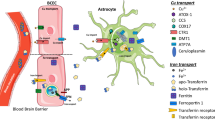
Abstract
Neurodegenerative disorders include a variety of pathological conditions, which share similar critical metabolic processes such as protein aggregation and oxidative stress, both of which are associated with the involvement of metal ions. In this review Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease are mainly discussed, with the aim of identifying common trends underlying these neurological conditions. Chelation therapy could be a valuable therapeutic approach, since metals are considered to be a pharmacological target for the rationale design of new therapeutic agents directed towards the treatment of neurodegeneration.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- Aβ :
-
β-Amyloid
- APP:
-
Amyloid precursor protein
- BBB:
-
Blood brain barrier
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- CQ:
-
Clioquinol
- DFO:
-
Desferrioxamine
- EDTA:
-
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
- IL:
-
Interleukine
- IRE:
-
Iron-responsive element
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
- PrP:
-
Prion protein
- PrPC :
-
Normal isoform of the prion protein
- PrPSc :
-
Scrapie isoform of the prion protein
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SN:
-
Substantia nigra
- SNc:
-
Substantia nigra pars compacta
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- TNF:
-
Tumour necrosis factor
References
Abeysinghe RD, Roberts PJ, Cooper, CE, Maclean KH, Hider RC, Porter JB (1996) The environment of the lipoxygenase iron binding site explored with novel hydroxypyridinone iron chelators. J Biol Chem 271:7965–7972
Alam ZI, Daniel SE, Lees AJ, Marsden DC, Jenner P, Halliwell B (1997) A generalised increase in protein carbonyls in the brain of Parkinson’s but not incidental Lewy body disease. J Neurochem 69:1326–1329
Allan SM, Rothwell NJ (2003) Inflammation in central nervous system injury. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 358:1669–1677
Allan SM, Tyrrell PJ, Rothwell NJ (2005) Interleukin-1 and neuronal injury. Nat Rev Immunol 5:629–640
Antzutkin ON, Leapman RD, Balbach JJ, Tycko R (2002) Sopramolecular structural constraints on Alzheimer’s β-amyloid fibrils from electron microscopy and solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance. Biochemistry 41:15436–15450
Atwood CS, Obrenovich ME, Liu T, Chan H, Perry G, Smith MA, Martins RN (2003) Amyloid-β: a chameleon walking in two worlds: a review of the trophic and toxic properties of amyloid-β. Brain Res Rev 43:1–16
Beard JL, Wiesinger JA, Connor JR (2003) Pre- and postweaning iron deficiency alters myelination in Sprague–Dawley rats. Dev Neurosci 25:308–315
Bence NF, Sampat RM, Kopito RR (2001) Impairment of the ubiquitin-proteosome system by protein aggregation. Science 292:1552–1555
Ben-Shacar D, Kahana N, Kampel V, Warshawsky A, Youdim MBH (2004) Neuroprotection by a novel brain permeable iron chelator, VK-28, against 6-hydroxydopamine lesion in rats. Neuropharmacology 46:254–263
Bonilla E (2000) Huntington disease. A review. J Clin Invest 41:117–141
Brion S, Mirol J, Psimaras A (1973) Recent findings in Pick’s disease. In: Zimmerman HM (eds) Progress in neuropathology, vol 2. Grune and Stratton, New York, pp 421–452
Brown DR (2001) Copper and prion disease. Br Res Bull 55:165–173
Brunk UT, Jones CB, Sohal RS (1992) A novel hypothesis of lipofuscinogenesis and cellular aging based on interactions between oxidative stress and autophagocytosis. Mut Res 275:395–403
Brunk UT, Terman A (2002) Lipofuscin: mechanisms of age-related accumulation and influence on cell function. Free Rad Biol Med 33:611–619
