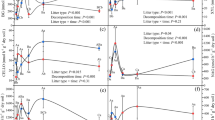
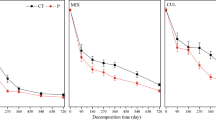
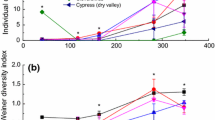
Abstract
We conducted over four months a short-term laboratory incubation experiment to find the best prediction parameters (i.e. initial chemical characteristics) to explain differences in microbial respiration rates and mineral N (DIN) release in different litter in an acidified spruce forest. In addition, we wanted to find the link between the activity of key extracellular ligninolytic enzymes, phenoloxidases (PhOx) and peroxidases (Perox), microbial respiration and composition of fungal and bacterial communities. Samples of spruce needles (Picea abies) and litter of four dominant understorey vegetation; lady fern (Athyrium alpestre), blueberry (Vaccinium myrtillus), reedgrass (Calamagrostis villosa) and hair grass (Avenella flexuosa), were collected in 2005, 2006 and 2007 from six sites located in watersheds of two glacial lakes (Plesne Lake and Certovo Lake) in the Bohemian Forest, Czech Republic. Litter samples were incubated at 0 and 10 °C in laboratory controlled conditions for 90 days. Activities of PhOx and PerOx, and C mineralization rate were measured regularly each 14 days. Litter quality characteristics and endophytic microbial community structure, based on 16SrDNA-DGGE fingerprint of bacteria and ITS-DGGE of fungi, were determined at the beginning and end of litter incubation. Our results showed a close correlation of phenolics/POX with DIN release (r > 0.74, p < 0.001). Using multivariate analyses, POX seems to play an important role in the change of litter fungal and bacterial community composition. At 0 °C the fungal and bacterial communities of reedgrass and blueberry litter changed in relation to POX and Perox activity, while at 10 °C the fungal communities after the incubation were additionally affected by the phenolics/NTOT and phenolics/PTOT ratios.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aber JD, Melillo JM, McClaugherty CA (1990) Predicting long-term patterns of mass loss, nitrogen dynamics, and soil organic matter formation from initial fine litter chemistry in temperate forest ecosystems. Can J Bot 68:2201–2208
Aber JD, McDowell W, Nadelhoffer K, Magill A, Berntson G, Kamakea M, McNulty S, Currie W, Rustad L, Fernandez I (1998) Nitrogen saturation in temperate forest ecosystem. Bioscience 48:921–934
Allison SD (2005) Cheaters, diffusion, and nutrients constrain decomposition by microbial enzymes in spatially structured environments. Ecol Lett 8:626–635
Baldrian P (2004) Increase of laccase activity during interspecific interactions of white-rot fungi. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 50:245–253
Bärlocher F, Graça MAS (2005) Total Phenolics. In: Graça MAS, Bärlocher F, Gessner MO (eds) Methods to study litter decomposition: a practical guide. Springer, Netherlands, pp 97–100
Berg B (1986) Nutrient release from litter and humus in coniferous forest soils–a mini review. Scand J For Res 1(3):359–369
Berg B, Ekbohm G (1991) Litter mass-loss rates and decomposition patterns in some needle and leaf litter types–long-term decomposition in Scots pine forest.7. Can J Bot 69:1449–1456
Berg B, McClaugherty CA, Johansson MB (1993) Litter mass-loss rates in late stages of decomposition at some climatically and nutritionally different pine sites. Long-term decomposition in a Scots pine forest.8. Can J Bot 71:680–692
Cappo KA, Blume LJ, Raab GA, Bartz JK, Engels JL (1987) Analytical methods manual for the direct/delayed response project soil survey. US EPA, Las Vegas, USA, Sections 8–11
Carlyle J, Lowther J, Smethurst P, Nambiar E (1990) Influence of chemical properties on nitrogen mineralization and nitrification in podzolized sands. Implications for forest management. Aust J Soil Res 28:981–1000
