Abstract
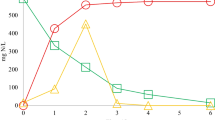
The assessment of biodegradation activity in contaminated aquifers is critical to demonstrate the performance of bioremediation and natural attenuation and to parameterize models of contaminant plume dynamics. Real time quantitative PCR (qPCR) was used to target the catabolic bssA gene (coding for benzylsuccinate synthase) and a 16S rDNA phylogenetic gene (for total Bacteria) as potential biomarkers to infer on anaerobic toluene degradation rates. A significant correlation (P = 0.0003) was found over a wide range of initial toluene concentrations (1–100 mg/l) between toluene degradation rates and bssA concentrations in anaerobic microcosms prepared with aquifer material from a hydrocarbon contaminated site. In contrast, the correlation between toluene degradation activity and total Bacteria concentrations was not significant (P = 0.1125). This suggests that qPCR targeting of functional genes might offer a simple approach to estimate in situ biodegradation activity, which would enhance site investigation and modeling of natural attenuation at hydrocarbon-contaminated sites.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen JP, Atekwana EA, Duris JW, Werkema DD, Rossbach S (2007) The microbial community structure in petroleum contaminated sediments corresponds to geophysical signatures. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:2860–2870
Alvarez PJJ, Illman W (2006) Bioremediation and natural attenuation: process fundamentals and mathematical models. In: Schnoor JL, Zehnder A (eds) Environmental science and technology. Wiley, Hoboken, pp 1–608
Baelum J, Henriksen T, Hansen HC, Jacobsen CS (2006) Degradation of 4-chloro-2-methylphenoxyacetic acid in top- and subsoil is quantitatively linked to the class III tfdA gene. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:1476–1486
Beller HR, Edwards EA (2000) Anaerobic toluene activation by benzylsuccinate synthase in a highly enriched methanogenic culture. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:5503–5505
Beller HR, Spormann AM (1997) Anaerobic activation of toluene and o-xylene by addition to fumarate in denitrifying strain T. J Bacteriol 179:670–676
Beller HR, Kane SR, Legler TC, Alvarez PJJ (2002) A real-time polymerase chain reaction method for monitoring anaerobic, hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria based on a catabolic gene. Environ Sci Technol 36:3977–3984
Beller HR, Kane SR, Legler TC, McKelvie JR, Lollar BS, Pearson F, Balser L, Mackay DM (2008) Comparative assessment of benzene, toluene, and xylene natural attenuation by quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis of a catabolic gene, signature metabolites, and compound-specific isotope analysis. Environ Sci Technol 42:6065–6072
Biegert T, Fuchs G, Heider J (1996) Evidence that anaerobic oxidation of toluene in the denitrifying bacterium Thauera aromatica is initiated by formation of benzylsuccinate from toluene and fumarate. Eur J Biochem 238:661–668
Chin K-J, Esteve-Nunez A, Leang C, Lovley DR (2004) Direct correlation between rates of anaerobic respiration and levels of mRNA for key respiratory genes in Geobacter sulfurreducens. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:5183–5189
Da Silva MLB, Alvarez PJJ (2004) Enhanced anaerobic biodegradation of benzene–toluene–ethylbenzene–xylene–ethanol mixtures in bioaugmented aquifer columns. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:4720–4726
Da Silva MLB, Alvarez PJJ (2008) Exploring the correlation between halorespirer biomarker concentrations and TCE dechlorination rates. J Environ Eng 134:895–901
Fleming JT, Sanseverino J, Sayler GS (1993) Quantitative relationship between naphthalene catabolic gene frequency and expression in predicting PAH degradation in soils at town gas manufacturing sites. Environ Sci Technol 27:1068–1074
Hutchins SR (1997) Effects of microcosm preparation on rates of toluene biodegradation under denitrifying conditions. J Ind Microbiol Biotech 18:170–176
Illman W, Alvarez PJJ (2009) Performance assessment of bioremediation and natural attenuation. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 39:209–270
