Abstract.
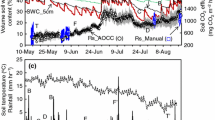
Soil respiration (Rs) was monitored periodically throughout 2001 and 2003 in a pedunculate oak (Quercus robur L.) stand located in the Belgian Campine region. An empirical model originally developed for a neighboring pine stand, that accounts for variation in temperature, soil moisture, rewetting of the surface layers by rain during dry periods and seasonal fresh litter inputs, was fitted to the data. The model explained 92% and 94% of the temporal variability in Rs during 2001 and 2003 respectively. Monthly measurements of Rs can suffice to build a robust empirical model if temperature is the main controlling factor. However, during the driest period of the year a weekly sampling schedule was needed to capture the combined effect of temperature, soil water content (SWC) and the short-term effect of rewetting played. Although the model was developed for gap-filling purposes it also showed a remarkable predictive ability for this site and these conditions. Annual emissions of carbon (C) estimated with the model were significantly higher in 2001 than in 2003 (7.8 and 5.9 ton C ha−1 year−1, respectively). The severe drought during most of the growing season in 2003 caused a high fine root mortality and a decrease in microbial activity, and was likely the main responsible factor of the almost 2 ton C ha−1 year−1 differences in Rs between both years. Pulses of Rs during drying/rewetting cycles accounted for a substantial fraction of the total flux, especially during the driest year. Finally, our results show that quality of the substrate may play an important role in both the intensity of the rewetting pulses of CO2 and the seasonality of Rs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Adu J. Oades (1978) ArticleTitlePhysical factors influencing decomposition of organic materials in soil aggregates Soil Biol. Biochem. 10 109–115 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0038-0717(78)90080-9 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE1cXkt1art7c%3D
J.M. Anderson (1973) ArticleTitleCarbon dioxide evolution from two temperate deciduous woodland soils J. Appl. Ecol. 10 361–378
T. Appel (1998) ArticleTitleNon-biomass soil organic N: the substrate for N mineralization flushes following soil drying–rewetting and for organic N rendered CaCl2-extractable upon soil drying Soil Biol. Biochem. 39 505–510
Baeyens L., Van Slycken J. and Stevens D. 1993. Institute for Forestry and Game ManagementGeraardsbergen, Belgium17 pp.
H. Birch (1958) ArticleTitleThe effect of soil drying on humus decomposition and nitrogen availability Plant Soil 10 9–31 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01343734 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaG1MXjs1ehug%3D%3D
H. Birch (1960) ArticleTitleNitrification of soil after different periods of dryness Plant Soil 12 81–96 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01377763 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaF3MXnsl2nsQ%3D%3D
W. Borken Y.-J. Xu R. Brumme N. Lamersdorf (1999) ArticleTitleA climate change scenario for carbon dioxide and dissolved organic carbon fluxes from a temperate forest soil: drought and rewetting effects Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 63 1848–1855 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXhsFyrsL4%3D
J.L. Campbell O.J. Sun B.E. Law (2004) ArticleTitleSupply-side controls on soil respiration among Oregon forest Global Change Biol. 10 1857–1869 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1365-2486.2004.00850.x
P. Coley J.P. Bryant F.S. Chapin SuffixIII. (1985) ArticleTitleResource availability and plant antiherbivore defenses Science 230 895–899
J. Curiel Yuste I.A. Janssens A. Carrara R. Ceulemans (2004) ArticleTitleAnnual Q10 of soil respiration reflects plant phenological patterns as well as temperature sensitivity Global Change Biol. 10 161–169 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1529-8817.2003.00727.x
Curiel Yuste J., Janssens I.A., Carrara A. and Ceulemans R. in press. Temporal and spatial variability in the contribution of soil respiration to total ecosystem respiration in a mixed temperate forest. Tree Physiol.
J. Curiel Yuste I.A. Janssens A. Carrara L. Meiresonne R. Ceulemans (2003) ArticleTitleInteractive effect of temperature and precipitation on soil respiration in a temperate maritime pine forest Tree Physiol. 23 1263–1270 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3srnt1Kjsg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle14652226
E.A. Davidson E. Belk R.D. Boone (1998) ArticleTitleSoil water content and temperature as independent or confounded factors controlling soil respiration in a temperate mixed hardwood forest Glob. Change Biol. 4 217–227 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2486.1998.00128.x
E.A. Davidson S.E. Trumbore R. Amundson (2000b) ArticleTitleSoil warming and organic carbon content Nature 408 789–790 Occurrence Handle10.1038/35048672 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXhtlWqtQ%3D%3D
E.A. Davidson L.V. Verchot J.H. Cattanio I.L. Ackerman J.E.M. Carvalho (2000a) ArticleTitleEffects of soil water content on soil respiration in forest and cattle pastures of eastern Amazonia Biogeochemistry 48 53–69 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1006204113917 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXitVOjsr0%3D
De Clerk J. 2004. Vergelijkende studie van de seizoenale dynamiek van bladeren en wortels inzomereik en grove den. University of Antwerp, Masters thesis (in dutch).
