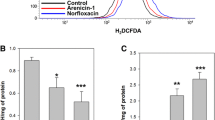
Abstract
Silver nanoparticles are known to have antimicrobial properties and have been used extensively in medicine, although the mechanism(s) of action have not yet been clearly established. In the present study, the findings suggest a novel mechanism for the antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles on Escherichia coli, namely, the induction of a bacterial apoptosis-like response. We propose a possible mechanism for the bacterial apoptosis-like response that includes the following: accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) (detected with H2DCFDA staining), increased intracellular calcium levels (detected with Fura-2 AM), phosphatidylserine exposure in the outer membrane (detected with Annexin V) which is the hallmarks of early apoptosis, disruption of the membrane potential [detected with DiBAC4(3)], activation of a bacterial caspase-like protein (detected by FITC-VAD-FMK staining) and DNA degradation (detected with TUNEL assay) which is the hallmarks of late apoptosis in bacterial cells treated with silver nanoparticles. We also performed RecA expression assay with western blotting and observed activation of SOS response to repair the damaged DNA. To summarize, silver nanoparticles are involved in the apoptosis-like response in E. coli and the novel mechanisms which were identified in this study, suggest that silver nanoparticles may be an effective antimicrobial agent with far lower propensity for inducing microbial resistance than antibiotics.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arduino DM, Esteves AR, Domingues AF, Pereira CM, Cardoso SM, Oliveira CR (2009) ER-mediated stress induces mitochondrial-dependent caspase activation in NT2 neuron-like cells. BMB Rep 42:719–724
Atiyeh BS, Costaqliola M, Hayek SN, Dibo SA (2007) Effect of silver on burn wound infection control and healing: review of the literature. Burns 33:139–148
Bos J, Yakhnina AA, Gitai Z (2012) BapE DNA endonuclease induces an apoptotic-like response to DNA damage in Caulobacter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:18096–18101
Bosetti M, Massè A, Tobin E, Cannas M (2002) Silver coated materials for external fixation devices: in vitro biocompatibility and genotoxicity. Biomaterials 23:887–892
Chakraborti T, Das S, Mondal M, Roychoudhury S, Chakraborti S (1999) Oxidant, mitochondria and calcium: an overview. Cell Signal 11:77–85
Costa V, Moradas-Ferreira P (2001) Oxidative stress and signal transduction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: insights into aging, apoptosis and disease. Mol Aspects Med 22:217–246
Crompton M (1999) The mitochondrial permeability transition pore and its role in cell death. Biochem J 341:233–249
Dominguez DC (2004) Calcium signaling in bacteria. Mol Microbiol 54:291–297
Dwyer DJ, Camacho DM, Kohanski MA, Callura JM, Collins JJ (2012) Antibiotic-induced bacterial cell death exhibits physiological and biochemical hallmarks of apoptosis. Mol Cell 46:561–572
Engelberg-Kulka H, Amitai S, Kolodkin-Gal I, Hazan R (2006) Bacterial programmed cell death and multicellular behavior in bacteria. PLoS Genet 2:e135
Fonville NC, Bates D, Hastings PJ, Hanawalt PC, Rosenberg SM (2010) Role of RecA and the SOS response in thymineless death in Escherichia coli. PLoS Genet 6:e1000865
Foti JJ, Devadoss B, Winkler JA, Collins JJ, Walker GC (2012) Oxidation of the guanine nucleotide pool underlies cell death by bactericidal antibiotics. Science 336:315–319
Furuya EY, Lowy FD (2006) Antimicrobial-resistant bacteria in the community setting. Nat Rev Microbiol 4:36–45
Hakansson AP, Roche-Hakansson H, Mossberg AK, Svanborg C (2011) Apoptosis-like death in bacteria induced HAMLET, a human milk lipid-protein complex. PLoS ONE 6:e17717
Halliwell B, Aruoma OI (1991) DNA damage by oxygen-derived species. Its mechanism and measurement in mammalian systems. FEBS Lett 281:9–19
Herrera M, Carrion P, Baca P, Liebana J, Castillo A (2001) In vitro antibacterial activity of glass-ionomer cements. J Clin Pediatr Dent 104:141–148
Hwang IS, Hwang JH, Choi H, Kim KJ, Lee DG (2012) Synergistic effects between silver nanoparticles and antibiotics and the mechanisms involved. J Med Microbiol 61:1719–1726
Jakubowski W, Biliński T, Bartosz G (2000) Oxidative stress during aging of stationary cultures of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Free Radic Biol Med 28:659–664
Jones SA, Bowler PG, Walker M, Parsons D (2004) Controlling wound bioburden with a novel silver-containing Hydrofiber dressing. Wound Repair Regen 12:288–294
Kamenšek S, Podlesek Z, Gillor O, Zgur-Bertok D (2010) Genes regulated by the Escherichia coli SOS repressor LexA exhibit heterogeneous expression. BMC Microbiol 10:283
Klasen HJ (2000) Historical review of the use of silver in the treatment of burns. I Early uses. Burns 33:117–138
