473–495, 1962.
Nakamura, Y., Kasamo, K., Shimosato, N., Sakata, M., Ohta, E.: Stimulation of the extrusion of protons and H+-ATPase activities with the decline in pyrophosphatase activity of the tonoplast in intact mung bean roots under high-NaCl stress and its relation to external levels of Ca2+ ions.-Plant Cell Physiol. 33: 139–149, 1992.
Ngo, T.T., Lenhoff, H.M.: A sensitive and versatile chromogenic assay for peroxidase and peroxidase-coupled reactions.-Anal. Biochem. 105: 389–397, 1980.
Panda, S.K., Upadhyay, R.K.: Salt stress injury induces oxidative alterations and antioxidative defence in the roots of Lemna minor.-Biol. Plant. 48: 249–253, 2004.
Pazdzioch-Czochra, M., Widenska, A.: Spectrofluorimetric determination of hydrogen peroxide scavenging activity.-Anal. chim. Acta 452: 177–184, 2002.
Romero-Aranda, R., Moya, J.L., Tadeo, F.R., Legaz, F., Primo-Millo, E., Talon, M.: Physiological and anatomical disturbances induced by chloride salts in sensitive and tolerant citrus: beneficial and detrimental effects of cations.-Plant Cell Environ. 21: 1243–1253, 1998.
Sam, O., Ramirez, C., Coronado, M.J., Testillano, P.S., Risueno, M.C.: Changes in tomato leaves induced by NaCl stress: leaf organization and cell ultrastructure.-Biol. Plant. 47: 361–366, 2003.
Shannon, M.C., Grieve, C.M., Francois, L.E.: Whole-plant response to salinity.-In: Wilkinson, R.E. (ed.): Plant-Environment Interactions. Pp. 199–204. Marcel Dekker, New York 1994.
Shimoni, M.: A method for activity staining of peroxidase and β-1, 3-glucanase isozymes in polyacrylamide electrophoresis gels.-Anal. Biochem. 220: 36–38, 1994.
Steer, M.W.: Understanding Cell Structure.-Cambridge University Press, Cambridge 1981.
Wang, C.Y.: Effect of temperature preconditioning on catalase, peroxidase and superoxide dismutase in chilled zucchini squash.-Postharvest Biol. Technol. 5: 67–76, 1995.
Wang, Z., Stutte, G.W.: The role of carbohydrates in active osmotic adjustment in apple under water stress.-J. amer. Soc. hort. Sci. 117: 816–823, 1992.
Wintermans, J.F., Mots, A.: Spectrophotometric characteristics of chlorophylls a and b and pheophytins in ethanol.-Biochim. biophys. Acta. 109: 448–453, 1965.
Woodbury, W., Spencer, A.K., Stahmann, M.A.: An improve procedure using ferricyanide for detecting catalase isozymes.-Anal. Biochem. 44: 301–305, 1971.
Xiong, L., Zhu, J.K.: Molecular and genetic aspects of plant responses to osmotic stress.-Plant Cell Environ. 25: 131–139, 2002.
Zhu, J.K.: Plant salt tolerance.-Trends Plant Sci. 6: 66–71, 2001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Molassiotis, A.N., Sotiropoulos, T., Tanou, G. et al. Antioxidant and anatomical responses in shoot culture of the apple rootstock MM 106 treated with NaCl, KCl, mannitol or sorbitol. Biol Plant 50, 61–68 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-005-0075-9
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-005-0075-9