Abstract
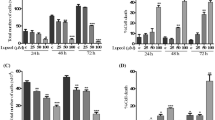
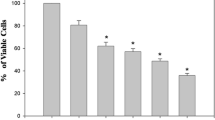
Lanthanides possess diverse biological effect and have been shown to promote cell proliferation and induce apoptosis. Our previous studies showing that lanthanide citrate complex has significant antitumor activity in human cervical cancer HeLa cells. This study aims at determining if [LaCit2]3− have the activity against another type of human cervical cancer cell line SiHa and the changes in protein expression that contribute to the mechanism(s) of [LaCit2]3−-mediated apoptosis in SiHa cells. Cell growth inhibition was measured by MTT method, and apoptosis was detected by means of Hoechst 33258 staining and flow cytometry analysis. After [LaCit2]3−-treatment the results show that the growth of SiHa cells was inhibited, the cells displayed typical apoptosis morphological changes, and increase in the rates of apoptosis. Using proteomics approaches, a variety of differentially expressed proteins were identified in SiHa cells before and after treatment with [LaCit2]3−. There were profound changes in 10 proteins relating to mitochondrial function and oxidative stress, suggesting that mitochondrial dysfunction plays a key role in [LaCit2]3−-induced apoptosis. This was confirmed by a decrease in the mitochondrial transmembrane potential (Δψm), and increases in H2O2 generation in [LaCit2]3−-treated cells. Among them the alerted proteins, Prx I, ANXA1 and TRAF5 were validated by western blotting analyses. These results suggest that there is an intrinsic molecular pathway of cell apoptosis in [LaCit2]3−-treated SiHa cells. This observation is in accordance with our previous reports about the effects of [LaCit2]3− and [YbCit2]3− on HeLa cells and it provide a molecular mechanism underlying lanthanide citrate complex-mediated cell apoptosis.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- [LaCit2]3− :
-
Lanthanum citrate complex
- [YbCit2]3− :
-
Ytterbium citrate complex
- 2-DE:
-
2-Dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazoliumbromide
- JC-1:
-
5′,6,6′-tetrachloro-1,1′,3,3′-tetraethylbenzimidazolcarbo-cyanineiodide
- DCFH-DA:
-
2′7′-dichlorofluorescein
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- Δψm :
-
Mitochondrial transmembrane potential
- ND2:
-
ND2 protein
- PrxI:
-
Peroxiredoxin-1
- ANXA1:
-
AnnexinI
- TRAF5:
-
TNF receptor-associated factor 5
References
Au PY, Yeh WC (2007) Physiological roles and mechanisms of signaling by TRAF2 and TRAF5. Adv Exp Med Biol 597:32–47. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-70630-6_3
Bae JY, Ahn SJ, Han W, Noh DY (2007) Peroxiredoxin I and II inhibit H2O2-induced cell death in MCF-7 cell lines. J Cell Biochem 101:1038–1045. doi:10.1002/jcb.21241
Barber GN (2005) The dsRNA-dependent protein kinase, PKR and cell death. Cell Death Differ 12:563–570. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4401643
Chae HZ, Kim IH, Kim K, Rhee SG (1993) Cloning, sequencing, and mutation of thiol-specific antioxidant gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 268:16815–16821
Debret R, El Btaouri H, Duca L, Rahman I, Radke S, Haye B, Sallenave JM, Antonicelli F (2003) Annexin A1 processing is associated with caspase-dependent apoptosis in BZR cells. FEBS Lett 546:195–202. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(03)00570-2
Dong S, Zhao YB, Liu HX, Yang XD, Wang K (2009) Duality of effect of La3+ on mitochondrial permeability transition pore depending on the concentration. Biometals 22:917–926. doi:10.1007/s10534-009-9244-1
Fan JL, Cai HB, Tan WS (2007) Role of the plasma membrane ROS-generating NADPH oxidase in CD34+ progenitor cells preservation by hypoxia. J Biotechnol 130:455–462. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2007.05.023