Bucciantini M, Giannoni F, Chiti F et al (2002) Inherent toxicity of aggregates implies a common mechanism for protein misfolding diseases. Nature 416:501–511
Bush AI, Huang X, Fairlie DP (1999) The possible origin of free radicals from amyloid β-peptides in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Ageing 20:335–337
Bush AI (2002) Metal complexing agents as therapies for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Ageing 23:1031–1038
Butterfield DA, Kanski J (2001). Brain oxidation in age-related neurodegenerative disorders that are associated with aggregated proteins. Mech Ageing Dev 122:945–962
Cherny RA, Barnham KJ, Lynch T et al (2000). Chelation and intercalation: complementary properties in a compound for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. J Struct Biol 130:209–216
Cherny RA, Atwood CS, Xilinas ME et al (2001) Treatment with a copper–zinc chelator markedly and rapidly inhibits b-amyloid accumulation in Alzheimer’s disease transgenic mice. Neuron 30:665–676
Chetley A, Gilbert D (1986) Health action international. International Organisation of Consumers Unions, The Hangue
Claesen ME, Clements ML (1989) Ridding the world of hydroxyquinolines. Br Med J 299:527–528
Cohen AS, Shirahama T, Skinner M (1982) Electron microscopy of amyloid. In: Harris JR (eds) Electron microscopy of proteins, vol 3. Academic Press, London UK, pp 165–205
Cohen FE (1999) Protein misfolding and prion diseases. J Mol Biol 293:313–320
Connor JR, Snyder BS, Arosio P, Loeffler DA, Lewitt P (1995) A quantitative analysis of isoferritins in select regions of aged, parkinsonian and Alzheimer’s diseased brains. J Neurochem 65:717–724
Cooper CE, Lynagh GR, Hoyes KP, Hider RC, Cammack R, Porter JB (1996) The relationship of intracellular iron chelation to the inhibition and regeneration of human ribonucleotide reductase. J Biol Chem 271:20291–20299
Crapper Mclachlan DR, Dalton AJ, Kruck TPA et al (1991) Effect of desferrioxamine on the clinical progress of Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 337:1304–1308
Crossthwaite AJ, Williams RJ (2002) Hydrogen peroxide-mediated phosphorilation of ERK1/2, Akt/PKB and JNK in cortical neurons: dependence on Ca2+ and PI 3-kinase. J Neurochem 80:24–36
Dexter DT, Wells FR, Lees AJ (1989) Increased nigral iron content and alterations in other metal ions occurring in brain in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 52:381–389
Dickson DW, Crystal HA, Bevona C, Honer W, Vincent I, Davies P (1995) Correlations of synaptic and pathological markers with cognition of the elderly. Neurobiol Aging 16:285–298
Di Patti MC, Persichini T, Mazzone V, Polticelli F, Colasanti M, Musci G (2004) Interleukin-1 beta up-regulates iron efflux in rat C6 glioma cells through modulation of ceruloplasmin and ferroportin-1 synthesis. Neurosci Lett 363:182–186
Dobson MC (2003a) Protein folding and disease: a view from the first horizon symposium. Nat Drug Disc 2:154–160
Dobson MC (2003b) Protein folding and misfolding. Nature 426:884–890
Duffy PE, Tennyson VM (1965) Phase and electron microscopic observations of Lewy bodies and melanin granules in the substantia nigra and Locus caeruleus in Parkinson’s disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 24:398–414
Floyd RA (1999) Antioxidants, oxidative stress, and degenerative neurological disorders. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 222:236–245
Floyd RA, Hensley K (2002) Oxidative stress in brain aging. Implications for therapeutics of neurodegenerative diseases. Neurobiol Aging 23:795–807
Gaeta A, Hider RC (2005) The crucial role of metal ions in neurodegeneration: the basis for a promising therapeutic strategy. Br J Pharmacol 146:1041–159
