Abstract.
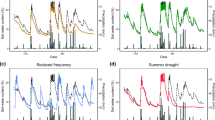
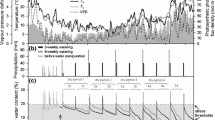
Changes in timing or amount of precipitation may be of great consequence for carbon cycling in the Mixedgrass Prairie of N. America, because CO2 fixation and efflux are tightly coupled to soil water properties. The objective of our project was to quantify how ecosystem respiration (Re) responds to experimental changes in winter and summer precipitation in a Mixedgrass Prairie using in situ field manipulations of snow depth and summer rain. Our study was conducted at the USDA-ARS High Plains Grasslands Research Station, west of Cheyenne, Wyoming. We installed three replicated 50 m snow fences to increase winter snow on the leeward side of the snow fence and experimentally manipulated summer precipitation by either increasing (+50%) or decreasing (−50%) precipitation amounts. We also measured ambient conditions. Re rates in May were around 2 g C m−2 d−1 for all treatments and increased to their greatest values in June, up to 10 g C m−2 d−1, with the ambient treatment having the largest flux rates. There were no treatment effects during the early summer, but by midsummer, Re rates were least in the reduced rainfall plots and greatest in the snow plots. Soil moisture and gross photosynthesis had strong influence on the daily Re rates, but soil temperature had little correlation with daily Re rates. In summary, the Re rates in this Mixedgrass Prairie are strongly influenced by changes in precipitation, especially winter snow accumulation. Thus, carbon cycle estimates under future climate change scenarios need to include not only the affects of changes in summer rain, but also, the consequences of deep snow in winter and itsȁ9 affect on carbon cycling processes in winter and subsequent summers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Allen-Diaz (1996) Rangelands in a changing climate: impacts, adaptations and mitigation R.T. Watson M.C. Zinyowera R.H. Moss D.J. Dokken (Eds) Climate Change 1995, Impacts, Adaptations and Mitigation of Climate Change: Scientific-Technical Analyses Cambridge Press CambridgeEngland 131–158
J.S. Amthor (1998) Terrestrial Ecosystem Responses to Global Change: A Research Strategy ORNL Technical Memorandum 1998/27, Oak Ridge National Laboratory Oak RidgeTennessee 37
Del Grosso S.J., Parton W.J., Mosier A.R., Holland E.A., Pendall E., Schimel D.S. and Ojima D.S. 2005. Modeling CO2 emissions from decomposition of soil organic carbon. Biogeochemistry, this special issue on recent advances in soil respiration. (this issue)
M.B. Dodd W.K. Lauenroth J.M. Welker (1998) ArticleTitleDifferential water resource use by herbaceous and woody plant life-forms in a shortgrass steppe community Oecologia 117 504–512 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s004420050686
H.E. Epstein I.C. Burke W.K. Lauenroth (2002) ArticleTitleRegional patterns of decomposition and primary production rates in the U.S. Great Plains Ecology 83 320–327
C. Fang J.B. Moncrieff (2001) ArticleTitleThe dependence of soil CO2 efflux on temperature Soil Biol. Biochem 33 155–165 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0038-0717(00)00125-5 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXht1Kmsbk%3D
J.T. Fahnestock M.H. Jones P.D. Brooks D.A. Walker J.M. Welker (1998) ArticleTitleWinter and early spring CO2 flux from tundra communities of northern Alaska J. Geophys. Res 102 IssueIDD22 29925–29931
J.T. Fahnestock M.H. Jones P.D. Brooks J.M. Welker (1999) ArticleTitleSignificant CO2 emissions from tundra soils during winter: implications for annual carbon budgets of arctic communities Global Biogeochem. Cycles 13 775–779 Occurrence Handle10.1029/1999GB900006 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXmtVWls7o%3D
Fahnestock J.T., Welker J.M., Piper R.E. and Smith W.K. (unpublished manuscript). Annual CO2 exchange in Mixed-grass Prairie and sagebrush ecosystems of southeast Wyoming, USA.
