Abstract
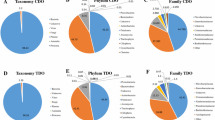
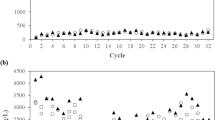
Triclosan, a widely used antimicrobial agent, is an emerging contaminant in the environment. Despite its antimicrobial character, biodegradation of triclosan has been observed in pure cultures, soils and activated sludge. However, little is known about the microorganisms responsible for the degradation in mixed cultures. In this study, active triclosan degraders in a triclosan-degrading enrichment culture were identified using stable isotope probing (SIP) with universally 13C-labeled triclosan. Eleven clones contributed from active microorganisms capable of uptake the 13C in triclosan were identified. None of these clones were similar to known triclosan-degraders/utilizers. These clones distributed among α-, β-, or γ-Proteobacteria: one belonging to Defluvibacter (α-Proteobacteria), seven belonging to Alicycliphilus (β-Proteobacteria), and three belonging to Stenotrophomonas (γ-Proteobacteria). Successive additions of triclosan caused a significant shift in the microbial community structure of the enrichment culture, with dominant ribotypes belonging to the genera Alicycliphilus and Defluvibacter. Application of SIP has successfully identified diverse uncultivable triclosan-degrading microorganisms in an activated sludge enrichment culture. The results of this study not only contributed to our understanding of the microbial ecology of triclosan biodegradation in wastewater, but also suggested that triclosan degraders are more phylogenetically diverse than previously reported.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allmyr M, Adolfsson-Erici M, McLachlan MS, Sandborgh-Englund G (2006) Triclosan in plasma and milk from Swedish nursing mothers and their exposure via personal care products. Sci Total Environ 372:87–93
Boonchan S, Britz ML, Stanley GA (1998) Surfactant-enhanced biodegradation of high molecular weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Biotechnol Bioeng 59:482–494
Braoudaki M, Hilton AC (2004) Low level of cross-resistance between triclosan and antibiotics in Escherichia coli K-12 and E. coli O55 compared to E.coli O157. FEMS Microbiol Lett 235:305–309
Brose U, Martinez ND, Williams RJ (2003) Estimating species richness: sensitivity to sample coverage and insensitivity to spatial patterns. Ecology 84:2364–2377
Buckley DH, Huangyutitham V, Hsu SF, Nelson TA (2007) Stable isotope probing with 15N achieved by disentangling the effects of genome G+C content and isotope enrichment on DNA density. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:3189–3195
Calafat AM, Ye X, Wong LY, Reidy JA, Needham LL (2008) Urinary concentrations of triclosan in the US population: 2003–2004. Environ Health Perspect 116:303–307
Chu KH, Alvarez-Cohen L (1996) Trichloroethylene degradation by methane-oxidizing cultures grown with various nitrogen sources. Water Environ Res 68:76–82
Ciba Specialty Chemical (1998) Irgasant DP 300, Irgacaret MP.Toxicological and Ecological Data. Official Registrations. Technical Brochure 2521. Ciba Specialty Chemical, Basel
Cole JR, Chai B, Farris RJ, Wang Q, Kulam-Syed-Mohideen AS, McGarrell DM, Bandela AM, Cardenas E, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM (2007) The ribosomal database project (RDP-II): introducing myRDP space and quality controlled public data. Nucleic Acids Res 35:D169–D172
Dann AB, Hontela A (2011) Triclosan: environmental exposure, toxicity and mechanisms of action. J Appl Toxicol 31:285–311
Di Gioia D, Fambrini L, Coppini E, Fava F, Barberio C (2004) Aggregation-based cooperation during bacterial aerobic degradation of polyethoxylated nonylphenols. Res Microbiol 155:761–769
Federle TW, Kaiser SK, Nuck BA (2002) Fate and effects of triclosan in activated sludge. Environ Toxicol Chem 21:1330–1337
Fluit ADC, Visser MR, Schmitz F-J (2001) Molecular detection of antimicrobial resistance. Clin Microbiol Rev 14:836–871
Friedrich MW (2006) Stable-isotope probing of DNA: insights into the function of uncultivated microorganisms from isotopically labeled metagenomes. Curr Opin Biotechnol 17:59–66
Fritsche K, Auling G, Andreesen JR, Lechner U (1999) Defluvibacter lusatiae gen. nov., sp nov., a new chlorophenol-degrading member of the α-2 subgroup of proteobacteria. Syst Appl Microbiol 22:197–204
Gallagher E, McGuinness L, Phelps C, Young LY, Kerkhof LJ (2005) 13C-carrier DNA shortens the incubation time needed to detect benzoate-utilizing denitrifying bacteria by stable-isotope probing. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:5192–5196
Gee RH, Charles A, Taylor N, Darbre PD (2008) Oestrogenic and androgenic activity of triclosan in breast cancer cells. J Appl Toxicol 28:78–91
Gray ND, Head IM (2001) Linking genetic identity and function in communities of uncultured bacteria. Environ Microbiol 3:481–492
