Abstract
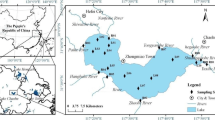
Phosphine (PH3) was monitored in the Taihu Lake in China by a GC/NPD method, coupled with cryo-trapping enrichment technology. Results showed that PH3 was universally detected in sediments, lake water and atmosphere of the Taihu Lake area. Total phosphorus (TPs) and fractions of different phosphorus species in lake sediments were separately measured as dissolved phosphate (DP), phosphorus bound to aluminum (Al-P), iron (Fe-P) and calcium (Ca-P), occluded phosphorus (OP), and organic phosphorus (Org-P) by sequential chemical extraction. High PH3 levels were correlated with high TPs values in sediments and with eutrophication at different sites. In addition, a positive linear correlation equation was obtained between the concentrations of PH3 in lake sediments and of the phosphorus fractions. The resulting multiple linear regression equation is PH3 = −165 + 63.3 DP + 0.736 Al-P + 2.33 Ca-P + 2.29 Org-P. The flux of PH3 across the sediment–water interface was estimated from sediment core incubation in May and October 2002. The annual average sediment–water flux of PH3 was estimated at ca. 0.0138±0.005 pg dm−2 h−1, the average yearly emission value of PH3 from Taihu Lake sediments to water was calculated to be 28.3±10.2 g year−1, which causes a water PH3 concentration of up to 0.178±0.064 pmol dm−3. The real importance of PH3 could be higher, because PH3 could be consumed in the oxic sediment–water boundary layer and in the water column. Spatial and temporal distributions of total phosphorus (TPw) and chlorophyll a (Chl-a) in the water column of Taihu Lake were measured over the study period. Higher water PH3 has also been found where the TPw content was high. Similarly, high Chl-a was consistent with higher water PH3. Positive relationships between PH3 and TPw (average R 2 = 0.47±0.26) and Chl-a (average R 2 = 0.23±0.31) were observed in Taihu Lake water.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
InstitutionalAuthorNameAgricultural chemistry specialty council of edaphic society in China. (1989) Conventional Analytical Methods of Soil Agricultural Chemistry China Science & Technology Press Beijing, China
H.K. Barrenscheen H.A. Beckh-Widmanstetter (1923) ArticleTitleUber bakterielle reduktion organisch gebundener phosphorsaure Biochem. Z. 140 279–283
L.E. Casida (1960) ArticleTitleMicrobial oxidation and utilization of orthophosphite during growth J. Bacteriol. 80 237–241
Y.B. Chang (1995) ArticleTitleMajor environmental changes since 1950 and the onset of accelerated eutrophication in Taihu LakeChina Acta Palaeontol. Sinica 35 155–174
Y.W. Chen C.X. Fan K. Teubner M. Dokulil (2003) ArticleTitleChanges of nutrients and phytoplankton chlorophyll-a in a large shallow lakeTaihuChina: an 8-year investigation Hydrobiologia 506–509 273–279
I. Dévai R.D. Delaune (1995) ArticleTitleEvidence for PH3 production and emission from Louisiana and Florida marsh soils Org. Geochem. 23 277–279
I. Dévai L. Felföldy I. Wittner S. Plósz (1988) ArticleTitleDetection of PH3: new aspects of phosphorus cycle in the hydrosphere Nature 333 IssueID26 343–345
F. Eismann D. Glindemann A. Bergmann P. Kuschk (1997) ArticleTitleSoils as source and sink of PH3 Chemosphere 35 IssueID3 523–533 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0045-6535(97)00117-3
R. Frank G. Rippen (1987) ArticleTitleVerhalten von PH3 in der atmosphere [Fate of PH3 in the atmosphere] Lebensmitteltechnik 17 409–411
G. Gassmann (1994) ArticleTitlePH3 in fluvial and marine hydrosphere Mar. Chem. 45 197–205 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0304-4203(94)90003-5
G. Gassmann D. Glindemann (1993) ArticleTitlePhosphane(PH3) in the biosphere Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 32 IssueID5 761–763 Occurrence Handle10.1002/anie.199307611
G. Gassmann F. Schorn (1993) ArticleTitlePH3 from harbor surface sediment Naturwissenschaften 80 78–80 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01140420
G. Gassmann J.E.E. Van Beusekom D. Glindemann (1996) ArticleTitleOffshore atmospheric PH3 Naturwissenschaften 83 IssueID3 129–131
D. Glindemann A. Bergmann (1995) ArticleTitleSpontaneous emission of phosphane from animals slurry treatment processing Zbl. Hyg. 198 49–56
D. Glindemann A. Bergmann U. Stottmeister G. Gassmann (1996b) ArticleTitlePH3 in the lower terrestrial troposphere Naturwissenschaften 83 IssueID3 131–133
D. Glindemann M. Edwards P. Kuschk (2003) ArticleTitlePH3 gas in the upper troposphere Atmos. Environ. 37 IssueID18 2429–2433 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1352-2310(03)00202-4
D. Glindemann F. Eismann A. Bergmann P. Kuschk U. Stottmeister (1998) ArticleTitlePH3 by bio-corrosion of phosphide-rich iron Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 5 IssueID2 71–74
D. Glindemann U. Stottmeister A. Bergmann (1996a) ArticleTitleFree PH3 from the anaerobic biosphere Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 3 IssueID1 17–19 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02986806
S.H. Han Z.J. Wang Y.H. Zhuang Z.M. Yu D. Glindemann (2003) ArticleTitlePH3 in various matrixes J. Environ. Sci. 15 IssueID3 339–341
S.H. Han Y.H. Zhuang J.A. Liu D. Glindemann (2000) ArticleTitlePhosphorus cycling through PH3 in paddy fields Sci. Total Environ. 258 IssueID3 195–203 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0048-9697(00)00570-2
Jin X.C. 2000. Control technology of eutrophic lake in china. In: Specialist dissertation of international learning workshop about eutrophic lake and its control technology in China, Oct. 25–28, 2000, Dali, China, pp. 215–223.