Gotz ME, Künig G, Riederer P, Youdim MBH (1994) Oxidative stress: Free radical production in neural degeneration. Pharmacol Ther 63:37–122
Grunblatt E, Mandel S, Youdim MB (2000) MPTP and 6-hydroxydopamine-induced neurodegeneration as models for Parkinson’s disease: neuroprotective strategies. J Neurol 247(Suppl 2):95–102
Habgood MD, Liu ZD, Dehkordi LS, Khodr HH, Abbott J, Hider RC (1999) Investigation into the correlation between the structure of hydroxypyridinones and blood–brain barrier permeability. Biochem Pharmacol 57:1305–1310
Halliwell B (1992) Reactive oxygen species the central nervous system. J Neurochem 59:1609–1623
Hardy J, Selkoe DJ (2002) The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 297:353–356
Harris DC, Aisen P (1973) Facilitation of Fe(II) autoxidation by Fe(III) complexing agents. Biochim Biophys Acta 329:156–158
Hartley DM, Walsh DM, Ye CP et al (1999) Protofibrillar intermediates of amyloid b-protein induce acute electrophysiological changes and progressive neurotoxicity in cortical neurones. J Neurosci 19(20):8876–8884
Hedge ML, Jagannatha Rao KS (2003) Challenges and complexities of α-synuclein toxicity: new postulates in unfolding the mystery associated with Parkinson’s disease. Arch Biochem Biophys 418:169–178
Hider RC, Hall AD (1991) Clinically useful chelators of tripositive elements. Prog Med Chem 28:41–173
Hider RC (1995) Potential protection from toxicity by oral iron chelators. Toxicol Lett 82–83:961–967
Hijazi N, Shaked Y, Rosenmann H, Ben-Hur T, Gabizon R (2003) Copper binding to PrPC may inhibit prion disease propagation. Br Res 993:192–200
Hirsh EC, Brandel J-P, Galle P (1991) Iron and aluminium increase in the substantia nigra of patients with Parkinson’s disease: an X-ray microanalysis. J Neurochem 56:446–451
Holander D, Ricketts D, Boyd CAR (1988) Importance of probe molecular geometry in determining intestinal permeability. Can J Gastroenterol 2:35A–38A
Hsiao K, Chapman P, Nilsen S et al (1996) Correlative memory deficits, Aβ elevation, and amyloid plaques in transgenic mice. Science 274:99–102
Huang X, Atwood CS, Hartshorn MA et al (1999) The Aβ peptide of Alzheimer’s disease directly produces hydrogen peroxide through metal ion reduction. Biochemistry 38:7609–7616
Jeffrey M, Goodsir CM, Bruce ME, Mcbride PA, Scott JR (1994) Infection-specific prion protein (PrP) accumulates on neuronal plasmalemma in scrapie-infected mice. Ann NY Acad Sci 724:327–330
Jelliger KA (1999) The role of iron in neurodegeneration: prospects for pharmacology of Parkinson’s disease. Drugs Aging 14:115–140
Kaur D, Yantiri F, Rajagopalan S et al (2003) Genetic or pharmacological iron chelation prevents MPTP-induced neurotoxicity in vivo: a novel therapy for Parkinson’s disease. Neuron 37:899–909
Kamenetz F, Tomita T, Hsieh H et al (2003) APP processing and synaptic function. Neuron 37:925–937
Klein WL, Krafft GA, Finch CE (2001) Targeting small Aβ oligomers: the solution to an Alzheimer’s disease conundrum? Trends Neurosci 24:219–224
Laine J, Marc M-E, Sy M-S, Axelrad H (2001) Cellular and subcellular morphological localization of normal prion protein in rodent cerebellum. Eur J Neurosci 14:47–56
Lambert MP, Barlow AK, Chromy BA et al (1998) Diffusible, nonfibrillar ligands derived from Aβ 1-42 are potent central nervous system neurotoxins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:6448–6453
Lan J, Jiang DH (1997) Desferrioxamine and vitamin E protect against iron and MPTP-induced neurodegeneration in mice. J Neural Transm 104:469–481
