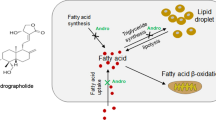
Abstract
Trivalent chromium [Cr(III)] has been shown as an essential trace element for human health. Previous studies depict that Cr(III) plays important roles in maintaining normal glucose and lipid metabolism, whereas its effect on the hepatic lipid metabolism is still unknown. In the present study, we investigated the effects and underlying mechanisms of Cr on hepatic steatosis induced by oleic acid (OA) in human hepatoma SMMC-7721 cells. Hepatic steatosis model was co-administered with Cr. Indexes of lipid accumulation were determined and associated genes expression were analyzed. The data showed that OA could induce lipid accumulation and triglyceride (TG) content in SMMC-7721 cells, and significantly increase the expression of cluster of differentiation 36 (CD36) and diacylglycerol acyltransferase 2 (DGAT2). This steatosis effect of OA was ameliorated by Cr. The TG accumulation and up-regulation of CD36 and DGAT2 genes followed steatosis induction were inhibited by Cr. After the treatment of Cr, excessive intracellular OA content was also attenuated. Furthermore, Cr still performed inhibitory effect of DGAT2 expression at the presence of DGAT2 agonist or inhibitor, which indicated that the inhibitory effect of Cr on lipogenesis is associated with the downregulation of DGAT2 expression. These findings demonstrate that Cr alleviates hepatic steatosis via suppressing CD36 expression to prevent fatty acid uptake, as well as suppressing DGAT2 expression to inhibit TG synthesis. It suggests that CD36 and DGAT2 might become the novel drug targets for their properties in hepatic steatosis. Most importantly, Cr may be a potential anti-steatosis candidate to offer protective effects against liver damage.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham AS, Brooks BA, Eylath U (1992) The effects of chromium supplementation on serum glucose and lipids in patients with and without non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Metabolism 41:768–771
Anderson RA (1997) Chromium as an essential nutrient for humans. Regul Toxicol Pharm 26:35–41
Angulo P (2002) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. New Engl J Med 346:1221–1231
Anstee QM, Goldin RD (2006) Mouse models in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and steatohepatitis research. Int J Exp Pathol 87:1–16
Bagchi D, Stohs SJ, Downs BW, Bagchi M, Preuss HG (2002) Cytotoxicity and oxidative mechanisms of different forms of chromium. Toxicology 180:5–22
Basaranoglu M, Kayacetin S, Yilmaz N, Kayacetin E, Tarcin O, Sonsuz A (2010) Understanding mechanisms of the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 16:2223–2226
Bieghs V, Wouters K, Gorp PJV, Gijbels MJ, Winther MPD, Binder CJ, Lütjohann D, Febbraio M, Moore KJ, Bilsen MV, Hofker MH, Shiri-Sverdlov R (2010) Role of scavenger receptor A and CD36 in diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in hyperlipidemic mice. Gastroenterology 138:2477–2486
Błasiak J, Kowalik J (2000) A comparison of the in vitro genotoxicity of tri-and hexavalent chromium. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ 469:135–145
Bona KRD, Love S, Rhodes NR, Mcadory D, Sinha SH, Kern N, Kent J, Strickland J, Wilson A, Beaird J, Ramage J, Rasco JF, Vincent JB (2011) Chromium is not an essential trace element for mammals: effects of a “low-chromium” diet. J Biol Inorg Chem 16:381–390
Bonen A, Tandon NN, Glatz JFC, Luiken JJFP, Heigenhauser GJF (2006) The fatty acid transporter FAT/CD36 is upregulated in subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissues in human obesity and type 2 diabetes. Int J Obes 30:877–883
Buqué X, Martínez MJ, Cano A, Miquilena-Colina ME, García-Monzón C, Aspichueta P, Ochoa B (2010) A subset of dysregulated metabolic and survival genes is associated with severity of hepatic steatosis in obese Zucker rats. J Lipid Res 51:500–513
Carmena R (2005) Type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia, and vascular risk: rationale and evidence for correcting the lipid imbalance. Am Heart J 150:859–870
Chen WY, Chen CJ, Liao JW, Mao FC (2009) Chromium attenuates hepatic damage in a rat model of chronic cholestasis. Life Sci 84:606–614
Chen WY, Chen CJ, Liu CH, Mao FC (2010) Chromium attenuates high-fat diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in KK/HlJ mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 397:459–464