França MB, Panek AD, Eleutherio EC (2007) Oxidative stress and its effects during dehydration. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 146:621–631. doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2006.02.030
Gusdon AM, Votyakova TV, Mathews CE (2008) mt-Nd2a suppresses reactive oxygen species production by mitochondrial complexes I and III. J Biol Chem 283:10690–10697. doi:10.1074/jbc.M708801200
Heffeter P, Jakupec MA, Körner W, Wild S, von Keyserlingk NG, Elbling L, Zorbas H, Korynevska A, Knasmüller S, Sutterlüty H, Micksche M, Keppler BK, Berger W (2006) Anticancer activity of the lanthanum compound [tris (1,10-phenanthroline) lanthanum (III)] trithiocyanate (KP772; FFC24). Biochem Pharmacol 71:426–440. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2005.11.009
Kataoka A, Kubota M, Watanabe K, Sawada M, Koishi S, Lin YW, Usami I, Akiyama Y, Kitoh T, Furusho K (1997) NADH dehydrogenase deficiency in an apoptosis-resistant mutant isolated from a human HL-60 leukemia cell line. Cancer Res 57:5243–5245
Khuntia D, Mehta M (2004) Motexafin gadolinium: a clinical review of a novel radio enhancer for brain tumors. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 6:981–989. doi:10.1586/14737140.4.6.981
Kostova I (2005) Lanthanides as anticancer agents. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents 5:591–602. doi:10.2174/156801105774574694
Kostova I, Momekov G, Zaharieva M, Karaivanova M (2005) Cytotoxic activity of new lanthanum (III) complexes of bis-coumarins. Eur J Med Chem 40:542–551. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2004.12.007
Kostova I, Momekov G, Tzanova T, Karaivanova M (2006) Synthesis, characterization, and cytotoxic activity of new lanthanum (III) complexes of bis-coumarins. Bioinorg Chem Appl 2006:1–9. doi:10.1155/BCA/2006/25651
Lee YS, Chung HW, Moon HS (2008) The expression of annexin I and thymosin beta4 in cervical cancer. Korean J Obstet Gynecol 51:313–323
Lew YO, Park TC, NamKoong SE, Park DC, Kim JH, Kim DH, Yang YJ, Lee JH, Cho SD, Jo HK (1999) Role of annexin-I in cervical cancer cell proliferation. Korean J Obstet Gynecol 42:2199–2204
Liu HX, Yuan L, Yang XD, Wang K (2003) La3+, Gd3+, and Yb3+ induced changes in mitochondrial structure, membrane permeability, cytochrome c release and intracellular ROS level. Chem-Biol Interact 146:27–37. doi:10.1016/S0009-2797(03)00072-3
Longworth DL (2008) Update on infectious disease prevention: human papillomavirus, hepatitis A. Cleve Clin J Med 75:402–410. doi:10.3949/ccjm.75.6.402
Matasunaga T, Kudo J, Takahashi K, Hayashida K, Okamura S, Ishibashi H, Niho Y (1996) Roteonone, a mitochondrial NADH dehydroganase inhibitor, induces cell surface expression of CD13 andCD38 and apoptosis in HL60 cells. Leuk Lymphoma 20:487–494. doi:10.3109/10428199609052434
Morley SJ, McKendrick L, Bushell M (1998) Cleavage of translation initiation factor 4G (eIF4G) during anti-Fas IgM-induced apoptosis does not require signalling through the p38 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase. FEBS Lett 438:41–48. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(98)01269-1
Shen LM, Lan ZY, Liu Q, Ni JZ (2009a) Apoptosis of cancer cells induced by lanthanum citrate. J Chin Rare Earths Soc 27:441–446
Shen LM, Liu Q, Ni JZ, Hong GY (2009b) A proteomic investigation into the human cervical cancer cell line HeLa treated with dicitratoytterbium (III) complex. Chem Biol Interact 181:455–462. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2009.07.013
Shen LM, Liu Q, Ni JZ (2009c) Comparative proteomics analysis of lanthanum citrate complex-induced apoptosis in HeLa cells. Sci China Ser B 52:1814–1820. doi:10.1007/s11426-009-0272-z