Kohanski MA, Dwyer DJ, Hayete B, Lawrence CA, Collins JJ (2007) A common mechanism of cellular death induced by bactericidal antibiotics. Cell 130:797–810
Kroemer G, Reed JC (2000) Mitochondrial control of cell death. Nat Med 6:513–519
Kyrylkova K, Kyryachenko S, Leid M, Kioussi C (2012) Detection of apoptosis by TUNEL assay. Methods Mol Biol 887:41–47
Labat-Moleur F, Guillermet C, Lorimier P, Robert C, Lantuejoul S, Brambilla E, Negoescu A (1998) TUNEL apoptotic cell detection in tissue sections: critical evaluation and improvement. J Histochem Cytochem 46:327–334
Li WR, Xie XB, Shi QS, Zeng HY, Ou-Yang YS, Chen YB (2010) Antibacterial activity and mechanism of silver nanoparticles on Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85:1115–1122
Liao RS, Rennie RP, Talbot JA (1999) Assessment of the effect of amphotericin B on the vitality of Candida albicans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 43:1034–1041
Ludovico P, Madeo F, Silva MT (2005) Yeast programmed cell death: an intricate puzzle. IUBMB Life 57:129–135
Madeo F, Fröhlich E, Fröhlich KU (1997) A yeast mutant showing diagnostic markers of early and late apoptosis. J Cell Biol 139:729–734
Madeo F, Herker E, Maldener C, Wissing S, Lächelt S, Herlan M, Fehr M, Lauber K, Sigrist SJ, Wesselborg S, Fröhlich KU (2002) A caspase-related protease regulates apoptosis in yeast. Mol Cell 9:911–917
Majno G, Joris I (1995) Apoptosis, oncosis, and necrosis. An overview of cell death. Am J Pathol 146:3–15
Marambio-Jones C, Hoek EMV (2010) A review of the antibacterial effects of silver nanomaterials and potential implications for human health and the environment. J Nanopart Res 12:1531–1551
Maul RW, Sutton MD (2005) Roles of the Escherichia coli RecA protein and the global SOS response in effecting DNA polymerase selection in vivo. J Bacteriol 187:7607–7618
Morones JR, Elechiguerra JL, Camacho A, Holt K, Kouri JB, Ramírez JT, Yacaman MJ (2005) The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 16:2346–2353
Morones-Ramirez JR, Winkler JA, Spina CS, Collins JJ (2013) Silver enhances antibiotic activity against gram-negative bacteria. Sci Transl Med 4:190ra81
Nagata A (1997) Apoptosis by death factor. Cell 88:355–365
Phillips AJ, Sudbery I, Ramsdale M (2003) Apoptosis induced by environmental stresses and amphothericin B in Candida albicans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:14327–14332
Rai M, Yadav A, Gade A (2009) Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of microbials. Biotechnol Adv 27:76–83
Rieger AM, Nelson KL, Konowalchuk JD, Barreda DR (2011) Modified annexin V/propidium iodide apoptosis assay for accurate assessment of cell death. J Vis Exp 50:2597
Sanchez L (2001) TCA protein precipitation. Protocols on line. http://www.its.caltech.edu/~bjorker/Protocols/TCA_ppt_protocol.pdf. Accessed 5 Aug 2014
Sintubin L, De Windt W, Dick J, Mast J, van der Ha D, Verstraete W, Boon N (2009) Lactic acid bacteria as a reducing and capping agent for the fast and efficient production of silver nanoparticles. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 84:741–749
Taylor RC, Cullen SP, Martin SJ (2008) Apoptosis: controlled demolition at the cellular level. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:231–241
Thornberry NA, Lazebnik Y (1998) Caspases: enemies within. Science 281:1312–1316
van den Eijnde SM, Boshart L, Baehrecke EH, De Zeeuw CI, Reutelingsperger CP, Vermeij-Keers C (1998) Cell surface exposure of phosphatidylserine during apoptosis is phylogenetically conserved. Apoptosis 3:9–16
Vercammen D, Declercq W, Vandenabeele P, Van Breusegem F (2007) Are metacaspases caspases? J Cell Biol 179:375–380
Verhoven B, Schlegel RA, Williamson P (1995) Mechanisms of phosphatidylserine exposure, a phagocyte recognition signal, on apoptotic T lymphocytes. J Exp Med 182:1597–1601
Widlak P, Li P, Wang X, Garrard WT (2000) Cleavage preferences of the apoptotic endonuclease DFF40 (caspase-activated DNase or nuclease) on naked DNA and chromatin substrates. J Biol Chem 275:8226–8232
Yoon MJ, Kim EH, Kwon TK, Park SA, Choi KS (2012) Simultaneous mitochondrial Ca2+ overload and proteasomal inhibition are responsible for the induction of paraptosis in malignant breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett 324:197–209
Zherebitskaya E, Schapansky J, Akude E, Smith DR, Van der Ploeg R, Solovyova N, Verkhratsky A, Fernyhough P (2012) Sensory neurons derived from diabetic rats have diminished internal Ca2+ stores linked to impaired re-uptake by the endoplasmic reticulum. ASN Neuro 4:e00072
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Next-Generation BioGreen 21 Program (No. PJ008158), Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, W., Kim, KJ. & Lee, D.G. A novel mechanism for the antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles on Escherichia coli . Biometals 27, 1191–1201 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-014-9782-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-014-9782-z