Coleman DC, Whitman WB (2005) Linking species richness, biodiversity and ecosystem function in soil systems. Pedobiologia (Jena) 49:479–497
Comerford NB, Skinner F (1989) Residual phosphorus solubility for an acid, clayey, forested soil in the presence of oxalate and citrate. Can J Soil Sci 69:111–117
Couteaux MM, Bottner P, Berg B (1995) Litter decomposition, climate and litter quality. Trends Ecol Evol 10:63–66
Cox P, Wilkinson SP, Anderson JM (2001) Effects of fungal inocula on the decomposition of lignin and structural polysaccharides in Pinus sylvestris litter. Biol Fertil Soils 33:246–251
Dauer JM, Chorover J, Chadwick OA, Oleksyn J, Tjoelker MG, Hobbie SE, Reich PB, Eissen-stat DM (2007) Controls over leaf and litter calcium concentrations among temperate trees. Biogeochemistry 86:175–187
Davidson EA, Janssens IA (2006) Temperature sensitivity of soil carbon decomposition and feedbacks to climate change. Nature 440:165–173
Di Nardo C, Cinquegrana A, Papa S, Fuggi A, Fioretto A (2004) Laccase and peroxidase isoenzymes during leaf litter decomposition of Quercus ilex in a Mediterranean ecosystems. Soil Biol Biochem 36:1539–1544
Dittmer JK, Patel NJ, Dhawale SW, Dhawale SS (1997) Production of multiple laccase isoforms by Phanerochaete chrysosporium grown under nutrient sufficiency. FEMS Microbiol Lett 149:65–70
Domisch T, Finér L, Laine J, Laiho R (2006) Decomposition and nitrogen dynamics of litter in peat soils from two climatic regions under different temperature regimes. Eur J Soil Biol 42:74–81
Dyck W, Mees C, Hodgkiss P (1987) Nitrogen availability and comparison to uptake in two New Zealand Pinus radiata forests. N Z J For Sci 17:338–352
Eriksson KEL, Blanchette RA, Ander P (1990) Microbial and enzymatic degradation of wood components. Springer, Berlin
Fackler K, Gradinger C, Hinterstoisser B, Messner K, Schwanninger M (2006) Lignin degradation by white rot fungi on spruce wood shavings during short-time solid-state fermentations monitored by near infrared spectroscopy. Enzyme Microb Technol 39:1476–1483
Fassnacht KS, Gower ST (1999) Comparison of the litterfall and forest floor organic matter and nitrogen dynamics of upland forest ecosystems in north central Wisconsin. Biogeochemistry 45:265–284
Fierer N, Schimel JP, Cates RG, Zou J (2001) Influence of balsam poplar tannin fractions on carbon and nitrogen dynamics in Alaskan taiga floodplain soils. Soil Biol Biochem 33:1827–1839
Fioretto A, Papa S, Pellegrino A, Fuggi A (2007) Decomposition dynamics of Myrtus communis and Quercus ilex leaf litter: mass loss, microbial activity and quality change. App Soil Ecol 36:32–40
Fitter AH, Gilligan CA, Hollingworth K, Kleczkowski A, Twyman RM, Pitchford JW (2005) Biodiversity and ecosystem function in soil. Funct Ecol 19:369–377
Fog K (1988) The effect of added nitrogen on the rate of decomposition of organic matter. Biol Rev 63:433–462
Fox RH, Myers RJK, Vallis I (1990) The nitrogen mineralization rate of legume residues in soil as influenced by their polyphenol, lignin, and nitrogen contents. Plant Soil 129:251–259
Frankland JC (1992) Mechanisms in fungal succession. In: Carroll GC, Wicklow DT (eds) The fungal community. Dekker, New York, pp 383–390
Fromin N, Hamelin J, Tarnawski S, Roesti D, Jourdain-Miserez K, Forestier N, Teyssier-Cuvelle S, Gillet F, Aragno M, Rossi P (2002) Statistical analysis of denaturing gel electrophoresis (DGE) fingerprinting patterns. Environ Microbiol 4:634–643
Gallet C, Lebreton P (1995) Evolution of phenolic patterns in plants and associated litters and humus of a mountain forest ecosystem. Soil Biol Biochem 27:157–165