R.K. Dixon S. Brown R.A. Houghton A.M. Soloman M.C. Trexler J. Wisniewski (1994) ArticleTitleCarbon pools and flux of global forest ecosystems Science 263 185–190 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXhs12gsbc%3D
D. Epron L. Farque E. Lucot P.-M. Badot (1999) ArticleTitleSoil CO2 efflux in a beech forest: dependence on soil temperature and soil water content Ann. Forest Sci. 56 221–226
Fairley R.I. and Alexander I.J. 1985. Methods of calculating fine root production in forests. In: Fitter A.H. (ed.), Ecological Interactions in Soil, Vol. 4. Special Publication of the British Ecological Society, pp. 37–42.
C.P. Giardina M.G. Ryan (2000) ArticleTitleEvidence that decomposition rates of organic carbon in mineral soil do not vary with temperature Nature 404 858–861
O.W. Heal P.W. Flanagan D.D. French SuffixJr. S.F. Maclean (1981) Decomposition and accumulation of organic matter in tundra L.C. Bliss (Eds) et al. Tundra Ecosystems: A Comparative Analysis Cambrigde University Press Cambrigde 587–633
S.E. Hobbie (1996) ArticleTitleTemperature and plant species control over litter decomposition in Alaskan tundra Ecol. Monogr. 66 IssueID4 503–522
P. Högberg A. Nordgren N. Buchmann A.F.S. Taylor A. Akblad M.N. Hogberg G. Nyberg M. Ottosson-Lofvenius D.J. Read (2001) ArticleTitleLarge-scale forest girdling shows that current photosynthesis drives soil respiration Nature 411 789–792
InstitutionalAuthorNameIPCC (2001) NoChapterTitle H.J. Houghton (Eds) et al. Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis. Contribution of Working group I to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Cambrigde University Press CambrigdeUK
I.A. Janssens S. Dore D. Epron H. Lankreijer N. Buchmann B. Longdoz J. Brossaud L. Montagnani (2003) Climatic influences on seasonal and spatial differences in soil CO2 efflux R. Valentini (Eds) Fluxes of Carbon water and Energy of European Forest Springer-Verlag Berlin 233–253
I.A. Janssens A.S. Kowalski B. Longdoz R. Ceulemans (2000a) ArticleTitleAssessing forest soil CO2 efflux: an in situ comparison of four techniques Tree Physiol. 20 23–32
I.A. Janssens A.S. Kowalski R. Ceulemans (2001a) ArticleTitleForest floor CO2 fluxes estimated by eddy covariance and chamber-based model Agr. Forest Meteorol. 106 61–69 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0168-1923(00)00177-5
I.A. Janssens H. Lankreijer G. Matteucci A.S. Kowalski N. Buchmann D. Epron K. Pilegaard W. Kutsch B. Longdoz T. Grünwald L. Montagnani S. Dore C. Rebmann E.J. Moors A. Grelle Ü. Rannik K. Morgenstern R. Clement S. Oltchev J. Gumundsson S. Minerbi P. Berbigier A. Ibrom J. Moncrieff M. Aubinet C. Bernhofer N.O. Jensen T. Vesala A. Granier E.-D. Schulze A. Lindroth A.J. Dolman P.G. Jarvis R. Ceulemans R. Valentini (2001b) ArticleTitleProductivity overshadows temperature in determining soil and ecosystem respiration across European forests Global Change Biol. 7 269–278 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2486.2001.00412.x
I.A. Janssens L. Meiresonne R. Ceulemans (2000b) Mean soil CO2 efflux from a mixed forest: temporal and spatial integration R. Ceulemans F. Veroustraete V. Gond J. Van Rensbergen (Eds) Forest Ecosystem Modeling, Upscaling and Remote Sensing SPB Academic Publishing The Hague 19–33
I.A. Janssens D.A. Sampson J. Cermak L. Meiresonne F. Riguzzi S. Overloop R. Ceulemans (1999) ArticleTitleAbove- and below-ground phytomass and carbon storage in a Belgian Scots pine stand Ann. Forest Sci. 56 81–90
F.M. Kelliher J. Lloyd A. Arneth B. Lühker J.N. Byers T.M. McSeveny I. Milukova S. Grigoriev M. Panfyorov A. Sogatchev A. Varlargin W. Ziegler G. Bauer S.-C. Wong E.-D. Schulze (1999) ArticleTitleCarbon dioxide efflux density from the floor of a central Siberian pine forest Agr. Forest Meteorol. 94 217–232 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0168-1923(99)00014-3
T.L. Kieft D.B. Rindelberg D.C. White (1994) ArticleTitleChanges in ester-linked phospholipid fatty acid profiles of subsurface bacteria during starvation and desiccation in a porous medium Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 60 3292–3299 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXlslGjtLw%3D
Konôpka B., Curiel Yuste J., Janssens I.A. and Ceulemans R. in press. Comparison of fine root dynamics in Scots pine and pedunculate oak in sandy soil. Plant Soil.