Lee J-Y, Friedman JE, Angel I, Kozak A, Kohj JY (2004) The lipophilic metal chelator DP-109 reduces amyloid pathology in brains of human β-amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice. Neurobiol aging 25:1315–1321
Levine SM, Chakrabarty A (2004) The role of iron in the pathogenesis of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis and multiple sclerosis. Ann NY Acad Sci 1012:252–266
Liu ZD, Lockwood M, Rose S, Theobald AE, Hider RC (2001) Structure-activity investigation of the inhibition of 3-hydroxypyridin-4-ones on mammalian tyrosine hydroxylase. Biochem Pharmacol 61:285–290
Liu ZD, Hider RC (2002a) Design of clinically useful iron(III)-selective chelators. Med Res Rev 22:26–64
Liu ZD, Hider RC (2002b). Design of iron chelators with therapeutic application. Coord Chem Rev 232:151–171
Liu ZD, Kayyali R, Hider RC, Porter JB, Theobald AE (2002) Design, synthesis, and evaluation of novel 2-substitued 3-hydroxypyridin-4-ones: structure-activity investigation of metalloenzyme inhibition by iron chelators. J Med Chem 45:631–639
Lovell MA, Robertson JD, Teesdal WJ, Campbell JL, Markesbery WR (1998). Copper, iron and zinc in Alzheimer’s disease senile plaques. J Neurol Sci 158:47–52
Lozoff B, Beard J, Connor J, Barbara F, Georgieff M, Schallert T (2006) Long-lasting neural and behavioural effects of iron deficiency in infancy. Nutr Rev 64:S34–43
Lue LF, Kuo Y-M, Roher AE et al (1999) Soluble amyloid β-peptide concentration as a predictor of synaptic change in Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Pathol 155:853–862
Maguire-Zeiss KA, Short DW, Federoff HJ (2005) Synuclein, dopamine and oxidative stress: co-conspirators in Parkinson’s disease? Brain Res Mol Brain 134(1):18–23
Mandel S, Weinreb O, Amit T, Youdim MB (2005) Mechanism of neuroprotective action of the anti-Parkinson drug rasagiline and its derivatives. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 48:379–387
Martell AE, Smith RM (1974–1989) Critical stability constant, vol 1–6. Plenum Press, London
Maxton DG, Bjarnason I, Reynolds AP, Catt SD, Peters TJ, Menzies IS (1986). Lactulose, 51Cr-labelled ethylenediaminetetra-acetate, L-rhamnose and polyethyleneglycol 400 [corrected] as probe markers for assessment in vivo of human intestinal permeability. Clin Sci 71:71–80
Mc Lean CA, Cherny RA, Fraser FW et al (1999) Soluble pool of Aβ amyloid as a determinant of severity of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Neurol 46:860–866
Merz PA, Sommerville RA, Wisniewsky HM, Ikbal K (1981). Abnormal fibrils from scrapie-infected brain. Acta Neuropathol 54:63–74 (Berlin)
Miranda S, Opazo C, Larrondo LF et al (2000) The role of oxidative stress in the toxicity induced by amyloid β-peptide in Alzheimer’s disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 62:633–648
Mizuno Y, Ohta S, Tanaka M et al (1989) Deficiencies in complex I subunits of the respiratory chain in Parkinson’s disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 163:1450–1455
Molina-Holgado F, Williams RJ, Gaeta A et al (2006) Neuroprotective actions of an iron chelator against Alzheimer’s disease-relevant insults. Poster session, 10th international conference on Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders’s, Madrid, Spain
Oakley GP (1973) The neurotoxicity of the halogenated hydroxyquinolines. JAMA 225(4):395–397
O’Brien-Ladner AR, Nelson SR, Murphy WJ, Blumer BM, Wesselius LJ (2000) Iron is a regulatory component of human IL-1beta production. Support for regional variability in the lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 23:112–119
Olanow CW (1992) Magnetic resonance imaging in parkinsonism. Neurol Clin North Am 405–420
Olanow CW, Youdim MB (1996) Neurodegeneration and neuroprotection in Parkinson’s disease. Academic Press, pp 55–59