Hay AG, Dees PM, Sayler GS (2001) Growth of a bacterial consortium on triclosan. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 36:105–112
Hirsch PR, Mauchline TH, Clark IM (2010) Culture-independent molecular techniques for soil microbial ecology. Soil Biol Biochem 42:878–887
Juretschko S, Loy A, Lehner A, Wagner M (2002) The microbial community composition of a nitrifying-denitrifying activated sludge from an industrial sewage treatment plant analyzed by the full-cycle rRNA approach. Syst Appl Microbiol 25:84–99
Kim YM, Murugesan K, Schmidt S, Bokare V, Jeon JR, Kim EJ, Chang YS (2011) Triclosan susceptibility and co-metabolism - a comparison for three aerobic pollutant-degrading bacteria. Bioresour Technol 102:2206–2212
Kolpin DW, Furlong ET, Meyer MT, Thurman EM, Zaugg SD, Barber LB, Buxton HT (2002) Response to comment on, “Pharmaceuticals, hormones, and other organic wastewater contaminants in US streams, 1999–2000: a national reconnaissance”. Environ Sci Technol 36:4007–4008
Latch DE, Packer JL, Arnold WA, McNeill K (2003) Photochemical conversion of triclosan to 2,8-dichlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in aqueous solution. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 158:63–66
Lee DG, Zhao F, Rezenom YH, Russell DH, Chu KH (2012) Biodegradation of triclosan by a wastewater microorganism. Water Res 46:4226–4234
Leigh MB, Pellizari VH, Uhlik O, Sutka R, Rodrigues J, Ostrom NE, Zhou JH, Tiedje JM (2007) Biphenyl-utilizing bacteria and their functional genes in a pine root zone contaminated with polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). ISME J 1:134–148
Li D, Qi R, Yang M, Zhang Y, Yu T (2011) Bacterial community characteristics under long-term antibiotic selection pressures. Water Res 45:6063–6073
Lin JL, Radajewski S, Eshinimaev BT, Trotsenko YA, McDonald IR, Murrell JC (2004) Molecular diversity of methanotrophs in Transbaikal soda lake sediments and identification of potentially active populations by stable isotope probing. Environ Microbiol 6:1049–1060
Liu M (2008) Effects of the antimicrobial agent triclosan on bacterial resistance to disinfection in wastewater treatment processes. West Virginia University, Morgantown
Liu Z, Yang C, Qiao CL (2007) Biodegradation of p-nitrophenol and 4-chlorophenol by Stenotrophomonas sp. FEMS Microbiol Lett 277:150–156
Lolas IB, Chen X, Bester K (2012) Nielsen JL (2012) Identification of triclosan-degrading bacteria using stable isotope probing, fluorescence in situ hybridization and microautoradiography. Microbiology 158:2796–2804
Manefield M, Whiteley AS, Griffiths RI, Bailey MJ (2002) RNA stable isotope probing, a novel means of linking microbial community function to phylogeny. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5367–5373
Manefield M, Griffiths R, McNamara NP, Sleep D, Ostle N, Whiteley A (2007) Insights into the fate of a 13C-labelled phenol pulse for stable isotope probing (SIP) experiments. J Microbiol Methods 69:340–344
McMurry LM, Oethinger M, Levy SB (1998) Triclosan targets lipid synthesis. Nature 394:531–532
Meade MJ, Waddell RL, Callahan TM (2001) Soil bacteria Pseudomonas putida and Alcaligenes xylosoxidans subsp denitrificans inactivate triclosan in liquid and solid substrates. FEMS Microbiol Lett 204:45–48
Mechichi T, Stackebrandt E, Fuchs G (2003) Alicycliphilus denitrificans gen. nov., sp. nov., a cyclohexanol-degrading, nitrate-reducing β-proteobacterium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:147–152
Morales SE, Cosart TF, Johnson JV, Holben WE (2009) Extensive phylogenetic analysis of a soil bacterial community illustrates extreme xaxon evenness and the effects of amplicon length, degree of coverage, and DNA fractionation on classification and ecological parameters. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:668–675
Morrall D, McAvoy D, Schatowitz B, Inauen J, Jacob M, Hauk A, Eckhoff W (2004) A field study of triclosan loss rates in river water (Cibolo Creek, TX). Chemosphere 54:653–660
Neumegen RA, Fernandez-Alba AR, Chisti Y (2005) Toxicities of triclosan, phenol, and copper sulfate in activated sludge. Environ Toxicol 20:160–164
Offhaus K, Klingl H, Scherb K, Wachs B (1978) Untersuchungen zum eines bakteriostatikums in klaranlagen. Muech Beitr Abwasser-Fisch Flussbiol 30:29–71
Orvos DR, Versteeg DJ, Inauen J, Capdevielle M, Rothenstein A, Cunningham V (2002) Aquatic toxicity of triclosan. Environ Toxicol Chem 21:1338–1349
Radajewski S, Webster G, Reay DS, Morris SA, Ineson P, Nedwell DB, Prosser JI, Murrell JC (2002) Identification of active methylotroph populations in an acidic forest soil by stable isotope probing. Microbiology 148:2331–2342
Rappe MS, Giovannoni SJ (2003) The uncultured microbial majority. Annu Rev Microbiol 57:369–394
Roesch LF, Fulthorpe RR, Riva A, Casella G, Hadwin AKM, Kent AD, Daroub SH, Camargo FAO, Farmerie WG, Triplett EW (2007) Pyrosequencing enumerates and contrasts soil microbial diversity. ISME J 1:283–290