P.A. Fay J.D. Carlisle A.K. Knapp J.M. Blair S.L. Collins (2000) ArticleTitleAltering rainfall timing and quantity in a mesic grassland ecosystem: design and performance of rainfall manipulation shelters Ecosystems 3 308–319 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s100210000028
P.A. Fay A.K. Knapp J.M. Blair J.D. Carlisle B.T. Danner J.K. McCarron (2002) Rainfall timing, soil moisture dynamics, and plant responses in a mesic tallgrass Prairie ecosystem J.F. Weltzin G.R. McPherson (Eds) Changing Precipitation Regimes and Terrestrial Ecosystems: A North American Perspective University of Arizona Press Tucson, USA 147–165
R.F. Follett J.M. Kimble R. Lal (2000) The potential of U.S. grazing lands to sequester carbon R.F. Follett J.M. Kimble R. Lal (Eds) The Potential of U.S. Grazing Lands to Sequester Carbon and Mitigate the Greenhouse Effect Lewis Publishers Boca Raton 401–430
A.B. Frank M.A. Liebig J.D. Hanson (2002) ArticleTitleSoil carbon dioxide fluxes in northern semiarid grasslands Soil Biol. Biochem 34 1235–1241 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0038-0717(02)00062-7 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XlvVemu7g%3D
E.W. Hamilton D.A. Frank (2001) ArticleTitleCan plants stimulate soil microbes and their own nutrient supply? Evidence from a grazing tolerant grass Ecology 82 2397–2402
S.E. Hobbie J.P. Schimel S.E. Trumbore J.R. Randerson (2000) ArticleTitleA mechanistic understanding of carbon storage and turnover in high-latitude soils Global Change Biol 6 196–210 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2486.2000.06021.x
J.N. Holland C. Weixin D.A.J. Crossley (1996) ArticleTitleHerbivore-induced changes in plant carbon allocation: assessment of below-ground C fluxes using carbon-14 Oecologia 107 87–94 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00582238
M.H. Jones J.T. Fahnestock D.A. Walker M.D. Walker J.M. Welker (1998) ArticleTitleCarbon dioxide fluxes in moist and dry arctic tundra during the snow-free season: responses to increases in summer temperature and winter snow accumulation Arctic Alpine Res 30 373–380
R.D. Kelly E.R. Hunt W.A. Reiners W.K. Smith J.M. Welker (2002) ArticleTitleRelationships between daytime carbon dioxide uptake and absorbed photosynthetically active radiation for three different mountain/plains ecosystems J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos 107 19.1–19.8 Occurrence Handle10.1029/2001JD001181
A.K. Knapp J.M. Briggs J.K. Koelliker (2001) ArticleTitleFrequency and extent of water limitation to primary production in a mesic temperate grassland Ecosystems 4 19–28 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s100210000057
A.K. Knapp P.A. Fay J.M. Blair S.L. Collins M.D. Smith J.D. Carlisle C.W. Harper B.T. Danner M.S. Lett J.K. Mccarron (2002) ArticleTitleRainfall variability, carbon cycling, and plant species diversity in a mesic grassland Science 298 2202–2205 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.1076347 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XpsVSktLg%3D Occurrence Handle12481139
W.K. Lauenroth (1979) Grassland primary production: North American grasslands in perspective N.R. French (Eds) Perspectives in Grassland Ecology Springer-Verlag New York 3–24
W.K. Lauenroth O.E. Sala (1992) ArticleTitleLong-term forage production of North-American shortgrass steppe Ecol. Appl 2 397–403
D.R. Lecain J.A. Morgan G.E. Schuman J.D. Reeder R.H. Hart (2000) ArticleTitleCarbon exchange rates in grazed and ungrazed pastures of Wyoming J. Range Manage 53 199–206
J. Lloyd J.A. Taylor (1994) ArticleTitleOn the temperature dependence of soil respiration Funct. Ecol 8 315–323
D.G. Milchunas J.R. Forwood W.K. Lauenroth (1994) ArticleTitleProductivity of long-term grazing treatments in response to seasonal precipitation J. Range Manage 47 133–139