Oldendorf WH (1974) Lipid solubility and drug penetration of the blood–brain barrier. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 147:813–816
Olivieri N, Koren G, Hermann C et al (1990) Comparison of oral iron chelator L1 and desferrioxamine in iron-loaded patients. Lancet 336:1275–1279
Paik SR, Shin H-J, Lee J-H, Chang C-S, Kim J (1999) Copper(II)-induced self-oligomerisation of α-synuclein. Biochem J 340:821–828
Palm A (1932) Untersuchung in des chinolin reihe. Arch Exp Pathol Pharmacol 199:176–185
Pan K, Baldwin M, Nguyen J et al (1993) Conversion of α-helices β-sheets features in the formation of the scrapie prion proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:10962–10966
Prusiner SB, Mckinley MP, Bowman KA et al (1983) Scrapie prions aggregate to form amyloid-like birefringent rods. Cell 35:349–358
Prusiner SB (1991) Molecular biology of prion disease. Science 252:1515–1522
Prusiner SB (2001) Neurodegenerative diseases and prions. N Engl J Med 344:1516–1526
Raymond KN, Müller G, Matzanke BF (1984) Complexation of iron by siderophores: a review of their solution and structural chemistry and biological function. Top Curr Chem 58:49–102
Riederer P, Sofic E, Rausch WD, Jellinger K, Youdim MBH (1989) Transition metals, ferritin, glutathione and ascorbic acid in Parkinsonian brains. J Neurochem 52:515–520
Rochet JC, Lansbury PT (2000) Amyloid fibrillogenesis: themes and variations. Curr Opin Struct Biol 10:60–80
Roher AE, Chaney MO, Kuo Y-M et al (1996) Morphology and toxicity of Aβ-(1–12) dimmer derived from neuritic and vascular amyloid deposits of Alzheimer’s disease. J Biol Chem 271:20631–20635
Rogers JT, Lahiri DK (2004) Metal and inflammatory targets for Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Drug Targets 5:535–551
Rogers JT, Leiter LM, Mcphee J et al (1999) Translation of the Alzheimer amyloid precursor protein mRNA is up-regulated by Interleukin-1 through 5’-untranslated region sequences. J Biol Chem 274:6421–6431
Rogers JT, Randall JD, Cahill CM et al (2002) An iron-responsive element type II in the 5’-untranslated region of the Alzheimer’s amyloid precursor protein transcript. J Biol Chem 277:45518–45528
Rose FC, Gawel M (1984) Clioquinol neurotoxicity: an overview. Acta Neurol Scand 80(Suppl 100):137–145
Saggu H, Cooksey J, Dexter D (1989) A selective increase in a particular superoxide dismutase activity in Parkinsonian substantia nigra. J Neurochem 53:692–697
Sanchez-Ramos J, Overvick E, Ames BN (1994) A marker of oxyradical-mediated DNA damage (8-hydroxy-2’-deoxy-guanoxine) is increased in nigro-striatum of Parkinson’s disease brain. Neurodegeneration 3:197–204
Serpell LC, Berriman J, Jakes R, Goedert M, Crowther RA (2000) Fiber diffraction of synthetic α-synuclein filaments shows amyloid-like cross β-conformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:4897–4902
Shastry BS (2003) Neurodegenerative disorders of protein aggregation. Neurochem Int 43:1–7
Sherki YG, Melamed E, Offen D (2001) Oxidative stress induced-neurodegenerative diseases: the need for antioxidants that penetrate the blood brain barrier. Neuropharmacology 40:959–975
Shin R-W, Kruck TPA, Murayama H, Kitamoto T (2003) A novel trivalent cation chelator Feralex dissociates binding of aluminum and iron associated with hyperphosphorylated τ of Alzheimer’s disease. Br Res 961:139–146
Sikorski P, Atkins EDT, Serpell LC (2003) Structure and texture of fibrous crystals formed by Alzheimer’s Aβ (11–15) peptide fragment. Structure 11:915–926
Sofic E, Riederer P, Heinsen H (1988) Increased Iron(Iii) and total iron content in post mortem, substantia nigra of parkinsonian brain. J Neural Trans 74:199–205