Roh H, Subramanya N, Zhao FM, Yu CP, Sandt J, Chu KH (2009a) Biodegradation potential of wastewater micropollutants by ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. Chemosphere 77:1084–1089
Roh H, Yu CP, Fuller ME, Chu KH (2009b) Identification of hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine-degrading microorganisms via 15N-stable isotope probing. Environ Sci Technol 43:2505–2511
Rule KL, Ebbett VR, Vikesland PJ (2005) Formation of chloroform and chlorinated organics by free-chlorine-mediated oxidation of triclosan. Environ Sci Technol 39:3176–3185
Saikaly PE, Stroot PG, Oerther DB (2005) Use of 16S rRNA gene terminal restriction fragment analysis to assess the impact of solids retention time on the bacterial diversity of activated sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:5814–5822
Shannon CE, Weaver W (1963) The mathematical theory of communication. University of Illinois Press, Urbana, IL
Simpson EH (1949) Measurement of diversity. Nature 163:688
Singer H, Muller S, Tixier C, Pillonel L (2002) Triclosan: occurrence and fate of a widely used biocide in the aquatic environment: field measurements in wastewater treatment plants, surface waters, and lake sediments. Environ Sci Technol 36:4998–5004
Soares A, Guieysse B, Delgado O, Mattiasson B (2003) Aerobic biodegradation of nonylphenol by cold-adapted bacteria. Biotechnol Lett 25:731–738
Sogin ML, Morrison HG, Huber JA, Mark Welch D, Huse SM, Neal PR, Arrieta JM, Herndl GJ (2006) Microbial diversity in the deep sea and the underexplored “rare biosphere”. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:12115–12120
Stasinakis AS, Petalas AV, Mamais D, Thomaidis NS, Gatidou G, Lekkas TD (2007) Investigation of triclosan fate and toxicity in continuous-flow activated sludge systems. Chemosphere 68:375–381
Stasinakis AS, Mainais D, Thomaidis NS, Danika E, Gatidou G, Lekkas TD (2008) Inhibitory effect of triclosan and nonylphenol on respiration rates and ammonia removal in activated sludge systems. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 70:199–206
Sun W, Sun X, Cupples AM (2012) Anaerobic methyl tert-butyl ether-degrading microorganisms identified in wastewater treatment plant samples by stable isotope probing. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:2973–2980
Thompson A, Griffin P, Stuetz R, Cartmell E (2005) The fate and removal of triclosan during wastewater treatment. Water Environ Res 77:63–67
Weelink SAB, Tan NCG, ten Broeke H, van Doesburg W, Langenhoff AAM, Gerritse J, Stams AJM (2007) Physiological and phylogenetic characterization of a stable benzene-degrading, chlorate-reducing microbial community. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 60:312–321
Whiteley AS, Manefield M, Ostle N, Ineson P, Bailey MJ (2002) Technical considerations for RNA-based stable isotope probing: an approach to associating microbial diversity with microbial community function. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 16:2179–2183
Wintzingerode FV, Stackebrandt E, Gobel UB (1997) Determination of microbial diversity in environmental samples: pitfalls of PCR-based rRNA analysis. FEMS Microbiol Rev 21:213–229
Yang C, Liu N, Guo XM, Qiao CL (2006a) Cloning of mpd gene from a chlorpyrifos-degrading bacterium and use of this strain in bioremediation of contaminated soil. FEMS Microbiol Lett 265:118–125
Yang HC, Im WT, Kang MS, Shin DY, Lee ST (2006b) Stenotrophomonas koreensis sp. nov., isolated from compost in South Korea. IJSEM 56:81–84
Yazdankhah SP, Scheie AA, Hoiby EA, Lunestad BT, Heir E, Fotland TO, Naterstad K, Kruse H (2006) Triclosan and antimicrobial resistance in bacteria: an overview. Microb Drug Resist Mechan Epidemiol Dis 12:83–90
Yu CP, Chu KH (2005) A quantitative assay for linking microbial community function and structure of a naphthalene-degrading microbial consortium. Environ Sci Technol 39:9611–9619
Yu CP, Chu KH (2009) Occurrence of pharmaceuticals and personal care products along the West Prong Little Pigeon River in east Tennessee, USA. Chemosphere 75:1281–1286
Yu CP, Ahuja R, Sayler G, Chu KH (2005) Quantitative molecular assay for fingerprinting microbial communities of wastewater and estrogen-degrading consortia. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:1433–1444
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Hyungkeun Roh for his assistance in the laboratory experiments. We also thank Mr. Doug Wallace for providing activated sludge used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, D.G., Cho, KC. & Chu, KH. Identification of triclosan-degrading bacteria in a triclosan enrichment culture using stable isotope probing. Biodegradation 25, 55–65 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-013-9640-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-013-9640-7