A.S. Kowalski S. Overloop R. Ceulemans (2000) Eddy fluxes above a Belgian, Campine forest and their relationship with predicting variables R. Ceulemans F. Veroustraete V. Gond J. Van Rensbergen (Eds) Forest Ecosystem Modeling, Upscaling and Remote Sensing SPB Academic Publishing The Hague 3–17
H. Lankreijer I.A. Janssens N. Buchmann (2003) Measurement of soil respiration within the EUROFLUX project R. Valentini (Eds) Canopy Fluxes of Energy, Water and Carbon Dioxide of European Forests Springer-Verlag Berlin
M.-S. Lee K. Nakane T. Nakatsubo W.-H. Mo H. Koizumi (2002) ArticleTitleEffects of rainfall events on soil CO2 flux in a cool temperature deciduous broad-leaved forest Ecol. Res. 17 401–409 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1440-1703.2002.00498.x
E. Lundquist L. Jackson K. Scow (1999) ArticleTitleRapid response of soil microbial communities from conventional, low inputand organic farming systems to a wet/dry cycle Soil Biol. Biochem. 31 1661–1675 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0038-0717(99)00080-2 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXmtFamu7c%3D
A.S. Mamilov M.D. Oliver (2002) ArticleTitleSoil microbial eco-physiology as affected by short-term variations in environmental conditions Soil Biol. Biochem. 34 1283–1290 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0038-0717(02)00071-8 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XlvVelsr8%3D
L. Meiresonne S. Overloop (1999) Transpiratiebegroting van een Grove dennenbestand: eerste modelmatige benadering Comm. Inst. For. Game Manage. Belgium 103–119
L. Meiresonne D.A. Sampson A.S. Kowalski I.A. Janssens N. Nadezhdina J. Cermak R. Ceulemans (2002) ArticleTitleResolving time scale dependence of water flux estimates from a Belgian Scots pine stand: sap flow, eddy covarianceand process simulations J. Hydrol. 270 IssueID3–4 230–252 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0022-1694(02)00284-6
C.D. Monk (1966) ArticleTitleAn ecological significance of evergreenness Ecology 47 504–505
V. Orchard F. Cook (1983) ArticleTitleRelationship between soil respiration and soil-moisture Soil Biol. Biochem. 15 447–453 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0038-0717(83)90010-X
W.J. Parton D.S. Schimel C.V. Cole D.S. Ojima (1987) ArticleTitleAnalysis of factors controlling soil organic matter levels in great plains grasslands Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 51 1173–1179 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2sXmtlGnsbw%3D
K.S. Pregitzer J.S. King A.J. Burton S.E. Brown (2000) ArticleTitleResponses of tree fine roots to temperature New Phytol. 147 105–115 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1469-8137.2000.00689.x Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXms1ylt7Y%3D
J. Pumpanen P. Kolari H. Ilvesniemi T. Vesala S. Niinistö A. Lohila T. Larmola M. Morero M. Pihlatie I.A. Janssens J. Curiel Yuste J. Gruenzweig S. Reth J.-A. Subke K. Savage W.L. Kutsch G. Østreng W. Ziegler P. Anthoni A. Lindroth P. Hari (2004) ArticleTitleCalibration of different chamber techniques for measuring soil CO2 efflux Agric. Forest Meteorol. 123 159–176 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.agrformet.2003.12.001
J.W. Raich W.H. Schlesinger (1992) ArticleTitleThe global carbon dioxide flux in soil respiration and its relationship to vegetation and climate Tellus 44B 81–99 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XksVOgsLY%3D
A. Rey E. Pegoraro V. Tedeschi I. De Parri P.G. Jarvis R. Valentini (2002) ArticleTitleAnnual variation in soil respiration and its components in a coppice oak forest in Central Italy Global Change Biol. 8 851–866 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2486.2002.00521.x
D.S. Schimel B.H. Braswell E.A. Holland R. McKeown D.S. Ojima T.H. Painter W.J. Parton A.R. Townsend (1994) ArticleTitleClimatic, edaphic, and biotic controls over storage and turnover of carbon in soils Global Biogeochem. Cycles 8 IssueID3 279–293 Occurrence Handle10.1029/94GB00993 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXmvVert70%3D
W.H. Schlesinger (1977) ArticleTitleCarbon balance in terrestrial detritus Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 8 51–81 Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.es.08.110177.000411 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE1cXlt1Cl
W. Schlesinger J. Andrews (2000) ArticleTitleSoil respiration and the global carbon cycle Biogeochemistry 48 7–20 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1006247623877 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXitVOjsr8%3D
D. Stanners P. Bourdeau (1995) Europe’s Environment European Environmental Agency Copenhagen
S.E. Trumbore G. Bonani W. Wölfli (1990) The rates of carbon cycling in several soils from AMS 14C measurements of fractionated soil organic matter A.F. Bouwman (Eds) Soils and the Greenhouse Effect John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New York 405–414
K. Van Cleve (1974) Organic matter quality in relation to decomposition A.J. Holding (Eds) et al. Soil Organism and Decomposition in Tundra Tundra Biome Steering Committee Stockholm 311–324
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuste, J., Janssens, I. & Ceulemans, R. Calibration and validation of an empirical approach to model soil CO2 efflux in a deciduous forest. Biogeochemistry 73, 209–230 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-004-7201-1
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-004-7201-1