Abstract.
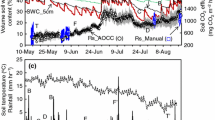
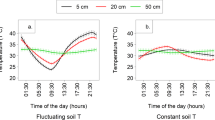
Soil CO2 efflux is a major component of net ecosystem productivity (NEP) of forest systems. Combining data from multiple researchers for larger-scale modeling and assessment will only be valid if their methodologies provide directly comparable results. We conducted a series of laboratory and field tests to assess the presence and magnitude of soil CO2 efflux measurement system × environment interactions. Laboratory comparisons were made with a dynamic, steady-state CO2 flux generation apparatus, wherein gas diffusion drove flux without creating pressure differentials through three artificial soil media of varying air-filled porosity. Under these conditions, two closed systems (Li-6400-09 and SRC-1) exhibited errors that were dependent on physical properties of the artificial media. The open system (ACES) underestimated CO2 flux. However, unlike the two other systems, the ACES results could be corrected with a single calibration equation that was unaffected by physical differences in artificial media. Both scale and rank changes occurred among the measurement systems across four sites. Our work clearly shows that soil CO2 efflux measurement system × environment interactions do occur and can substantially impact estimates of soil CO2 efflux. Until reliable calibration techniques are developed and applied, such interactions make direct comparison of published rates, and C budgets estimated using such rates, difficult.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Bekku H. Koizumi T. Oikawa H. Iwaki (1997) ArticleTitleExamination of four methods for measuring soil respiration Appl. Soil Ecol 5 247–254 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0929-1393(96)00131-X
J.R. Butnor K.H. Johnsen R. Oren G.G. Katul (2003) ArticleTitleReduction of forest floor respiration by fertillization on both carbon dioxide-enriched and reference 17-year-old loblolly pine stands Global Change Biol 9 849–861 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2486.2003.00630.x
Butnor J.R. and Johnsen K.H. 2004. Calibrating soil respiration measures with a dynamic flux apparatus using artificial soil media of varying porosity. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 55: 639–647.
F. Conen K.A. Smith (2000) ArticleTitleAn explanation of linear increases in gas concentration under closed chambers used to measure gas exchange between soil and the atmosphere Eur. J. Soil Sci 51 111–117 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2389.2000.00292.x Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXisVKmsbw%3D
W.P. Cropper K.C. Ewel J.W. Raich (1985) ArticleTitleThe measurement of soil CO2 evolution in situ Pedobiologia 28 35–40
E.A. Davidson K. Savage L.V. Verchot R. Navarro (2002) ArticleTitleMinimizing artifacts and biases in chamber-based measurements of soil respiration Agric. Forest Meteorol 113 21–37 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0168-1923(02)00100-4
E. de Jong R.E. Redmann E.A. Ripley (1979) ArticleTitleA comparison of methods to measure soil respiration Soil Sci 127 300–306
C. Fang J.B. Moncrieff (1996) ArticleTitleAn improved dynamic chamber technique for measuring CO2 efflux from the soil surface Funct. Ecol 10 297–305
C. Fang J.B. Moncrieff (1998) ArticleTitleAn open-top chamber for measuring soil respiration and the influence of pressure difference on CO2 efflux measurement Funct. Ecol 12 319–325 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2435.1998.00189.x
O.A. Folorunso D.E. Rolston (1984) ArticleTitleSpatial variability of field-measured denitrification gas fluxes Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J 48 1213–1219
J.I. Freijer W. Bouten (1991) ArticleTitleA comparison of field methods for measuring soil carbon dioxide evolution: experiments and simulation Plant Soil 135 13–142 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00014786
J. Gliński W. Stępniewski (1985) Soil Aeration and its Role for Plants CRC Press Boca Raton, FL
P.J. Hanson S.D. Wullschleger S.A. Bohlman D.E. Todd (1993) ArticleTitleSeasonal and topographic patterns of forest floor CO2 efflux from an upland oak forest Tree Physiol 13 1–15 Occurrence Handle14969897
I.A. Janssens A.S. Kowalski B. Longdoz R. Ceulemans (2000) ArticleTitleAssessing forest soil CO2 efflux: an in situ comparison of four techniques Tree Physiol 20 23–32 Occurrence Handle12651523
L.S. Jensen T. Mueller K.R. Tate D.J. Ross J. Magid N.E. Nielsen (1996) ArticleTitleSoil surface CO2 flux as an index of soil respiration in situ: a comparison of two chamber methods Soil Biol. Biochem 28 1297–1306 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0038-0717(96)00136-8 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXosFCntg%3D%3D
K.L. Kabwe M.J. Hendry G.W. Wilson J.R. Lawrence (2002) ArticleTitleQuantifying CO2 fluxes from soil surfaces to the atmosphere J. Hydrol 260 1–14 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0022-1694(01)00601-1 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xis1agtrg%3D
B.A. Kimball E.R. Lemon (1971) ArticleTitleAir turbulence effects upon gas exchange Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc 35 16–21