Sofic E, Lange KW, Jellinger K, Riederer P (1992) Reduced and oxidized glutathione in the substantia nigra of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 142:128–130
Stahl N, Borchelt DR, Hsiao K, Prusiner SB (1987) Scrapie prion protein contains a phosphatidylinositol glycolipid. Cell 51:229–240
Terry RD, Masliah E, Salmon DP et al (1991) Physical basis of cognitive alterations in Alzheimer’s disease: Synapse loss is the major correlate of cognitive impairment. Ann Neurol 30:572–580
Torok M, Milton S, Kayed R et al (2002) Structural and dynamic features of Alzheimer’s Aβ peptide in amyloid fibrils studied by site-directed spin labelling. J Biol Chem 277:40810–40815
Tsubaki T, Honma Y, Hosh M (1971) Neurological syndrome associated with clioquinol. Lancet 1:696–697
Tycko R (2004) Progress towards a molecular-level structural understanding of amyloid fibrils. Curr Opin Struct Biol 14:1–8
Uversky VN, Li J, Fink AL (2001) Metal-triggered structural transformations, aggregation and fibrillation of human α-synuclein. J Biol Chem 276:10737–10744
Vigo-Pelfrey C, Lee D, Keim P, Lieberburg I, Schenk DB (1993) Characterisation of amyloid peptide from human cerebrospinal fluid. J Neurochem 61:1965–1968
Walsh DM, Hartley DM, Kusumoto Y et al (1999) Amyloid β protein fibrillogenesis: structure and biological activity of protofibrillar intermediates. J Biol Chem 274:25945–25952
Walsh DM, Klyubin I, Fadeeva JV et al (2002) Naturally secreted oligomers of amyloid β protein potently inhibit hippocampal long-term potentiation in vivo. Nature 416:535–539
Wang SS, Becerra-Arteaga A, Good TA (2002) Development of a novel diffusion-based method to estimate the size of the aggregated Aβ species responsible for neurotoxicity. Biotechnol Bioeng 80:50–59
Warshawsky B., Youdim MBH, Ben-Shacar D (2000) Pharmaceutical compositions compromising iron chelators for the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders and some novel iron chelators. International Publication number WO 00/74664A2
Wisniewsky HM, Coblentz JM, Terry RD (1972) Pick’s disease. A clinical and ultrastructural study. Arch Neurol 26:97–108
Xu J, Kao S-Y, Lee FJS, Song W, Jin L-W, Yankner BA (2002) Dopamine-dependent neurotoxicity of α-synuclein: a mechanism for selective neurodegeneration in Parkinson disease. Nat Med 8:600–606
Ye FQ, Allen PS, Martin WRW (1996) Basal ganglia iron content in Parkinson’s disease measured with magnetic resonance. Mov Disord 11:243–249
Yokel RA, Fredenburg AM, Meurer KA, Skinner TL (1995) Influence of lipophilicity on the bioavailability and disposition of orally active 3-hydroxypyridin-4-one metal chelators. Drug Metab Dispos 23:1178–1180
Youdim MB, Grunblatt E, Mandel S (1999) The pivotal role of iron in NF-kappa B activation and nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurodegeneration. Prospects for neuroprotection in Parkinson’s disease with iron chelators. Ann NY Acad Sci 890:7–25
Zecca L, Fariello R, Riederer P, Sulzer D, Gatti A, Tampellini D (2002) The absolute concentration of nigral neuromelanin, assayed by a new sensitive method, increases throughout the life and is dramatically decreased in Parkinson’s disease. FEBS Lett 510:216–220
Zhang X, Haaf M, Todorich B et al (2005) Cytokine toxicity to oligodendrocyte precursors is mediated by iron. Glia 52(3):199–208
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Molina-Holgado, F., Hider, R.C., Gaeta, A. et al. Metals ions and neurodegeneration. Biometals 20, 639–654 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-006-9033-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-006-9033-z