Shen X, Lv SL, Zhang J, Li SN, Gao JY, Pan CE (2009d) Effects of Res on proliferation and apoptosis of human cervical carcinoma cell lines C33A, SiHa and HeLa. J Med Coll PLA 24:148–154. doi:10.1016/S1000-1948(09)60031-9
Simon HU, Haj-Yehia A, Levi-Schaffer F (2000) Role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in apoptosis induction. Apoptosis 5:415–418. doi:10.1023/A:1009616228304
Steben M, Duarte-Franco E (2007) Human papillomavirus infection: epidemiology and pathophysiology. Gynecol Oncol 107:S2–S5. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2007.07.067
Walboomers JM, Jacobs MV, Manos MM, Bosch FX, Kummer JA, Shah KV, Snijders PJ, Peto J, Meijer CJ, Muñoz N (1999) Human papillomavirus is a necessary cause of invasive cervical cancer worldwide. J Pathol 189:12–19. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(199909)189:1<12:AID-PATH431>3.CO;2-F
Wang Y, Chiu JF (2008) Proteomic approaches in understanding action mechanisms of metal-based anticancer drugs. Met Based Drugs 2008:1–9. doi:10.1155/2008/716329
Wang ZM, Lin HK, Zhu SR, Liu TF, Zhou ZF, Chen YT (2000) Synthesis, characterization and cytotoxicity of lanthanum (III) complexes with novel 1,10-phenanthroline-2,9-bis-alpha-amino acid conjugates. Anticancer Drug Des 5:405–411. doi:10.1016/S0162-0134(03)00313-1
Wang ZM, Lin HK, Zhu SR, Liu TF, Zhou ZF, Chen YT (2002) Spectroscopy, cytotoxicity and DNA-binding of the lanthanum(III) complex of an L-valine derivative of 1,10-phenanthroline. J Inorg Biochem 89:97–106. doi:10.1016/S0162-0134(01)00395-6
Wang Y, He QY, Che CM, Chiu JF (2006a) Proteomic characterization of the cytotoxic mechanism of gold (III) porphyrin 1a, a potential anticancer drug. Proteomics 6:131–142. doi:10.1002/pmic.200402027
Wang Y, Cheung YH, Yang Z, Chiu JF, Che CM, He QY (2006b) Proteomic approach to study the cytotoxicity of doiscin (saponin). Proteomics 6:2422–2432. doi:10.1002/pmic.200500595
Wengler G, Wengler G, Koschinski A (2007) A short treatment of cells with the lanthanide ions La3+, Ce3+, Pr3+ or Nd3+ changes the cellular chemistry into a state in which RNA replication of flaviviruses is specifically blocked without interference with host-cell multiplication. J Gen Virol 88:3018–3026. doi:10.1099/vir.0.83146-0
Wong CC, Wang Y, Cheng KW, Chiu JF, He QY, Chen F (2008) Comparative proteomic analysis of indioside D-triggered cell death in HeLa cells. J Proteome Res 7:2050–2058. doi:10.1021/pr800019k
Wullaert A, Heyninck K, Beyaert R (2006) Mechanisms of crosstalk between TNF-induced NF-kappaB and JNK activation in hepatocytes. Biochem Pharmacol 72:1090–1101. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2006.07.003
Zeng YB, Yang N, Liu WS, Tang N (2003) Synthesis, characterization and DNA-binding properties of La (III) complex of chrysin. J Inorg Biochem 97:258–264. doi:10.1016/S0162-0134(03)00313-1
Zhang Y, Fu LJ, Li JX, Yang XG, Yang XD, Wang K (2009) Gadolinium promoted proliferation and enhanced survival in human cervical carcinoma cells. Biometals 22:511–519. doi:10.1007/s10534-009-9208-5
Acknowledgments
This work was supported financially by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 20637010) and Shenzhen Bureau of Science, Technology and Information (FG200805230223A).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Liming Shen and Ziyao Lan made an equal contribution to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, L., Lan, Z., Sun, X. et al. Proteomic analysis of lanthanum citrate-induced apoptosis in human cervical carcinoma SiHa cells. Biometals 23, 1179–1189 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-010-9368-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-010-9368-3