J.A. King R. Harrison (2002) ArticleTitleMeasuring soil respiration in the field: an automated closed chamber system compared with portable IRGA and alkali absorption methods Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal 33 403–423 Occurrence Handle10.1081/CSS-120002753 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XislCqs78%3D
V. Le Dantec D. Epron E. Dufrene (1999) ArticleTitleSoil CO2 efflux in a beech forest: comparison of two closed dynamic systems Plant Soil 214 125–132 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1004737909168 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXptlyrtA%3D%3D
C.A. Maier L.W. Kress (2000) ArticleTitleSoil CO2 evolution and root respiration in 11 year-old loblolly pine (Pinus taeda) plantations as affected by moisture and nutrient availability Can. J. Forest Res 30 347–359 Occurrence Handle10.1139/cjfr-30-3-347
C.A. Maier S.J. Zarnoch P.M. Dougherty (1998) ArticleTitleEffects of temperature and tissue nitrogen on dormant season stem and branch maintenance respiration in a young loblolly pine (Pinus taeda) plantation Tree Physiol 18 11–20 Occurrence Handle12651294
S.M. Nay K.G. Mattson B.T. Bormann (1994) ArticleTitleBiases of chamber methods for measuring soil CO2 efflux demonstrated with a laboratory apparatus Ecology 75 2460–2463
J.M. Norman C.J. Kucharik S.T. Gower D.D. Baldocchi P.M. Crill M. Rayment K. Savage R.G. Striegel (1997) ArticleTitleA comparison of six methods for measuring soil-surface carbon dioxide fluxes J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos 102 28771–28777 Occurrence Handle10.1029/97JD01440 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXnslyiug%3D%3D
R. Oren B.E. Ewers P. Todd N. Phillips G. Katul (1998) ArticleTitleWater balance delineates the soil layer in which moisture affects canopy conductance Ecol. Appl 8 990–1002
D.E. Pataki R. Oren (2003) ArticleTitleSpecies differences in stomatal control of water loss at the canopy scale in a mature bottomland deciduous forest Adv. Water Resour 26 1267–1278 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.advwatres.2003.08.001
S. Pongracic M.U.F. Kirschbaum R.J. Raison (1997) ArticleTitleComparison of soda lime and infrared gas analysis techniques for an in situ measurement of forest soil respiration Can. J. Forest Res 27 1890–1895 Occurrence Handle10.1139/cjfr-27-11-1890
J. Pumpanen H. Ilvesniemi M. Peramaki P. Hari (2003) ArticleTitleSeasonal patterns of soil CO2 efflux and soil air CO2 concentration in a Scots pine forest: comparison of two chamber techniques Global Change Biol 9 371–382 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2486.2003.00588.x
J.W. Raich R.D. Bowden P.A. Steudler (1990) ArticleTitleComparison of two static chamber techniques for determining carbon dioxide efflux from forest soils Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J 54 1754–1757 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXht1Sks7Y%3D
M.B. Rayment (2000) ArticleTitleClosed chamber systems underestimate soil CO2 efflux Eur. J. Soil Sci 51 107–110 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2389.2000.00283.x
M.B. Rayment P.G. Jarvis (1997) ArticleTitleAn improved open chamber system for measuring soil CO2 effluxes in the field J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos 102 28779–287884 Occurrence Handle10.1029/97JD01103 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXnslyiuw%3D%3D
P. Rochette B. Ellert E.G. Gregorich R.L. Desjardins E. Pattey R. Lessard B.G. Johnson (1997) ArticleTitleDescription of a dynamic closed chamber for measuring soil respiration and its comparison with other techniques Can. J. Soil Sci 77 195–203
P. Rochette E.G. Gregorich R.L. Desjardins (1992) ArticleTitleComparison of static and dynamic closed chambers for measurement of soil respiration under field conditions Can. J. Soil Sci 72 605–609
E.S. Takle J.R. Brandle R.A. Schmidt R. Garcia I.V. Litvina W.J. Massman X. Zhou G. Doyle C.W. Rice (2003) ArticleTitleHigh-frequency pressure variations in the vicinity of a surface CO2 flux chamber Agric. Forest Meteorol 114 245–250 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0168-1923(02)00174-0
J.M. Welles T.H. Demetriades-Shah D.K. McDermitt (2001) ArticleTitleConsiderations for measuring ground CO2 effluxes with chambers Chem. Ecol 177 3–13 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXkt1Kgt7g%3D
B. Widen A. Lindroth (2003) ArticleTitleA calibration system for soil carbon dioxide-efflux measurement: description and application Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J 67 327–334 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXnvFSgsA%3D%3D
M.H. Yim S.J. Joo K. Nakane (2002) ArticleTitleComparison of field methods for measuring soil respiration: a static alkali absorption method and two dynamic closed chamber methods Forest Ecol. Manage 170 189–197 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0378-1127(01)00773-3
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Butnor, J.R., Johnsen, K.H. & Maier, C.A. Soil properties differently influence estimates of soil CO2 efflux from three chamber-based measurement systems. Biogeochemistry 73, 283–301 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-004-4022-1
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-004-4022-1