Hammel KE (1997) Fungal degradation of lignin. In: Cadisch G, Giller KE (eds) Driven by nature: plant litter quality and decomposition. CAB International, Wallingford, pp 33–46
Hendel B, Sinsabaugh RL, Marxsen J (2005) Lignin-degrading enzymes: phenoloxidase and peroxidase. In: Graça MAS, Bärlocher F, Gessner MO (eds) Methods to study litter decomposition: a practical guide. Springer, Netherlands, pp 273–278
Heuer H, Smalla K (1997) Application of denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and temperature gradient gel electrophoresis for studying soil microbial communities. In: van Elsas JD, Wellington EMH, Trevors JT (eds) Modern soil microbiology. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, pp 353–373
Hoshino YT, Matsumoto N (2004) An improved DNA extraction method using skim milk from soils that strongly adsorb DNA. Microbes Environ 19:13–19
Hoshino YT, Matsumoto N (2007) DNA- versus RNA-based denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis profiles of a bacterial community during replenishment after soil fumigation. Soil Biol Biochem 39:434–444
Hurt RA, Qiu X, Wu L, Roh Y, Palumbo AV, Tiedje JM, Zhou J (2001) Simultaneous recovery of RNA and DNA from soils and sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4495–4503
Izumi H, Anderson IC, Killham K, Moore ERB (2008) Diversity of predominant endophytic bacteria in European deciduous and coniferous trees. Can J Microbiol 54:173–179
Jansson PE, Berg B (1985) Temporal variation of litter decomposition in relation to simulated soil climate. Long-term decomposition in a Scots pine forest. Can J Bot 63:1008–1016
Kaňa J, Kopáček J (2006) Impact of soil sorption characteristics and bedrock composition on phosphorus concentrations in two Bohemian Forest Lakes. Water Air Soil Pollut 173:243–259
Kanerva S, Kitunen V, Kiikkila O, Loponen J, Smolander A (2006) Response of soil C and N transformations to tannin fractions originating from Scots pine and Norway spruce needles. Soil Biol Biochem 38:1364–1374
Killham K (1994) Soil ecology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Kirk TK, Farrell RL (1987) Enzymatic ‘combustion’: the microbial degradation of lignin. Annu Rev Microbiol 41:465–505
Koch AL (1985) The macroeconomics of bacterial growth. In: Fletcher M, Floodgate GD (eds) Bacteria in their natural environments. Academic Press, London, pp 1–42
Koopmans GF, Chardon WJ, de Willigen P, van Riemsdijk WH (2004) Phosphorus desorption dynamics in soil and the link to a dynamic concept of bioavailability. J Environ Qual 33:1393–1402
Kopáček J, Kaňa J, Šantrůčková H, Porcal P, Hejzlar J, Picek T, Veselý J (2002a) Physical, chemical, and biochemical characteristics of soils in watersheds of the Bohemian Forest Lakes: I. Plešné Lake. Silva Gabreta 8:43–62
Kopáček J, Kaňa J, Šantrůčková H, Porcal P, Hejzlar J, Picek T, Šimek M, Veselý J (2002b) Physical, chemical, and biochemical characteristics of soils in watersheds of the Bohemian Forest Lakes: II. Čertovo and Černé Lakes. Silva Gabreta 8:63–93
Kopáček J, Turek J, Hejzlar J, Kaňa J, Porcal P (2006a) Element fluxes in watershed-lake ecosystems recovering from acidification: Plešné Lake, the Bohemian Forest, 2001–2005. Biologia (Bratisl) 61:S427–S440
Kopáček J, Turek J, Hejzlar J, Kaňa J, Porcal P (2006b) Element fluxes in watershed-lake ecosystems recovering from acidification: Čertovo Lake, the Bohemian Forest, 2001–2005. Biologia (Bratisl) 61:S413–S426
Kulhankova A, Beguiristain T, Moukoumi J, Berthelin J, Ranger J (2006) Spatial and temporal diversity of wood decomposer communities in different forest stands, determined by ITS rDNA targeted TGGE. Ann For Sci 63:547–556
Larrondo LF, Salas L, Melo F, Vicuña R, Cullen D (2003) A novel extracellular multicopper oxidase from Phanerochaete chrysosporium with ferroxidase activity. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:6257–6263