Choi CS, Savage DB, Kulkarni A, Yu XX, Liu ZX, Morino K, Kim S, Distefano A, Samuel VT, Neschen S, Zhang D, Wang A, Zhang XM, Kahn M, Cline GW, Pandey SK, Geisler JG, Bhanot S, Monia BP, Shulman GI (2007) Suppression of diacylglycerol acyltransferase-2 (DGAT2), but not DGAT1, with antisense oligonucleotides reverses diet-induced hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance. J Biol Chem 282:22678–22688
Choi YJ, Lee CH, Lee KY, Jung SH, Lee BH (2015) Increased hepatic fatty acid uptake and esterification contribute to tetracycline-induced steatosis in mice. Toxicol Sci 145(2):273–282
Clugston RD, Yuen JJ, Hu Y, Abumrad NA, Berk PD, Goldberg IJ, Blaner WS, Huang LS (2014) CD36-deficient mice are resistant to alcohol-and high-carbohydrate-induced hepatic steatosis. J Lipid Res 55:239–246
Day CP, James OF (1998) Steatohepatitis: a tale of two “hits”? Gastroenterology 114:842–845
Feldstein AE, Canbay A, Guicciardi ME, Higuchi H, Bronk SF, Gores GJ (2003) Diet associated hepatic steatosis sensitizes to Fas mediated liver injury in mice. J Hepatol 39:978–983
Ganji SH, Kashyap ML, Kamanna VS (2015) Niacin inhibits fat accumulation, oxidative stress, and inflammatory cytokine IL-8 in cultured hepatocytes: impact on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Metabolism 64(9):982–990
Hajri T, Abumrad NA (2002) Fatty acid transport across membranes: relevance to nutrition and metabolic pathology 1. Annu Rev Nutr 22:383–415
Ibrahimi A, Abumrad NA (2002) Role of CD36 in membrane transport of long-chain fatty acids. Curr Opin Clin Nutr 5:139–145
Iqbal J, Hussain MM (2009) Intestinal lipid absorption. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 296:1183–1194
Jain SK, Rogier K, Prouty L, Jain SK (2004) Protective effects of 17β-estradiol and trivalent chromium on interleukin-6 secretion, oxidative stress, and adhesion of monocytes: relevance to heart disease in postmenopausal women. Free Radic Bio Med 37:1730–1735
Jornayvaz FR, Birkenfeld AL, Jurczak MJ, Kanda S, Guigni BA, Jiang DC, Zhang D, Lee HY, Samuel VT, Shulman GI (2011) Hepatic insulin resistance in mice with hepatic overexpression of diacylglycerol acyltransferase 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108:5748–5752
Kamanna VS, Kashyap ML (2008) Mechanism of action of niacin. Am J Cardiol 101:20–26
Kennedy DJ, Kuchibhotla S, Westfall KM, Silverstein RL, Morton RE, Febbraio M (2011) A CD36-dependent pathway enhances macrophage and adipose tissue inflammation and impairs insulin signalling. Cardiovasc Res 89:604–613
Koonen DP, Jacobs RL, Febbraio M, Young ME, Soltys CLM, Ong H, Vance DE, Dyck JR (2007) Increased hepatic CD36 expression contributes to dyslipidemia associated with diet-induced obesity. Diabetes 56:2863–2871
Li YS, Zhu NH, Niu PP, Shi FX, Hughes CL, Tian GX, Huang RH (2013) Effects of dietary chromium methionine on growth performance, carcass composition, meat colour and expression of the colour-related gene myoglobin of growing-finishing pigs. Asian Aust J Anim 26(7):1021–1029
Li C, Li L, Lian J, Watts R, Nelson R, Goodwin B, Lehner R (2015) Roles of Acyl-CoA: diacylglycerol acyltransferases 1 and 2 in triacylglycerol synthesis and secretion in primary hepatocytes. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 35:1080–1091
Mahdi GS (1996) Chromium deficiency might contribute to insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes mellitus, dyslipidaemia, and atherosclerosis. Diabet Med 13:389–390
Malhi H, Bronk SF, Werneburg NW, Gores GJ (2006) Free fatty acids induce JNK-dependent hepatocyte lipoapoptosis. J Biol Chem 281:12093–12101
Maples NL, Bain L (2004) Trivalent chromium alters gene expression in the mummichog (Fundulus heteroclitus). Environ Toxicol Chem 23:626–631
Miquilena-Colina ME, Lima-Cabello E, Sánchez-Campos S, García-Mediavilla MV, Fernández-Bermejo M, Lozano-Rodríguez T, Vargas-Castrillón J, Buqué X, Ochoa B, Aspichueta P, González-Gallego J, García-Monzón C (2011) Hepatic fatty acid translocase CD36 upregulation is associated with insulin resistance, hyperinsulinaemia and increased steatosis in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and chronic hepatitis C. Gut 60:1394–1402
Mo X, Yang C, Wang X, Burkhardt BR, Li Y, Xia H, Cao X (2015) F3MB (PANDER) Decreases mice hepatic triglyceride and is associated with decreased DGAT1 expression. PloS One 10(2):e0117156
Najafpanah MJ, Sadeghi M, Zali A, Moradi-Shahrebabak H, Mousapour H (2014) Chromium downregulates the expression of Acetyl CoA Carboxylase 1 gene in lipogenic tissues of domestic goats: a potential strategy for meat quality improvement. Gene 543:253–258
Nanthirudjanar T, Furumoto H, Hirata T, Sugawara T (2013) Oxidized eicosapentaenoic acids more potently reduce LXR alpha-induced cellular triacylglycerol via suppression of SREBP-1c, PGC-1 beta and GPA than its intact form. Lipids Health Dis 12(1):1–11