K.L. Povirk J.M. Welker G.F. Vance (2000) Carbon sequestration in arctic and alpine tundra and mountain meadow ecosystems R.F. Follett J.M. Kimble R. Lal (Eds) The Potential of U.S. Grazing Lands to Sequester Carbon and Mitigate the Greenhouse Effect Lewis Publishers Boca Raton 189–228
J.W. Raich C.S. Potter (1995) ArticleTitleGlobal patterns of carbon dioxide emissions from soils Global Biogeochem. Cycles 9 23–36 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXktFGitL0%3D
J.W. Raich W.H. Schlesinger (1992) ArticleTitleThe global carbon dioxide flux in soil respiration and its relationship to vegetation and climate Tellus 44B 81–99 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XksVOgsLY%3D
G.E. Schuman J.D. Reeder J.T. Manley R.H. Hart W.A. Manley (1999) ArticleTitleImpact of grazing management on the carbon and nitrogen balance of a mixed-grass rangeland Ecol. Appl 9 65–71
G.E. Schuman J.E. Herrick H.H. Janzen (2000) The dynamics of soil carbon in rangelands R.F. Follett J.M. Kimble R. Lal (Eds) The Potential of U.S. Grazing Lands to Sequester Carbon and Mitigate the Greenhouse Effect Lewis Publishers Boca Raton 267–290
J.P. Schimel C. Bilbrough J.M. Welker (2004) ArticleTitleIncreased snow depth affects microbial activity and nitrogen mineralization in two Arctic tundra communities Soil Biol. Biochem 36 217–227 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.soilbio.2003.09.008 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXmvFGkug%3D%3D
D.S. Schimel B.H. Braswell E.A. Holland R. McKeown D.S. Ojima T.H. Painter W.J. Parton A.R. Townsend (1994) ArticleTitleClimatic, edaphic, and biotic controls over storage and turnover of carbon in soils Global Biogeochem. Cycles 8 279–293 Occurrence Handle10.1029/94GB00993 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXmvVert70%3D
M.C. Serreze J.E. Walsh F.S. Champin SuffixIII T. Osterkamp M. Dyurgerov V. Romanovsky W.C. Oechel J. Morison T. Zhang R.G. Berry (2000) ArticleTitleObservational evidence of recent change in the northern high-latitude environment Climatic Change 46 159–207 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1005504031923
H.G. Stefan X. Fang (1997) ArticleTitleSimulated climate change effects on ice and snow covers on lakes in a temperate region Cold Reg. Sci. Technol 25 IssueID2 137–152 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0165-232X(96)00023-7
G.L. Vourlitis W.C. Oechel S.J. Hastings M.A. Jenkins (1993) ArticleTitleA system for measuring in situ CO2 and CH4 flux in unmanaged ecosystems: an arctic example Funct. Ecol 7 369–379
M.D. Walker D.A. Walker J.M. Welker A.M. Arft T. Bardsley P.D. Brooks J.T. Fahnestock M.H. Jones M. Losleben A.N. Parsons T.R. Seastedt P.L. Turner (1999) ArticleTitleLong-term experimental manipulation of winter snow regime and summer temperature in arctic and alpine tundra Hydrol. Process 13 2315–2330 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1099-1085(199910)13:14/15<2315::AID-HYP888>3.0.CO;2-A
J.M. Welker J.T. Fahnestock M.H. Jones (2000) ArticleTitleAnnual CO2 flux in dry and moist arctic tundra: Field responses to increases in summer temperatures and winter snow depth Climatic Change 44 139–150 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1005555012742 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXhtFOksLw%3D
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chimner, R., Welker, J. Ecosystem respiration responses to experimental manipulations of winter and summer precipitation in a Mixedgrass Prairie, WY, USA. Biogeochemistry 73, 257–270 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-004-1989-6
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-004-1989-6