Li J, Zhao GZ, Chen HH, Qin S, Xu LH, Jiang CL, Li WJ (2008) Rhodococcus cercidiphylli sp nov., a new endophytic actinobacterium isolated from a Cercidiphyllum japonicum leaf. Syst Appl Microbiol 31:108–113
Lindahl BD, Ihrmark K, Boberg J, Trumbore SE, Högberg P, Stenlid J, Finlay RD (2007) Spatial separation of litter decomposition and mycorrhizal nitrogen uptake in a boreal forest. New Phytol 173:611–620
Livsey S, Barklund P (1992) Lophodermium piceae and Rhizosphaera kalkhoffii in fallen needles of Norway spruce (Picea abies). Eur J For Pathol 22:204–216
Lucas RW, Casper BB, Jackson JK, Balser TC (2007) Soil microbial communities and extracellular enzyme activity in the New Jersey Pinelands. Soil Biol Biochem 39:2508–2519
Lynch JM, Benedetti A, Insan H, Nuti MP, Smalla K, Torsvik V, Nannipieri P (2004) Microbial diversity in soil: ecological theories, the contribution of molecular techniques and the impact of transgenic plants and transgenic microorganisms. Biol Fertil Soils 40:363–385
Meentemeyer V (1978) Macroclimate and lignin control of litter decomposition rates. Ecology 59:465–472
Muller M, Sundman V, Soininvaara O, Merilainen A (1988) Effect of chemical composition on the release of nitrogen from agricultural plant materials decomposting in soil under field conditions. Biol Fertil Soils 6:78–83
Nannipieri P, Ascher J, Ceccherini MT, Landi L, Pietramellara G, Renella G (2003) Microbial diversity and soil functions. Eur J Soil Sci 54:655–670
Northup RR, Yu Z, Dahlgren RA, Vogt KA (1995) Polyphenol control of nitrogen release from pine litter. Nature 377:227–229
Northup RR, Dahlgren RA, McColl JG (1998) Polyphenols as regulators of plant-litter-soil interactions in northern Californias pygmy forest: a positive feedback? Biogeochemistry 42:189–220
Park JH, Matzner E (2003) Controls on the release of dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen from a deciduous forest floor investigated by manipulations of aboveground litter inputs and water flux. Biogeochemistry 66:265–286
Pawłowski L (1997) Acidification: its impact on the environment and mitigation strategies. Ecol Eng 8:271–288
Podgornik H, Stegu M, Zibert E, Perdih A (2001) Laccase production by Phanerochaete chrysosporium—an artifact caused by Mn(III)? Lett Appl Microbiol 32:407–411
Pote DH, Daniel TC, Sharpley AN, Moore PA, Edwards DR, Nichols DJ (1996) Relating extractable soil phosphorus to phosphorus losses in runoff. Soil Sci Am J 60:855–859
Pregitzer KS, Zak DR, Burton AJ, Ashby JA, Macdonald NW (2004) Chronic nitrate additions dramatically increase the export of carbon and nitrogen from northern hardwood ecosystems. Biogeochemistry 68:179–197
Prescott CE (2005) Do rates of litter decomposition tell us anything we really need to know? For Ecol Manag 220:66–74
Rodriguez S, Longo MA, Cameselle C, Sanroman A (1999) Production of manganese peroxidase and laccase in laboratory-scale bioreactors by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Bioproc Eng 20:531–535
Šantrůčková H, Vrba J, Picek T, Kopáček J (2004) Soil biochemical activity and phosphorus transformations and losses from acidified forest soils. Soil Biol Biochem 36:1569–1576
Šantrůčková H, Krištůfková M, Vaněk D (2006) Decomposition rate and nutrient release from plant litter of Norway spruce forest in the Bohemian Forest. Biologia (Bratisl) 61:S499–S508
Šantrůčková H, Šantrůček J, Setlik J, Svoboda M, Kopacek J (2007) Carbon isotopes in tree rings of Norway spruce exposed to atmospheric pollution. Environ Sci Technol 41:5778–5782
Schwertmann U (1964) Differenzierung der eisenoxiden des bodens duerch extraction mit amoniumoxalaat lösung. Z Pflanzenerähr Düng Bodenkd 105:194–202