Jeffrey WH, Nazaret S, Barkay T (1996) Detection of the merA gene and its expression in the environment. Microb Ecol 32:293–303
Kane SR, Beller HR, Legler TC, Anderson RT (2002) Biochemical and genetic evidence of benzylsuccinate synthase in toluene-degrading, ferric iron-reducing Geobacter metallireducens. Biodegradation 13:149–154
Krajmalnik-Brown R, Holscher T, Thomson IN, Saunders MF, Ritalahti KM, Loffler FE (2004) Genetic identification of a putative vinyl chloride reductase in Dehalococcoides sp. strain BAV1. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:6347–6351
Nakatsu CH, Carmosini N, Baldwin B, Beasly F, Kourtev P, Konopka A (2005) Soil microbial community responses to additions of organic carbon substrates and heavy metals (Pb and Cr). Appl Environ Microbiol 71:7679–7689
Nazaret S, Jeffrey WH, Saouter E, Haven RV, Barkay T (1994) merA Gene expression in aquatic environments measured by mRNA production and Hg(II) volatilization. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:4059–4065
Neidhardt FC (1987) Chemical composition of Escherichia coli. In: Neidhardt FC (ed) Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: cellular and molecular biology, edn 1, vol 1. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 3–6
Park JW, Crowley DE (2006) Dynamic changes in nahAc gene copy numbers during degradation of naphthalene in PAH-contaminated soils. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:1322–1329
Porteous LA, Seidler RJ, Watrud LS (1997) An improved method for purifying DNA from soil for polymerase chain reaction amplification and molecular ecology applications. Mol Ecol 6(8):787–791
Rabus R, Heider J (1998) Initial reactions of anaerobic metabolism of alkylbenzenes in denitrifying and sulfate-reducing bacteria. Arch Microbiol 170:377–384
Ritalahti KM, Amos KK, Sung Y, Wu Q, Koenigsberg SS, Löffler FE (2006) Quantitative PCR targeting 16S rRNA and reductive dehalogenase genes simultaneously monitors multiple Dehalococcoides strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:2765–2774
Scow KM, Hicks KA (2005) Natural attenuation and enhanced bioremediation of organic contaminants in groundwater. Curr Opin Biotechnol 16:246–253
Spormann AM, Widdel F (2000) Metabolism of alkylbenzenes, alkanes, and other hydrocarbons in anaerobic bacteria. Biodegradation 11:85–105
Suzuki MT, Taylor LT, Delong EF (2000) Quantitative analysis of small-subunit rRNA genes in mixed microbial populations via 59-nuclease assays. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:4605–4614
Von Gunten U, Zobrist J (1993) Biogeochemical changes in groundwater-infiltration systems: column studies. J Geochim Cosmochim Acta 57:3895–3906
Weiss JV, Cozzarelli IM (2008) Biodegradation in contaminated aquifers: incorporating microbial molecular methods. Ground Water 46:305–322
Winderl C, Schaefer S, Lueders T (2007) Detection of anaerobic toluene and hydrocarbon degraders in contaminated aquifers using benzylsuccinate synthase (bssA) genes as a functional marker. Environ Microbiol 9:1035–1046
Winderl C, Anneser B, Griebler C, Meckenstock RU, Lueders T (2008) Depth-resolved quantification of anaerobic toluene degraders and aquifer microbial community patterns in distinct redox zones of a tar oil contaminated plume. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:792–801
Zengler K, Heider J, Rossello-Mora R, Widdel F (1999) Phototrophic utilization of toluene under anoxic conditions by a new strain of Blastochloris sulfoviridis. Arch Microbiol 172:204–212
Zhou JZ, Bruns MA, Tiedje JM (1996) DNA recovery from soils of diverse composition. Appl Environ Microbiol 62(2):316–322
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Rick Ahlers for providing the aquifer material samples used in this work. Funding for this was provided by NSF (CBET-0729700). Amy Monier was partially supported by the American Petroleum Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kazy, S.K., Monier, A.L. & Alvarez, P.J.J. Assessing the correlation between anaerobic toluene degradation activity and bssA concentrations in hydrocarbon-contaminated aquifer material. Biodegradation 21, 793–800 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-010-9344-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-010-9344-1