X.C. Jin Q. Tu (Eds) (1990) The Standard Methods for Observation and Analysis in Lake Eutrophication EditionNumber2 Chinese Environmental Science Press Beijing 240
F. Libert (1927) ArticleTitleReduzieren mikroben phosphate? Zentbl. Bakt. ParasitKde, Abt. II. 72 369–374
J.A. Liu H.F. Cao Y.H. Zhuang P. Kuschk F. Eismann D. Glindemann (1999) ArticleTitlePH3 in the urban air of Beijing and its possible source Water Air Soil Pollut. 116 597–604
C.J. Lorenzen (1967) ArticleTitleDetermination of chlorophyll and phaeopigments: spectrophotometric equations Limnol. Oceanogr. 12 343–346 Occurrence Handle10.4319/lo.1967.12.2.0343
G. Malacinski W.A. Konetzka (1966) ArticleTitleBacterial oxidation of orthophosphite J. Bacteriol. 91 578–582
C. McAullife (1971) ArticleTitleGas chromatographic determination of solutes by multiple phase equilibrium Chem. Technol. 1 46–51
S.C. Morton D. Glindemann M. Edwards (2003) ArticleTitlePhosphates, phosphites, and phosphides in environmental samples Environ. Sci. Technol. 37 IssueID6 1169–1174 Occurrence Handle10.1021/es020738b
X.J. Niu J.J. Geng X.R. Wang C.H. Wang X.H. Gu M. Edwards D. Glindemann (2004) ArticleTitleTemporal and spatial distributions of PH3 in Taihu LakeChina Sci. Total Environ. 323 169–178
R. Portielje L. Lijklema (1999) ArticleTitleEstimation of sediment-water exchange of solutes in lake Veluwethe Netherlands Water Res. 33 IssueID1 279–285 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0043-1354(98)00202-4
J. Roels W. Verstraete (2004) ArticleTitleOccurrence and origin of PH3 in landfill gas Sci. Total Environ. 327 185–196
K.I. Rudakov (1927) ArticleTitleDie reduktion der mineralischen phosphate auf biologischem wege Zentbl. Bakt. ParasitKde, Abt. II. 70 202–214
F.A. Skinner (1968) The anaerobic bacteria of soil T.R.G. Gray D. Parkinson (Eds) The Ecology of Soil Bacteria Liverpool University Press England 573–592
W.L. Stigniali P. Dodman W. Salomons R. Schulin G.R.B. Smidt Seatm der Zee ParticleVan (1991) ArticleTitleChemical time bombs Environment 33 IssueID4 4–9–26–30
G. Tsubota (1959) ArticleTitlePhosphate reduction in the paddy field. I. Soil Plant Food (Tokyo) 5 10–15
Yu D.H. 2000. The status and problem about eutrophic lake in China. In: Specialist dissertation of international learning workshop about eutrophic lake and its control technology in China, Oct. 25–28, 2000, Dali, China, pp. 207–214.
Z.M. Yu X.X. Song (2003) ArticleTitleMatrix-bound PH3: A new form of phosphorus found in sediment of Jiaozhou Bay Chin. Sci. Bull. 48 IssueID1 31–35 Occurrence Handle10.1360/03tb9006
Wang X.R. and Guo H.Y. 2000. Lake. In: Discussion about control countermeasure of eutrophic Taihu Lake. In: Specialist dissertation of international learning workshop about eutrophic lake and its control technology in ChinaOct. 25–28, 2000. DaliChinapp. 229–235
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Geng, J., Niu, X., Jin, X. et al. Simultaneous Monitoring of Phosphine and of Phosphorus Species in Taihu Lake Sediments and Phosphine Emission from Lake Sediments. Biogeochemistry 76, 283–298 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-005-5422-6
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-005-5422-6