Sinsabaugh RL, Carreiro MM, Repert DA (2002) Allocation of extracellular enzymatic activity in relation to litter composition, N deposition, and mass loss. Biogeochemistry 60:1–24
Sinsabaugh RL, Gallo ME, Lauber C, Waldrop MP, Zak DR (2005) Extracellular enzyme activities and soil organic matter dynamics for northern hardwood forests receiving simulated nitrogen deposition. Biogeochemistry 75:201–215
Snajdr J, Valaskova V, Merhautova V, Herinkova J, Cajthaml T, Baldrian P (2008) Spatial variability of enzyme activities and microbial biomass in the upper layers of Quercus petraea forest soil. Soil Biol Biochem 40:2068–2075
Söderström B, Bååth E, Lundgren B (1983) Decrease in soil microbial activity and biomasses owing to nitrogen amendments. Can J Microbiol 29:1500–1506
Srinivasan C, D’Souza T, Boominathan K, Reddy CA (1995) Demonstration of laccase in the white rot basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium BKM-F1767. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:4274–4277
Svoboda M, Matějka K, Kopáček J (2006) Biomass and element pools of understory vegetation in the catchments of Čertovo Lake and Plešné Lake in the Bohemian Forest. Biologia(Bratisl) 61:S509–S521
ter Braak CJF, Šmilauer P (1998) CANOCO Reference manual and user’s guide to Canoco for Windows. Microcomputer Power, Ithaca, 351 pp
Tomlinson GH (2003) Acid deposition, nutrient leaching and forest growth. Biogeochemistry 65:51–81
Uchida M, Mo W, Nakatsubo T, Tsuchiya Y, Horikoshi T, Koizumi H (2005) Microbial activity and litter decomposition under snow cover in cool-temperate broadleaved deciduous forest. Agric For Meteorol 134:102–109
Valaskova V, Snajdr J, Bittner B, Cajthaml T, Merhautova V, Hoffichter M, Baldrian P (2007) Production of lignocellulose-degrading enzymes and degradation of leaf litter by saprotrophic basidiomycetes isolated from a Quercus petraea forest. Soil Biol Biochem 39:2651–2660
van der Zee SEATM, Fokkink LGJ, van Riemsdijk WH (1987) A new technique for assessment of reversibly adsorbed phosphate. Soil Sci Am J 51:599–604
Velicer GJ (2003) Social strife in the microbial world. Trends Microbiol 11:330–336
Veselý J (1994) Investigation of the nature of the Šumava lakes: a review. J Natl Mus (Prague) Nat Hist Ser 163:103–120
Waldrop MP, Zak DR (2006) Response of oxidative enzyme activities to nitrogen deposition affects soil concentrations of dissolved organic carbon. Ecosystems 9:921–933
Waldrop MP, Zak DR, Sinsabaugh RL (2004) Microbial community response to nitrogen deposition in northern forest ecosystems. Soil Biol Biochem 36:1443–1451
Weintraub MN, Scott-Denton LE, Schmidt SK, Monson RK (2007) The effects of tree rhizodeposition on soil exoenzyme activity, dissolved organic carbon, and nutrient availability in a subalpine forest ecosystem. Oecologia 154:327–338
Yuan G, Lavkulich LM (1994) Phosphate sorption in relation to extractable iron and aluminium in spodosols. Soil Sci Soc Am J 58:343–346
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Czech Science Foundation, project 526/08/0751 and 206/07/1200 and the project MSM 6007665801. We acknowledge the laboratory and field assistance provided by our colleagues and students. We also thank the authorities of NP Šumava for permission to study the watershed ecosystems. We thank our American colleague Dr Keith Edwards for language correction.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bárta, J., Applová, M., Vaněk, D. et al. Effect of available P and phenolics on mineral N release in acidified spruce forest: connection with lignin-degrading enzymes and bacterial and fungal communities. Biogeochemistry 97, 71–87 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-009-9363-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-009-9363-3