Ouwens DM, Diamant M, Fodor M, Habets DDJ, Pelsers MMAL, El Hasnaoui M, Dang ZC, van den Brom CE, Vlasblom R, Rietdijk A, Boer C, Coort SL, Glatz JF, Luiken JJFP (2007) Cardiac contractile dysfunction in insulin-resistant rats fed a high-fat diet is associated with elevated CD36-mediated fatty acid uptake and esterification. Diabetologia 50:1938–1948
Ramirez-Zacarias JL, Castro-Munozledo F, Kuri-Harcuch W (1992) Quantitation of adipose conversion and triglycerides by staining intracytoplasmic lipids with Oil red O. Histochemistry 97:493–497
Reddy JK (2001) III Peroxisomal β-oxidation, PPARα, and steatohepatitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 281:G1333–G1339
Rogue A, Anthérieu S, Vluggens A, Umbdenstock T, Claude N, De La Moureyre-Spire C, Weaver RJ, Guillouzo A (2014) PPAR agonists reduce steatosis in oleic acid-overloaded HepaRG cells. Toxicol Appl Pharm 276:73–81
Roling JA, Baldwin WS (2006) Alterations in hepatic gene expression by trivalent chromium in Fundulus heteroclitus. Mar Environ Res 62:S122–S127
Sahin K, Sahin N, Kucuk O (2003) Effects of chromium, and ascorbic acid supplementation on growth, carcass traits, serum metabolites, and antioxidant status of broiler chickens reared at a high ambient temperature (32 °C). Nutr Res 23:225–238
Sato T, Morita A, Mori N, Miura S (2014) The role of glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1 in the progression of fatty liver after acute ethanol administration in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 444:525–530
Stone SJ, Myers HM, Watkins SM, Brown BE, Feingold KR, Elias PM, Farese RV (2004) Lipopenia and skin barrier abnormalities in DGAT2-deficient mice. J Biol Chem 279:11767–11776
Sumida Y, Niki E, Naito Y, Yoshikawa T (2013) Involvement of free radicals and oxidative stress in NAFLD/NASH. Free Radic Res 47:869–880
Wakil SJ, Abu-Elheiga LA (2009) Fatty acid metabolism: target for metabolic syndrome. J Lipid Res 50:138–143
Wang ZQ, Qin J, Martin J, Zhang XH, Sereda O, Anderson RA, Pinsonat P, Cefalu WT (2007) Phenotype of subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus may determine clinical response to chromium supplementation. Metabolism 56:1652–1655
Wang GL, Fu YC, Xu WC, Feng YQ, Fang SR, Zhou XH (2009) Resveratrol inhibits the expression of SREBP1 in cell model of steatosis via Sirt1–FOXO1 signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 380:644–649
Wang C, Lv ZL, Kang YJ, Xiang TX, Wang PL, Jiang Z (2013) Aquaporin-9 downregulation prevents steatosis in oleic acid-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease cell models. Int J Mol Med 32:1159–1165
Wang S, Kuang X, Fang Z, Huang Z, Shi P (2014) Effect of Oleic Acid on the Levels of Eight Metal Ions in Human Hepatoma SMMC-7721 Cells. Biol Trace Elem Res 159:445–450
Yen CLE, Stone SJ, Koliwad S, Harris C, Farese RV (2008) Thematic review series: glycerolipids DGAT enzymes and triacylglycerol biosynthesis. J Lipid Res 49:2283–2301
Yu XX, Murray SF, Pandey SK, Booten SL, Bao D, Song XZ, Kelly S, Chen S, McKay R, Monia BP, Bhanot S (2005) Antisense oligonucleotide reduction of DGAT2 expression improves hepatic steatosis and hyperlipidemia in obese mice. Hepatology 42:362–371
Zhao Y, Pan Y, Yang Y, Batey R, Wang J, Li Y (2015) Treatment of rats with Jiangzhi Capsule improves liquid fructose-induced fatty liver: modulation of hepatic expression of SREBP-1c and DGAT-2. J Transl Med 13:1–12
Ziamajidi N, Khaghani S, Hassanzadeh G, Vardasbi S, Ahmadian S, Nowrouzi A, Ghaffari SM, Abdirad A (2013) Amelioration by chicory seed extract of diabetes-and oleic acid-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)/non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) via modulation of PPARα and SREBP-1. Food Chem Toxicol 58:198–209
Acknowledgments
This work was sponsored by grants from Shanghai Scientific and Technological Innovation Project (14520720700), the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (15ZR1400200), State Education Ministry and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (222201313010 and 2232014A3-03), the Applied Basic Research Project of Promotion Plan for Scientific and Technological Innovation in Qinghai Province (2015-ZJ-703).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Wang, J., Zhang, X. et al. Trivalent chromium alleviates oleic acid induced steatosis in SMMC-7721 cells by decreasing fatty acid uptake and triglyceride synthesis. Biometals 29, 881–892 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-016-9960-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-016-9960-2